Short answers : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 252
Q1 : State the difference between dissolution of partnership and dissolution of partnership firm.
Answer :
|
Basis of Difference |
Dissolution of Partnership |
Dissolution of Partnership firm |
|
Meaning |
It means change in the partnership deed (or the agreement) among the partners. |
It means that the business is wound up and the firm is dissolved. |
|
Discontinuation |
Business is not discontinued. |
Business is discontinued, as the firm is dissolved. |
|
Closure of Books of Accounts |
Books of accounts are not closed, as there is only change in the existing agreement between the partners. |
Books of accounts are closed, as the business is discontinued. |
|
Assets and Liabilities |
In this case, the assets and liabilities are revalued. |
In this case, all the assets are sold off in order to pay the liabilities of the business. |
|
Role of Court |
There is no intervention by the court. |
Dissolution of a partnership firm may be done with the consent of the court. |
|
Nature |
It is voluntary in nature. |
It may be voluntary (as per the discretion of the partners) or compulsory (as per the order of the court). |
|
Effect |
It may or may not involve dissolution of the firm. |
It necessarily involves dissolution of both the partnership as well as of the partnership firm. |
Q2 :State the accounting treatment for:
i. Unrecorded assets
ii. Unrecorded liabilities
Answer :
i) Accounting Treatment for Unrecorded Assets
Unrecorded asset is an asset, the value of which has been written off in the books of accounts but the asset is still in usable position. The accounting treatment for unrecorded asset is:
a) When the unrecorded asset is sold for cash
|
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
|
|
To Realisation A/c |
||
|
(Unrecorded assets sold for cash) |
||
b) When the unrecorded asset is taken over by any partner
|
Partner’s Capital A/c |
Dr. |
|
|
To Realisation A/c |
||
|
(Unrecorded asset taken over by the partner) |
||
ii) Accounting Treatment for Unrecorded Liabilities
Unrecorded liabilities are those liabilities which are not recorded in the books of account. The accounting treatment for unrecorded liability is:
a) When the unrecorded liability is paid off
|
Realisation A/c |
Dr. |
|
|
To Cash A/c |
||
|
(Unrecorded liability paid in cash) |
||
b) When the unrecorded liability is taken over by a partner
|
Realisation A/c |
Dr. |
|
|
To Partner’s Capital A/c |
||
|
(Unrecorded liability taken over by the partner) |
||
Q3 : On dissolution, how you deal with partner’s loan if it appears on the
(a) Assets side of the Balance Sheet
(b) Liabilities side of the Balance Sheet
Answer :
a) If partner’s loan appears on the assets side of the Balance Sheet then it implies that the partner has taken loan from the business and is liable to pay back to the business. In such case, the loan amount is transferred to his capital
account. Thus the accounting entry will be:
|
Partner’s Capital A/c |
Dr. |
|
|
To Partner’s Loan A/c |
||
|
(Partner’s loan transferred |
||
b) If partner’s loan appears on the liabilities side of the Balance Sheet then it implies that the partner has forwarded loan to the firm and the firm is liable to pay back the amount to the partner. In such case, partner’s loan is paid off after paying all the external liabilities. The partner’s loan is not transferred to the Realisation Account, in fact, it is
paid in cash. The following accounting entry is passed.-
|
Partner’s Loan A/c |
Dr. |
|
|
To Cash/Bank A/c |
||
|
(Partner’s loan paid in |
||
Q4: Distinguish between firm’s debts and partner’s private debts.
Answer:
|
Basis of Difference |
Firm’s |
Partner’s |
|
Meaning |
It refers to those debts that |
It refers to those debts that |
|
Liability |
All the partners of the firm are |
The concerned partner is |
|
Settlement of debts by private |
If the firm’s debt exceeds the |
Private debts are settled |
|
Settlement of debts by firm’s |
Firm’s debts are settled against |
After paying off firm’s debts, |
Q5: State the order of settlement of accounts on dissolution.
Answer: The following are the rules of settlement of accounts on dissolution as per the Section 48 of Partnership Act 1932.
1. Application of Assets: Amount received by the realisation (sale) of the assets shall be used in the following order:
a) First of all the external liabilities and expenses are to be paid.
b) Then, all loans and advances forwarded by the partners should be paid.
c) Then, the capital of each partner should be paid off. If there remains any surplus after the payment of (a), (b)and (c), then it should be distributed among the partners in their profitsharing ratio.
2. Treatment of Loss: In case of loss and any deficiency of capital this should be paid in the following order:
a) First these should be adjusted against firm’s profits.
b) Then, against the total capital of the firm.
c)Even if there exists any loss and deficiencies then it should be borne by all the partners individually in their profit sharing ratio.
Q6: On what account realisation account differs from revaluation account.
Answer:
|
Basis of Difference |
Realisation Account |
Revaluation Account |
|
Meaning |
It records the sale of various assets and payment of various liabilities.
|
It records the effect of revaluation of assets and liabilities on the eve of admission, retirement, death and change in the profit sharing ratio. |
|
Time |
It is prepared at the time of dissolution of firm.
|
It is prepared when admission/retirement/death or change in profit sharing ratio takes place. |
|
Objective |
To find profit or loss on realisation of assets and payment of liabilities. |
To find out profit or loss on revaluation of assets and liabilities. |
|
Amount |
Assets and liabilities are shown at the book value. |
Increase or decrease in the value of assets and liabilities are shown in this account. |
|
Records |
All assets and liabilities are recorded here.
|
Only those assets and liabilities are recorded here whose values have changed over a period of time. |
|
Effect |
All accounts of assets and liabilities are closed. |
No account is closed on revaluation of assets and liabilities. |
Short answers numerical questions long answers : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 253
Q1 :Journalise the following transactions regarding Realisation expenses:
[a] Realisation expenses amounted to Rs 2,500.
[b] Realisation expenses amounting to Rs 3,000 were paid by Ashok, one of the partners.
[c] Realisation expenses Rs 2,300 borne by Tarun, personally.
[d] Amit, a partner was appointed to realise the assets, at a cost of Rs 4,000. The actual amount of Realisation amounted to Rs 3,000.
Answer:
|
Journal
|
|||||||
|
|
Particulars |
L.F. |
Amount Rs |
Amount Rs |
|||
|
(a) |
Realisation A/c |
Dr. |
2,500 |
||||
|
To Bank A/c |
2,500 |
||||||
|
(Realisation expenses paid) |
|||||||
|
(b) |
Realisation A/c |
Dr. |
3,000 |
||||
|
To Ashok’s |
3,000 |
||||||
|
(Realisation expenses paid |
|||||||
|
(c) |
No entry, as all Realisation |
||||||
|
(d) |
Realisation A/c |
Dr. |
4,000 |
||||
|
To Amit’s |
4,000 |
||||||
|
(Realisation expenses paid |
|||||||
Q2 :Explain the process of dissolution of a partnership firm?
Answer : Dissolution of partnership firm implies discontinuation of the business of the partnership firm. According to the Section 39 of Partnership Act, dissolution of partnership between all the partners of a firm is called dissolution of partnership firm. Dissolution involves winding up of business, disposal of assets and paying off the liabilities and distribution of any surplus or borne of loss by the partners of the firm. As per the Partnership Act 1932, a partnership firm may be dissolved in the following manners:
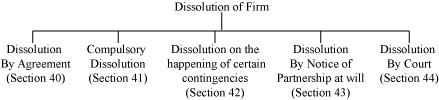
1) Dissolution by Agreement
A firm may be dissolved with:
a) the consent of all the partners, or
b) the contract between the partners
2) Compulsory Dissolution
A firm may be dissolved by:
a) the adjudication of all the partners or of all partners but one as insolvent
b) happening of an event or change in government policies that make the business unlawful.
3) Dissolution on the happening of Certain Contingencies
Subject to the contract between the partners, a firm is dissolved
a) if formed for a specific period then on the expiry of the period
b) if formed for a specific purpose then on completion of the purpose
c) on the death of partner/partners
d) on insolvency of a partner/partners
4) Dissolution by Notice
If partnership is at will then the partnership firm is dissolved if any partner giving notice in writing to all the other partners expressing his/her intention to dissolve the firm.
5) Dissolution by Court
The court may order to dissolve a partnership firm when:
a) a partner becomes insane or lunatic.
b) a partner becomes permanently incapable of performing the duties.
c) a partner is guilty of misconduct and affects the business activities.
d) a partner repeatedly breaks the terms of agreement .
e) a partner transfers his interest to a third party without the consent of other partners.
f) a business persistently incurs losses.
Besides these above mentioned circumstances, a partnership firm may be dissolved if the court at any stage finds dissolution of the firm to be justified and inevitable.
The following are the rules of settlement of accounts on dissolution as per the Section 48 of Partnership Act 1932.
1. Application of Assets: Amount received by the realisation (sale) of the assets shall be used in the following order:
a) First of all the external liabilities and expenses are to be paid.
b) Then, all loans and advances forwarded by the partners should be paid.
c) Then, the capital of each partners should be paid off. If there remains any surplus after the payment of (a), (b) and (c), then it should be distributed among the partners in their profit sharing ratio.
2. Treatment of Loss: In case of loss and any deficiency of capital, then this should be paid in the following order:
a) First these should be adjusted against firm’s profits.
b) Then, against the total capital of the firm.
c) If still there exists any loss and deficiencies, then it should be borne by all the partners individually in their profit sharing ratio.
Q3 : Record necessary journal entries in the following cases:
[a] Creditors worth Rs 85,000 accepted Rs 40,000 as cash and Investment worth Rs 43,000, in full settlement of their claim.
[b] Creditors were Rs 16,000. They accepted Machinery valued at Rs 18,000 in settlement of their claim.
[c] Creditors were Rs 90,000. They accepted Buildings valued Rs 1,20,000 and paid cash to the firm Rs 30,000.
Answer :
|
Journal
|
|||||||
|
|
Particulars |
L.F. |
Amount Rs |
Amount Rs |
|||
|
(a) |
Realisation A/c |
Dr. |
40,000 |
||||
|
To Cash A/c |
40,000 |
||||||
|
(Creditors worth Rs 85,000 accepted 40,000 as cash and worth Rs 43,000 in their full settlement) |
|||||||
|
(b) |
No Entry |
||||||
|
(Creditors Rs 16,000 accepted Machinery Rs 18,000 in settlement. No entry is required since both asset and already transferred to the Realisation Account) |
|||||||
|
(c) |
Cash A/c |
Dr. |
30,000 |
||||
|
To Realisation A/c |
30,000 |
||||||
|
(Creditors worth Rs 90,000 accepted buildings worth Rs returned Rs 30,000 as cash after settlement of claim to |
|||||||
Q4 :What is a Realisation Account?
Answer : On dissolution of a firm, all the books of account are closed, all assets are sold and all liabilities are paid off. In order to record the sale of assets and discharge of liabilities, a nominal account is opened named Realisation Account. The main purpose to open Realisation Account is to ascertain the profit or loss due to the realisation of assets and liabilities. Realisation profit (if credit side > debit side) or realisation loss (if debit side > credit side) are transferred to the Partner’s Capital Account in their profit sharing ratio.
Concisely, following are the important objectives of preparing Realisation Account.
1) To close all the books of account.
2) To record transactions relating to the sale of assets and discharge of liabilities.
3) To determine profit or loss due to the realisation of assets and liabilities.
Accounting treatment of items related to Realisation Account
1) For transfer of assets
|
Realisation A/c |
Dr. |
|
|
To Sundry Assets A/c |
||
|
(All Assets transferred to Cash/Bank, P and L debit |
||
2) For transfer of liabilities
|
Sundry Liabilities A/c |
Dr. |
|
|
To Realisation A/c |
||
|
(All Liabilities transferred Partner’s Capitals, P and L |
||
3) For sale of assets
|
Bank A/c (Amount received) |
Dr. |
|
|
To Realisation A/c |
||
|
(Assets sold for cash) |
||
4) For payment of liabilities
|
Realisation A/c |
Dr. |
|
|
To Bank A/c |
||
|
(Liabilities paid in cash) |
||
5) For payment of realisation expenses
|
Realisation A/c |
Dr. |
|
|
To Bank A/c |
||
|
(Expenses paid) |
||
6) For transfer of profit on realisation
|
Realisation A/c |
Dr. |
|
|
To Partner’s Capital A/c |
||
|
(Profit on realisation |
||
7) For transfer of loss on realisation
|
Partner’s Capital A/c |
Dr. |
|
|
To Realisation A/c |
||
|
(Loss transferred to |
||
|
Format of |
||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|||
|
Various Assets (Excluding Cash/Bank, fictitious assets, Debit balance of
Cash/Bank (Payment for realisation
Cash/Bank (Payment to outside and
Partner’s Capital A/c (If any liability taken on expenses paid by him or Partner Capital A/c (Profit on realisation distributed in the profit sharing |
– – – – |
Various Liabilities (Excluding Partner Capital account, reserves, P and L A/c,
Provision on assets (like, Provision for doubtful debts; Provision for
Cash/Bank (Amount received from
Partner ‘s Capital A/c (If any asset taken over by any partner) Partner Capital A/c (Loss on realisation borne by all the partners in their |
– – – – |
|||
|
– |
– |
|||||
Q5 : There was an old computer which was written-off in the books of Accounts in the pervious year. The same has been taken over by a partner Nitin for Rs 3,000. Journalise the transaction, supposing. That the firm has been dissolved.
Answer :
|
Journal
|
||||
|
Particulars |
L.F. |
Amount Rs |
Amount Rs |
|
|
Nitin’s |
Dr. |
3,000 |
||
|
To Realisation A/c |
3,000 |
|||
|
(Unrecorded computer taken over by Nitin) |
||||
Q6 : Reproduce the format of Realisation Account.
Answer :
|
Format of |
||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|||
|
Various Assets (Excluding Cash/Bank, fictitious assets, Debit balance of
Cash/Bank (Payment for realisation
Cash/Bank (Payment to outside and
Partner’s Capital A/c (If any liability taken on expenses paid by him or Partner Capital A/c (Profit on realisation distributed in the profit sharing |
– – – – |
Various Liabilities (Excluding Partner Capital account, reserves, P and L A/c,
Provision on assets (like, Provision for doubtful debts; Provision for
Cash/Bank (Amount received from
Partner ‘s Capital A/c (If any asset taken over by any partner) Partner Capital A/c (Loss on realisation borne by all the partners in their |
– – – – |
|||
|
– |
– |
|||||
Q7: What journal entries will be recorded for the following transactions on the dissolution of a firm:
[a] Payment of unrecorded liabilities of Rs 3,200.
[b] Stock worth Rs 7,500 is taken by a partner Rohit.
[c] Profit on Realisation amounting to Rs 18,000 is to be distributed between the partners Ashish and Tarun in the ratio of 5:7.
[d] An unrecorded asset realised Rs 5,500.
Answer :
|
Journal |
||||||
|
Particulars |
L.F. |
Amount Rs |
Amount Rs |
|||
|
(a) |
Realisation |
Dr. |
3,200 |
|||
|
To Bank A/c |
3,200 |
|||||
|
|
(Unrecorded liabilities |
|||||
|
(b) |
(Rohit’s |
Dr. |
7,500 |
|||
|
To Realisation A/c |
7,500 |
|||||
|
(Stock is taken over by Rohit) |
||||||
|
(c) |
Realisation |
Dr. |
18,000 |
|||
|
To Ashish’s Capital A/c |
7,500 |
|||||
|
To Tarun’s Capital A/c |
10,500 |
|||||
|
(Profit on Realisation is transferred to Partners’ Capital Account) |
||||||
|
(d) |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
5,500 |
|||
|
To Realisation A/c |
5,500 |
|||||
|
(Unrecorded asset sold) |
||||||
Q8: How deficiency of creditors is paid off?
Answer : At the time of dissolution of a firm, the amount received from the sale of firm’s assets are utilised to pay the creditors. If the sale receipts fall short, then partners’ private assets are used for settling the dues of the firm’s creditors. Even if some portion of the amount due to creditors is left unpaid, then there arises deficiency of creditors. There are generally two procedures to be followed to treat the deficiency of creditors.
1. Transferring deficiency to the Deficiency Account
2. Transferring deficiency to the Partner’s Capital Account
In the former procedure, a separate account is prepared for the firm’s creditors. Then in order to ascertain the firm’s cash balance accruing from the sale of the firm’s assets and partners’ private assets, Cash Account is prepared. After ascertaining the cash availability with the firm, the creditors and the external liabilities are paid proportionately (partially). The remaining unpaid creditors or the deficiency is transferred to the Deficiency Account.
In the latter procedure, creditors are paid by the cash available with the firm including the partners individual contribution. The deficiency or unpaid creditors amount is transferred to the Partner’s Capital Account. Thus the deficiency of the creditors is borne by all the partners in their profit sharing ratio. If any partner becomes insolvent and is unable to bear the deficiency, then this will be regarded as a capital loss to the firm. If the partnership deed is silent about such capital loss in the facet of insolvency of a partner, then according to the Garner v/s Murray case, such capital loss need to be borne by the solvent partners in their capital ratio.
Q9: Give journal entries for the following transactions:
1. To record the Realisation of various assets and liabilities,
2. A Firm has a Stock of Rs 1,60,000. Aziz, a partner took over 50% of the Stock at a discount of 20%,
3. Remaining Stock was sold at a profit of 30% on cost,
4. Land and Buildging (book value Rs 1,60,000) sold for Rs 3,00,000 through a broker who charged 2%, commission on the deal,
5. Plant and Machinery (book value Rs 60,000) was handed over to a Creditor at an agreed valuation of 10% less than the book value,
6. Investment whose face value was Rs 4,000 was realised at 50%.
Answer:
|
Journal |
||||||
|
|
Particulars |
L.F. |
Amount Rs |
Amount Rs |
||
|
1) |
||||||
|
(a) |
For Transfer of Assets |
|||||
|
Realisation |
Dr. |
– |
||||
|
To Assets |
– |
|||||
|
(Assets transferred to Realisation Account) |
||||||
|
(b) |
For Transfer of Liabilities |
|||||
|
Liabilities A/c |
Dr. |
– |
||||
|
To Realisation A/c |
– |
|||||
|
(Liabilities transferred to Realisation Account) |
||||||
|
(c) |
For sale of Asset |
|||||
|
Cash/Bank A/c |
Dr. |
– |
||||
|
To Realisation A/c |
– |
|||||
|
(Assets sold) |
||||||
|
(d) |
For liabilitiy |
|||||
|
Realisation |
Dr. |
– |
||||
|
To |
– |
|||||
|
(Liabilities paid) |
||||||
|
2) |
Aziz’s Capital A/c |
Dr. |
64,000 |
|||
|
To Realisation A/c |
64,000 |
|||||
|
(Aziz, a partner took over of the total stock was [1,60,000 × (50/100) × |
||||||
|
3) |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
1,04,000 |
|||
|
To Realisation A/c |
1,04,000 |
|||||
|
(Stock worth Rs 80,000 [80,000 × (130/100 = Rs |
||||||
|
4) |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
2,94,000 |
|||
|
To Realisation A/c |
2,94,000 |
|||||
|
(Land and Building sold for paid to the broker) |
||||||
|
5) |
No entry |
|||||
|
(Plant and Machinery Rs discount are already transferred to |
||||||
|
6) |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
2,000 |
|||
|
To Realisation A/c |
2,000 |
|||||
|
(Investments worth Rs 4,000 |
||||||
NOTE: In this chapter, it has been assumed that all receiving and payments are made through bank.
Q10: How will you deal with the Realisation expenses of the firm of Rashim and Bindiya in the following cases:
1. Realisation expenses amounts to Rs 1,00,000,
2. Realisation expenses amounting to Rs 30,000 are paid by Rashim, a partner.
3. Realisation expenses are to be borne by Rashim for which he will be paid Rs 70,000 as remuneration for completing the dissolution process. The actual expenses incurred by Rashim were Rs 1,20,000.
Answer :
|
Books of Rashim and Bindiya
Journal
|
|||||||
|
|
Particulars |
L.F. |
Amount Rs |
Amount Rs |
|||
|
1) |
Realisation A/c |
Dr. |
1,00,000 |
||||
|
To Bank A/c |
1,00,000 |
||||||
|
(Realisation expenses paid) |
|||||||
|
2) |
Realisation A/c |
Dr. |
30,000 |
||||
|
To Rashim’s |
30,000 |
||||||
|
(Realisation expenses borne |
|||||||
|
3) |
Realisation A/c |
Dr. |
70,000 |
||||
|
To Rashim’s |
70,000 |
||||||
|
(Realisation expenses borne for dissolution Rs 70,000) |
|||||||
Q11: The book value of assets (other than cash and bank) transferred to Realisation Account is Rs 1,00,000. 50% of the assets are taken over by a partner Atul, at a discount of 20%; 40% of the remaining assets are sold at a profit of 30% on cost; 5% of the balance being obsolete, realised nothing and remaining assets are handed over to a Creditor, in full settlement of his claim.
You are required to record the journal entries for Realisation of assets.
Answer :
|
Journal
|
||||||
|
Particulars |
L.F. |
Amount Rs |
Amount Rs |
|||
|
Realisation A/c |
Dr. |
1,00,000 |
||||
|
To Sundry |
1,00,000 |
|||||
|
(Assets other than cash and |
||||||
|
Atul’s Capital A/c |
Dr. |
40,000 |
||||
|
To |
40,000 |
|||||
|
(Atul took over 50% of [1,00,000 × (50/100) × |
||||||
|
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
26,000 |
||||
|
To |
26,000 |
|||||
|
(Assets worth Rs 20,000, at a profit of 30%) [50,000 |
||||||
|
No entry is made for to the creditors in the full the Realisation Account and |
||||||
Q12: Record necessary journal entries to record the following unrecorded assets and liabilities in the books of Paras and Priya:
1. There was an old furniture in the firm which had been written-off completely in the books. This was sold for Rs 3,000,
2. Ashish, an old customer whose Account for Rs 1,000 was written-off as bad in the previous year, paid 60%, of the amount,
3. Paras agreed to take over the firm’s goodwill (not recorded in the books of the firm), at a valuation of Rs 30,000,
4. There was an old typewriter which had been written-off completely from the books. It was estimated to realize Rs 400. It was taken away by Priya at an estimated price less 25%,
5. There were 100 shares of Rs 10 each in Star Limited acquired at a cost of Rs 2,000 which had been written-off completely from the books. These shares are valued @ Rs 6 each and divided among the partners in their profit sharing ratio.
Answer :
|
Books of Paras and Priya
Journal
|
|||||||
|
|
Particulars |
L.F. |
Amount Rs |
Amount Rs |
|||
|
1) |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
3,000 |
||||
|
To |
3,000 |
||||||
|
(Unrecorded furniture sold) |
|||||||
|
2) |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
600 |
||||
|
To |
600 |
||||||
|
(Bad Debt recovered which |
|||||||
|
3) |
Paras’s Capital A/c |
Dr. |
30,000 |
||||
|
To Realisation A/c |
30,000 |
||||||
|
(Unrecorded goodwill taken |
|||||||
|
4) |
Priya’s Capital A/c |
Dr. |
300 |
||||
|
To |
300 |
||||||
|
(Unrecorded Typewriter estimated 25% less price) |
|||||||
|
5) |
Paras’s Capital A/c |
Dr. |
300 |
||||
|
Priya’s Capital A/c |
Dr. |
300 |
|||||
|
To |
600 |
||||||
|
(100 shares of Rs 10 each taken @ Rs 6 each by Paras their profit sharing ratio) |
|||||||
Q13: All partners wishes to dissolve the firm. Yastin, a partner wants that her loan of Rs 2,00,000 must be paid off before the payment of capitals to the partners. But, Amart, another partner wants that the capitals must be paid before the payment of Yastin’s loan. You are required to settle the conflict giving reasons.
Answer :
As per section 48 of Partnership Act 1932, at the time of dissolution, loans and advances from the partners must be paid off before the settlement of their capital accounts. Hence, Yastin’s argument is correct that her loan of Rs 2,00,000 must be paid off before the payment of partners’ capital.
Q14: What journal entries would be recorded for the following transactions on the dissolution of a firm after various assets (other than cash) on the third party liabilities have been transferred to Reliasation Account.
1. Arti took over the Stock worth Rs 80,000 at Rs 68,000.
2. There was unrecorded Bike of Rs 40,000 which was taken over By Mr. Karim.
3. The firm paid Rs 40,000 as compensation to employees.
4. Sundry creditors amounting to Rs 36,000 were settled at a discount of 15%.
5. Loss on Realisation Rs 42,000 was to be distributed between Arti and Karim in the ratio of 3:4.
Answer :
|
Journal
|
|||||||
|
|
Particulars |
L.F. |
Amount Rs |
Amount Rs |
|||
|
1 |
Arti’s |
Dr. |
68,000 |
||||
|
To Realisation A/c |
68,000 |
||||||
|
(Arti |
|||||||
|
2. |
Karim’s |
Dr. |
40,000 |
||||
|
To Realisation A/c |
40,000 |
||||||
|
(Karim |
|||||||
|
3. |
Realisation |
Dr. |
40,000 |
||||
|
To Bank A/c |
40,000 |
||||||
|
(Compensation paid to the |
|||||||
|
4. |
Realisation |
Dr. |
30,600 |
||||
|
To Bank A/c |
30,600 |
||||||
|
(Creditors amounting Rs [36,000 × (85/100)] |
|||||||
|
5. |
Arti’s |
Dr. |
18,000 |
||||
|
Karim’s |
Dr. |
24,000 |
|||||
|
To Realisation A/c |
42,000 |
||||||
|
(Loss on Realisation |
|||||||
Q15: Rose and Lily shared profits in the ratio of 2:3. Their Balance Sheet on March 31, 2012 was as follows:
|
Balance Sheet of Rose and Lily as on March 31, 2006*
|
|
||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
||
|
Creditors |
40,000 |
Cash |
|
16,000 |
|
|
Lily’s loan |
32,000 |
Debtors |
80,000 |
|
|
|
Profit and Loss |
50,000 |
Less: Provision for doubtful Debts |
3,600 |
76,400 |
|
|
Capitals: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lily |
1,60,000 |
Inventory |
|
1,09,600 |
|
|
Rose |
2,40,000 |
Bills Receivable |
|
40,000 |
|
|
|
|
Buildings |
|
2,80,000 |
|
|
|
5,22,000 |
|
|
5,22,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rose and Lily decided to dissolve the firm on the above date. Assets (except bills receivables) realised Rs 4,84,000. Bills Receivable were taken over by Rose at Rs 30,000. Creditors agreed to take Rs 38,000. Cost of Realisation was Rs 2,400. There was a Motor Cycle in the firm which was bought out of the firm’s money, was not shown in the books of the firm. It was now sold for Rs 10,000. There was a contingent liability in respect of outstanding electric bill of Rs 5,000, Bill Receivable taken over by Rose at Rs 33,000.
Show Realisation Account, Partners Capital Account, Loan Account and Cash Account.
* As per the question, this should be March 31, 2012
Answer:
|
Books of Rose and Lily
Realisation Account |
|||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||
|
Debtors |
80,000 |
Provision for Doubtful Debts |
3,600 |
||||
|
Inventory |
1,09,600 |
Creditors |
40,000 |
||||
|
Bills Receivables |
40,000 |
Cash: |
|||||
|
Buildings |
2,80,000 |
Motor cycle |
10,000 |
||||
|
Cash: |
Other Assets |
4,84,000 |
4,94,000 |
||||
|
Outstanding Electricity Bill |
5,000 |
Rose’s Capital (Bills Receivable) |
33,000 |
||||
|
Creditors |
38,000 |
||||||
|
Expenses |
2,400 |
45,400 |
|||||
|
Profit transferred to: |
|||||||
|
Rose’ Capital |
6,240 |
||||||
|
Lily’s Capital |
9,360 |
15,600 |
|||||
|
5,70,600 |
5,70,600 |
||||||
|
Partners’ Capital Account |
|||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Rose |
Lily |
Particulars |
Rose |
Lily |
||
|
Realisation (Bills Receivable) |
33,000 |
Balance b/d |
2,40,000 |
1,60,000 |
|||
|
Cash A/c |
2,33,240 |
1,99,360 |
Profit and Loss |
20,000 |
30,000 |
||
|
Realisation (Profit) |
6,240 |
9,360 |
|||||
|
2,66,240 |
1,99,360 |
2,66,240 |
1,99,360 |
||||
|
Lily’s Loan Account |
||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|||
|
Cash |
32,000 |
Balance b/d |
32,000 |
|||
|
32,000 |
32,000 |
|||||
|
Cash Account |
||||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|||||
|
Balance b/d |
16,000 |
Realisation: |
||||||
|
Realisation: |
Creditors |
38,000 |
||||||
|
Motor Cycle |
10,000 |
Outstanding Electricity Bill |
5,000 |
|||||
|
Other Assets |
4,84,000 |
4,94,000 |
Expenses |
2,400 |
45,400 |
|||
|
Lily’s Loan |
32,000 |
|||||||
|
Rose’s Capital A/c |
2,33,240 |
|||||||
|
Lily’s Capital A/c |
1,99,360 |
|||||||
|
5,10,000 |
5,10,000 |
|||||||
Note: In the solution Contingent Liability of Electricity Bill has been treated as Electricity Bill Payable. Further, it is also been assumed that Rosy has taken over Bills Receivable at Rs 33,000.
Q16: Shilpa, Meena and Nanda decided to dissolve their partnership on March 31,2006. Their profit sharing ratio was 3:2:1 and their Balance Sheet was as under:
|
Balance Sheet of Shilpa, Meena and Nanda as on
|
||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
|
|
Capitals: |
Land |
81,000 |
||
|
Shilpa |
80,000 |
Stock |
56,760 |
|
|
Meena |
40,000 |
Debtors |
18,600 |
|
|
Bank |
20,000 |
Nanda’s Capital Account |
23,000 |
|
|
Creditors |
37,000 |
Cash |
10,840 |
|
|
Provision |
1,200 |
|||
|
General |
12,000 |
|||
|
|
1,90,200 |
1,90,200 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
The stock of value of Rs 41,660 are taken over by Shilpa for Rs 35,000 and she agreed to discharge bank loan. The remaining stock was sold at Rs 14,000 and debtors amounting to Rs 10,000 realised Rs 8,000. land is sold for Rs 1,10,000. The remaining debtors realised 50% at their book value. Cost of Realisation amounted to Rs 1,200. There was a typewriter not recorded in the books worth Rs 6,000 which were taken over by one of the Creditors at this value. Prepare Realisation Account.
Answer:
|
In the books of Shilpa, Meena and Nanda
|
|||||||||
|
Realisation Account |
|||||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||||
|
Land |
81,000 |
Bank Loan |
20,000 |
||||||
|
Stock |
56,760 |
Creditors |
37000 |
||||||
|
Debtors |
18,600 |
Provision for doubtful debts |
1,200 |
||||||
|
Shilpa’s |
20,000 |
Shilpa’s |
35,000 |
||||||
|
Cash : |
Cash: |
||||||||
|
Creditors |
31000 |
Stock |
14000 |
||||||
|
Realisation Expenses |
1,200 |
32200 |
Debtors |
12300 |
|||||
|
Profit transferred to |
Land |
1,10,000 |
1,36,300 |
||||||
|
Shilpa’s Capital A/c |
10,470 |
||||||||
|
Meena’s Capital A/c |
6,980 |
||||||||
|
Nanda’s Capital A/c |
3,490 |
20,940 |
|||||||
|
2,29,500 |
2,29,500 |
||||||||
|
Partners’ Capital Account |
|||||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Particulars |
Shilpa |
Meena |
Nanda |
Particulars |
Shilpa |
Meena |
Nanda |
||
|
Balance b/d |
– |
– |
23,000 |
Balance |
80,000 |
40,000 |
– |
||
|
Realisation |
35,000 |
General Reserve |
6,000 |
4,000 |
2,000 |
||||
|
(Stock) |
Realisation |
20,000 |
|||||||
|
Cash |
81,470 |
50,980 |
(Bank Loan) |
||||||
|
Realisation |
10,470 |
6,980 |
3,490 |
||||||
|
Cash |
17,510 |
||||||||
|
1,16,470 |
50,980 |
23,000 |
1,16,470 |
50,980 |
23,000 |
||||
|
Cash Account |
||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|||
|
Balance b/d |
10,840 |
Realisation |
32,200 |
|||
|
Realisation |
1,36,300 |
Shilpa’s |
81,470 |
|||
|
Nanda’s |
17,510 |
Meena’s |
50,980 |
|||
|
1,64,650 |
1,64,650 |
|||||
Q17: Surjit and Rahi were sharing profits (losses) in the ratio of 3:2, their Balance Sheet as on March 31, 2004* is as follows:
|
Balance Sheet of Surjit and Rahi as on March 31, 2012
|
||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
|
|
Creditors |
38,000 |
Bank |
11,500 |
|
|
Mrs. Surjit loan |
10,000 |
Stock |
6,000 |
|
|
Reserve |
15,000 |
Debtors |
19,000 |
|
|
Rahi’s loan |
5,000 |
Furniture |
4,000 |
|
|
Capital’s: |
Plant |
28,000 |
||
|
Surjit |
10,000 |
Investment |
10,000 |
|
|
Rahi |
8,000 |
Profit and Loss |
7,500 |
|
|
|
86,000 |
86,000 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
The firm was dissolved on March 31, 2012 on the following terms:
1. Surjit agreed to take the investments at Rs 8,000 and to pay Mrs. Surjit’s loan.
2. Other assets were realised as follows:
|
Stock |
Rs |
5,000 |
|
Debtors |
Rs |
18,500 |
|
Furniture |
Rs |
4,500 |
|
Plant |
Rs |
25,000 |
3. Expenses on Realisation amounted to Rs 1,600.
4. Creditors agreed to accept Rs 37,000 as a final settlement.
You are required to prepare Realisation Account, Partners’ Capital Account and Bank Account.
* As per the question, the year should be 2012 and not 2004
Answer:
|
Books of Surjit and Rahi
Realisation Account |
|||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||
|
Stock |
6,000 |
Creditors |
38,000 |
||||
|
Debtors |
19,000 |
Mrs. Surjit’s Loan |
10,000 |
||||
|
Furniture |
4,000 |
Surjit’s Capital A/c (Investment) |
8,000 |
||||
|
Plant |
28,000 |
Bank: |
|||||
|
Investment |
10,000 |
Stock |
5,000 |
||||
|
Surjit’s Capital A/c |
10,000 |
Debtors |
18,500 |
||||
|
(Mrs. Surjit’s Loan) |
Furniture |
4,500 |
|||||
|
Bank: |
Plant |
25,000 |
53,000 |
||||
|
Expenses |
1,600 |
Loss transferred to: |
|||||
|
Creditors |
37,000 |
38,600 |
Surjit’s Capital A/c |
3,960 |
|||
|
Rahi’s Capital A/c |
2,640 |
6,600 |
|||||
|
1,15,600 |
1,15,600 |
||||||
|
Partners’ Capital Account |
|||||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||||||
|
Particulars |
Surjit |
Rahi |
Particulars |
Surjit |
Rahi |
||||
|
Realisation (Investment) |
8,000 |
Balance b/d |
10,000 |
8,000 |
|||||
|
Realisation (Loss) |
3,960 |
2,640 |
Realisation (Mrs. Surjit Loan) |
10,000 |
|||||
|
Profit and Loss |
4,500 |
3,000 |
|||||||
|
Bank |
12,540 |
8,360 |
Reserve |
9,000 |
6,000 |
||||
|
29,000 |
14,000 |
29,000 |
14,000 |
||||||
|
Rahi’s Loan Account |
||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|||
|
Balance b/d |
5,000 |
|||||
|
Bank |
5,000 |
|||||
|
5,000 |
5,000 |
|||||
|
Bank Account |
|||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||
|
Balance b/d |
11,500 |
Realisation (Creditors and Expenses) |
38,600 |
||||
|
Realisation A/c (Assets realised) |
53,000 |
Rahi’s Loan |
5,000 |
||||
|
Surjit’s Capital A/c |
12,540 |
||||||
|
Rahi’s Capital A/c |
8,360 |
||||||
|
64,500 |
64,500 |
||||||
Q18: Rita, Geeta and Ashish were partners in a firm sharing profits/losses in the ratio of 3:2:1. On March 31, 2012 their balance sheet was as follows:
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
|
|
Capitals: |
Cash |
22,500 |
||
|
Rita |
80,000 |
Debtors |
52,300 |
|
|
Geeta |
50,000 |
Stock |
36,000 |
|
|
Ashish |
30,000 |
1,60,000 |
Investments |
69,000 |
|
Creditors |
65,000 |
Plant |
91,200 |
|
|
Bills payable |
26,000 |
|||
|
General reserve |
20,000 |
|||
|
|
|
2,71,000 |
2,71,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
On the date of above mentioned date the firm was dissolved:
1. Rita was appointed to realise the assets. Rita was to receive 5% commission on the rate of assets (except cash) and was to bear all expenses of Realisation,
2. Assets were realised as follows:
|
|
Rs |
|
Debtors |
30,000 |
|
Stock |
26,000 |
|
Plant |
42,750 |
3. Investments were realised at 85% of the book value,
4. Expenses of Realisation amounted to Rs 4,100,
5. Firm had to pay Rs 7,200 for outstanding salary not provided for earlier,
6. Contingent liability in respect of bills discounted with the bank was also materialised and paid off Rs 9,800,
Prepare Realisation Account, Capital Accounts of Partners’ and Cash Account.
Answer:
|
In the books of Rita, Geeta and Ashish
Realisation Account |
|
||||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|
||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||||
|
Debtors |
52,300 |
Creditors |
65,000 |
||||||
|
Stock |
36,000 |
Bills Payable |
26,000 |
||||||
|
Investment |
69,000 |
Cash: |
|
||||||
|
Plant |
91,200 |
Debtors |
30,000 |
|
|||||
|
Cash: |
|
Stock |
26,000 |
|
|||||
|
Outstanding Salaries |
7,200 |
|
Plant |
42,750 |
|
||||
|
Discounted Bill |
9,800 |
|
Investment |
58,650 |
1,57,400 |
||||
|
Creditors |
65,000 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
Bills Payable |
26,000 |
1,08,000 |
Loss transferred to |
|
|||||
|
Rita’s Capital A/c |
|
7,870 |
Rita’s Capital A/c |
57,985 |
|
||||
|
(Commission- 1,57,400 ´ 5/100) |
|
Geeta’s Capital A/c |
38,657 |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
Ashish’s Capital A/c |
19,328 |
1,15,970 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
364370 |
|
|
364370 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Partners’ Capital Account |
|
||||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|
||||||
|
Particulars |
Rita |
Geeta |
Ashish |
Particulars |
Rita |
Geeta |
Ashish |
||
|
Realisation (Loss) |
57,985 |
38,657 |
19,328 |
Balance b/d |
80,000 |
50,000 |
30,000 |
||
|
Bank |
39,885 |
18,010 |
14,005 |
General Reserve |
10,000 |
6,667 |
3,333 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Realisation |
7,870 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
97,870 |
56667 |
33333 |
|
97870 |
56,667 |
33,333 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Cash Account |
|
|||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|
|||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|
||
|
Balance b/d |
22,500 |
Realisation A/c |
1,08,000 |
|
||
|
Realisation |
1,57,400 |
Rita’s Capital |
39,885 |
|
||
|
|
|
Geeta’s Capital A/c |
18,010 |
|
||
|
|
|
Ashish’s Capital A/c |
14,005 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
1,79,900 |
|
1,79,900 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
NOTE: As per the solution, the Loss on Realisation should be Rs 1,15,970 and the total of Cash Account should be Rs 1,79,900; however, the answer given in the book shows Rs 1,29,455 and Rs 1,65,705 respectively.
Q19: Anup and Sumit are equal partners in a firm. They decided to dissolve the partnership on December 31, 2012. When the balance sheet is as under:
|
Balance Sheet of Anup and Sumit as on December 31, 2012
|
|||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
||
|
Sundry Creditors |
27,000 |
Cash at bank |
11,000 |
||
|
Reserve fund |
10,000 |
Sundry Debtors |
12,000 |
||
|
Loan |
40,000 |
Plants |
47,000 |
||
|
Capital |
Stock |
42,000 |
|||
|
Anup |
60,000 |
Lease hold land |
60,000 |
||
|
Sumit |
60,000 |
1,20,000 |
Furniture |
25,000 |
|
|
|
|
1,97,000 |
1,97,000 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Assets were realised as follows:
|
|
Rs |
|
Lease hold land |
72,000 |
|
Furniture |
22,500 |
|
Stock |
40,500 |
|
Plant |
48,000 |
|
Sundry Debtors |
10,500 |
The Creditors were paid Rs 25,500 in full settlement. Expenses of Realisation amount to Rs 2,500.
Prepare Realisation Account, Bank Account, Partners Capital Accounts to close the books of the firm.
Answer:
|
Books of Anup and Sumit
Realisation Account |
||||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|||||
|
Sundry Debtors |
12,000 |
Sundry Creditors |
27,000 |
|||||
|
Plants |
47,000 |
Loan |
40,000 |
|||||
|
Stock |
42,000 |
Bank: |
||||||
|
Lease hold land |
60,000 |
Lease hold Land |
72,000 |
|||||
|
Furniture |
25,000 |
Furniture |
22,500 |
|||||
|
Bank: |
Stock |
40,500 |
||||||
|
Creditors |
25,500 |
Plant |
48,000 |
|||||
|
Loan |
40,000 |
Sundry Debtors |
10,500 |
1,93,500 |
||||
|
Expenses |
2500 |
68,000 |
||||||
|
Profit transferred to |
||||||||
|
Anup’s Capital A/c |
3,250 |
|||||||
|
Sumit’s Capital A/c |
3250 |
6,500 |
||||||
|
2,60,500 |
2,60,500 |
|||||||
|
Partners’ Capital Account |
||||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
||||||
|
Particulars |
Anup |
Sumit |
Particulars |
Anup |
Sumit |
|||
|
Bank |
68,250 |
68,250 |
Balance b/d |
60,000 |
60,000 |
|||
|
Reserve Fund |
5,000 |
5,000 |
||||||
|
Realisation |
3,250 |
3,250 |
||||||
|
68,250 |
68,250 |
68,250 |
68,250 |
|||||
|
Bank Account |
||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|||
|
Balance b/d |
11,000 |
Realisation (Expenses and Liabilities) |
68,000 |
|||
|
Realisation (Assets ) |
1,93,500 |
Anup’s Capital A/c |
68,250 |
|||
|
Sumit’s Capital A/c |
68,250 |
|||||
|
2,04,500 |
2,04,500 |
|||||
NOTE: As per the solution, Profit on Realisation is Rs 6,500; however as per the answer given in the book is Rs 46,500. If Loan is not transferred to the Realisation Account and paid directly from Loan Account, then the answer would match with that of the book.
Q20: Ashu and Harish are partners sharing profit and losses as 3:2. They decided to dissolve the firm on December 31, 2012. Their balance sheet on the above date was:
|
Balance Sheet of Ashu and Harish as on December 31, 2012
|
|||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
||
|
Capitals: |
Building |
80,000 |
|||
|
Ashu |
1,08,000 |
Machinery |
70,000 |
||
|
Harish |
54,000 |
1,62,000 |
Furniture |
14,000 |
|
|
Creditors |
88,000 |
Stock |
20,000 |
||
|
Bank overdraft |
50,000 |
Investments |
60,000 |
||
|
Debtors |
48,000 |
||||
|
Cash in hand |
8,000 |
||||
|
|
|
3,00,000 |
3,00,000 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ashu is to take over the building at Rs 95,000 and Machinery and Furniture is take over by Harish at value of Rs 80,000. Ashu agreed to pay Creditor and Harish agreed to meet Bank overdraft. Stock and Investments are taken by both partner in profit sharing ratio. Debtors realised for Rs 46,000, expenses of Realisation amounted to Rs 3,000. Prepare necessary ledger Account.
Answer:
|
Books of Ashu and Harish
Realisation Account |
|||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||
|
Building |
80,000 |
Creditors |
88,000 |
||||
|
Machinery |
70,000 |
Bank overdraft |
50,000 |
||||
|
Furniture |
14,000 |
Ashu’s Capital A/c (Assets taken) |
1,43,000 |
||||
|
Stock |
20,000 |
Harish’s Capital A/c (Assets taken) |
1,12,000 |
||||
|
Investments |
60,000 |
Cash (Debtors) |
46,000 |
||||
|
Debtors |
48,000 |
||||||
|
Ashu’s Capital A/c (Creditors) |
88,000 |
||||||
|
Harish’s Capital A/c (Bank Overdraft) |
50,000 |
||||||
|
Cash (Expenses) |
3,000 |
||||||
|
Profit transferred to |
|||||||
|
Ashu’s Capital A/c |
3,600 |
||||||
|
Harish’s Capital A/c |
2,400 |
6,000 |
|||||
|
4,39,000 |
4,39,000 |
||||||
|
Partners’ Capital Account |
||||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
||||||
|
Particulars |
Ashu |
Harish |
Particulars |
Ashu |
Harish |
|||
|
Realisation (Assets taken) |
1,43,000 |
1,12,000 |
Balance b/d |
1,08,000 |
54,000 |
|||
|
Cash |
56,600 |
Realisation (Liabilities) |
88,000 |
50,000 |
||||
|
Realisation (Profit) |
3,600 |
2,400 |
||||||
|
Cash |
5,600 |
|||||||
|
1,99,600 |
1,12,000 |
1,99,600 |
1,12,000 |
|||||
|
Cash Account |
||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|||
|
Balance b/d |
8,000 |
Realisation (Expenses) |
3,000 |
|||
|
Realisation (Debtors) |
46,000 |
Ashu’s Capital A/c |
56,600 |
|||
|
Harish’s Capital A/c |
5,600 |
|||||
|
59,600 |
59,600 |
|||||
NOTE: As per the solution, the Profit on Realisation is Rs 6,000; however, the answer mentioned in the book is Rs 14,000.
Working Notes:
|
Ashu |
Harish |
|
|
Building |
95,000 |
|
|
Machinery and Furniture |
80,000 |
|
|
Stock (3:2) |
12,000 |
8,000 |
|
Investment (3:2) |
36,000 |
24,000 |
|
Rs 1,43,000 |
Rs 1,12,000 |
Q21: Sanjay, Tarun and Vineet shared profit in the ratio of 3:2:1. On December 31,2012 their balance sheet was as follows:
|
Balance Sheet of Sanjay, Tarun and Vineet as on December 31, 2012
|
|||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
||
|
Capitals: |
Plant |
90,000 |
|||
|
Sanjay |
1,00,000 |
Debtors |
60,000 |
||
|
Tarun |
1,00,000 |
Furniture |
32,000 |
||
|
Vineet |
70,000 |
2,70,000 |
Stock |
60,000 |
|
|
Creditors |
80,000 |
Investments |
70,000 |
||
|
Bills payable |
30,000 |
Bills receivable |
36,000 |
||
|
Cash in hand |
32,000 |
||||
|
|
|
3,80,000 |
3,80,000 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
On this date the firm was dissolved. Sanjay was appointed to realise the assets. Sanjay was to receive 6% commission on the sale of assets (except cash) and was to bear all expenses of Realisation.
Sanjay realised the assets as follows: Plant Rs 72,000, Debtors Rs 54,000, Furniture Rs 18,000, Stock 90% of the book value, Investments Rs 76,000 and Bills receivable Rs 31,000. Expenses of Realisation amounted to Rs 4,500.
Prepare Realisation Account, Capital Accounts and Cash Account
|
Books of Sanjay, Tarun and Vineet
Realisation Account |
|||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||
|
Plant |
90,000 |
Creditors |
80,000 |
||||
|
Debtors |
60,000 |
Bills Payable |
30,000 |
||||
|
Furniture |
32,000 |
Cash: |
|||||
|
Stock |
60,000 |
Plant |
72,000 |
||||
|
Investment |
70,000 |
Debtors |
54,000 |
||||
|
Bills Receivable |
36,000 |
Furniture |
18,000 |
||||
|
Cash : |
Stock |
54,000 |
|||||
|
Creditors |
80,000 |
Investments |
76,000 |
||||
|
Bills Payable |
30,000 |
1,10,000 |
Bills Receivable |
31,000 |
3,05,000 |
||
|
Sanjay’s Capital A/c |
18,300 |
Loss transferred to |
|||||
|
(6% commission) |
Sanjay’s Capital |
30,650 |
|||||
|
Tarun’s Capital A/c |
20,433 |
||||||
|
Vineet’s Capital A/c |
10,217 |
61,300 |
|||||
|
4,76,300 |
4,76,300 |
||||||
|
Partners’ Capital Account |
|||||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Particulars |
Sanjay |
Tarun |
Vineet |
Particulars |
Sanjay |
Tarun |
Vineet |
||
|
Realisation (Loss) |
30,650 |
20,433 |
10,217 |
Balance b/d |
1,00,000 |
1,00,000 |
70,000 |
||
|
Cash |
87,650 |
79,567 |
59,783 |
Realisation (commission) |
18,300 |
||||
|
1,18,300 |
1,00,000 |
70,000 |
1,18,300 |
1,00,000 |
70,000 |
||||
|
Cash Account |
||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|||
|
Balance b/d |
32,000 |
Realisation |
1,10,000 |
|||
|
Realisation |
3,05,000 |
Sanjay’s Capital A/c |
87,650 |
|||
|
Tarun’s Capital A/c |
79,567 |
|||||
|
Vineet’s Capital A/c |
59,783 |
|||||
|
3,37,000 |
3,37,000 |
|||||
Q22: The following is the Balance Sheet of Gupta and Sharma as on December 31,2012:
|
Balance Sheet of Gupta and Sharma as on December 31, 2012
|
|||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
||
|
Sundry Creditors |
38,000 |
Cash at Bank |
12,500 |
||
|
Mrs.Gupta’s loan |
20,000 |
Sundry Debtors |
55,000 |
||
|
Mrs.Sharma’s loan |
30,000 |
Stock |
44,000 |
||
|
Reserve fund |
6,000 |
Bills Receivable |
19,000 |
||
|
Provision of doubtful debts |
4,000 |
Machinery |
52,000 |
||
|
Capital |
Investment |
38,500 |
|||
|
Gupta |
90,000 |
Fixtures |
27,000 |
||
|
Sharma |
60,000 |
1,50,000 |
|||
|
|
2,48,000 |
2,48,000 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||
The firm was dissolved on December 31, 2012 and asset realised and settlements of liabilities as follows:
(a) The Realisation of the assets were as follows:
|
Rs |
|
|
Sundry Debtors |
52,000 |
|
Stock |
42,000 |
|
Bills receivable |
16,000 |
|
Machinery |
49,000 |
(b) Investment was taken over by Gupta at agreed value of Rs 36,000 and agreed to pay of Mrs. Gupta’s loan.
(c) The Sundry Creditors were paid off less 3% discount.
(d) The Realisation expenses incurred amounted to Rs 1,200.
Journalise the entries to be made on the dissolution and prepare Realisation Account, Bank Account and Partners Capital Accounts.
Answer
|
Books of Gupta and Sharma
Journal
|
|
||||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
L.F. |
Amount Rs |
Amount Rs |
|||
|
2012 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Dec. 31 |
Realisation A/c |
Dr. |
|
2,35,500 |
|
||
|
|
To Sundry Debtors A/c |
|
|
|
55,000 |
||
|
|
To Stock A/c |
|
|
|
44,000 |
||
|
|
To Bills Receivable A/c |
|
|
|
19,000 |
||
|
|
To Machinery A/c |
|
|
|
52,000 |
||
|
|
To Investment A/c |
|
|
|
38,500 |
||
|
|
To Fixtures A/c |
|
|
|
27,000 |
||
|
|
(Assets transferred to Realisation Account) |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Sundry Creditors A/c |
Dr. |
|
38,000 |
|
||
|
|
Mrs. Gupta’s Loan A/c |
Dr. |
|
20,000 |
|
||
|
|
Mrs. Sharma’s Loan A/c |
Dr. |
|
30,000 |
|
||
|
|
Provision for Doubtful Debts |
Dr. |
|
4,000 |
|
||
|
|
To Realisation A/c |
|
|
|
92,000 |
||
|
|
(Liabilities transferred to Realisation Account) |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Bank A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,59,000 |
|
||
|
|
To Realisation A/c |
|
|
|
1,59,000 |
||
|
|
(Assets realised: Sundry Debtors Rs 52,000, Stock Rs 42,000, Bills Receivable Rs 16,000, Machinery Rs 49,000) |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Realisation A/c |
Dr. |
|
20,000 |
|
||
|
|
To Gupta’s Capital A/c |
|
|
|
20,000 |
||
|
|
(Gupta took over Mrs. Gupta’s Loan) |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Gupta’s Capital A/c |
Dr. |
|
36,000 |
|
||
|
|
To Realisation A/c |
|
|
|
36,000 |
||
|
|
(Investment taken over by Gupta) |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Realisation A/c |
Dr. |
|
66,860 |
|
||
|
|
To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
66,860 |
||
|
|
(Liabilities paid: Mrs. Sharma’s Loan Rs 30,000 and Creditors Rs 38,000 paid off less 3% discount) |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Realisation A/c |
Dr. |
|
1,200 |
|
||
|
|
To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
1,200 |
||
|
|
(Realisation expenses paid) |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Gupta’s Capital A/c |
Dr. |
|
18,280 |
|
||
|
|
Sharma’s Capital A/c |
Dr. |
|
18,280 |
|
||
|
|
To Realisation A/c |
|
|
|
36,560 |
||
|
|
(Loss on Realisation transferred to Partners’ capital Account) |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Reserve Fund A/c |
Dr. |
|
6,000 |
|
||
|
|
To Gupta’s Capital A/c |
|
|
|
3,000 |
||
|
|
To Sharma’s Capital A/c |
|
|
|
3,000 |
||
|
|
(Reserve fund distributed among partners ratio) |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec. 31 |
Gupta’s Capital A/c |
Dr. |
|
58,720 |
|
||
|
|
Sharma’s Capital A/c |
Dr. |
|
44,720 |
|
||
|
|
To Bank A/c |
|
|
|
1,03,440 |
||
|
|
(Final payment made to partners) |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Realisation Account |
|
||||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|
||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||||
|
Sundry Debtors |
55,000 |
Sundry Creditors |
38,000 |
||||||
|
Stock |
44,000 |
Mrs. Gupta’s Loan |
20,000 |
||||||
|
Bills Receivable |
19,000 |
Mrs. Sharma’s Loan |
30,000 |
||||||
|
Machinery |
52,000 |
Provision for Doubtful Debts |
4,000 |
||||||
|
Investment |
38,500 |
Bank : |
|
||||||
|
Fixtures |
27,000 |
Sundry Debtors |
52,000 |
|
|||||
|
Gupta’s Capital A/c (Mrs. Gupta Loan) |
20,000 |
Stock |
42,000 |
|
|||||
|
Bank A/c: |
|
Bills Receivable |
16,000 |
|
|||||
|
Creditors |
36,860 |
|
Machinery |
49,000 |
1,59,000 |
||||
|
Mrs. Sharma’s Loan |
30,000 |
|
Gupta’s Capital A/c (Investment) |
36,000 |
|||||
|
Expense |
1,200 |
68,060 |
Loss transferred to |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
Gupta’s Capital A/c |
18,280 |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
Sharma’s Capital A/c |
18,280 |
36,560 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
3,23,560 |
|
3,23,560 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Partners’ Capital Account |
|
|||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|
|||||
|
Particulars |
Gupta |
Sharma |
Particulars |
Gupta |
Sharma |
|||
|
Realisation (Investment) |
36,000 |
|
Balance b/d |
90,000 |
60,000 |
|||
|
Realisation (Loss) |
18,280 |
18,280 |
Realisation (Mrs. Gupta Loan) |
20,000 |
|
|||
|
Bank |
58,720 |
44,720 |
Reserve Fund |
3,000 |
3,000 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
1,13,000 |
63,000 |
|
1,13,000 |
63,000 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Bank Account |
|
|||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|
|||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|||
|
Balance b/d |
12,500 |
Realisation |
68,060 |
|||
|
Realisation (Assets realised) |
1,59,000 |
(Payment of expenses and liabilities) |
|
|||
|
|
|
Gupta’s Capital A/c |
58,720 |
|||
|
|
|
Sharma’s Capital A/c |
44,720 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
1,71,500 |
|
1,71,500 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
NOTE: As per the solution, Loss on Realisation is Rs 36,560 and the total of Bank Account is Rs 1,71,500. However, the answers mentioned in the book are Rs 19,660 and Rs 1,88,500 respectively.
Q23: Ashok, Babu and Chetan are in partnership sharing profit in the proportion of 1/2, 1/3, 1/6 respectively. They dissolve the partnership of the December 31, 2012, when the balance sheet of the firm as under:
|
Balance Sheet of Ashok, Babu and Chetan as on December 31, 2012
|
|||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
||
|
Sundry Creditors |
20,000 |
Bank |
7,500 |
||
|
Bills payable |
25,500 |
Sundry Debtors |
58,000 |
||
|
Babu’s loan |
30,000 |
Stock |
39,500 |
||
|
Capital’s: |
Machinery |
48,000 |
|||
|
Ashok |
70,000 |
Investment |
42,000 |
||
|
Babu |
55,000 |
Freehold Property |
50,500 |
||
|
Chetan |
27,000 |
1,52,000 |
|||
|
Current Accounts : |
|||||
|
Ashok |
10,000 |
||||
|
Babu |
5,000 |
||||
|
Chetan |
3,000 |
18,000 |
|||
|
|
|
2,45,500 |
2,45,500 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Machinery was taken over by Babu for Rs 45,000, Ashok took over the Investment for Rs 40,000 and Freehold property took over by Chetan at Rs 55,000. The remaining Assets realised as follows: Sundry Debtors Rs 56,500 and Stock Rs 36,500. Sundry Creditors were settled at discount of 7%. A Office computer, not shown in the books of Accounts realised Rs 9,000. Realisation expenses amounted to Rs 3,000.
Prepare Realisation Account, Partners Capital Account, Bank Account.
Answer:
|
Realisation Account |
|||||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||||
|
Sundry Debtors |
58,000 |
Sundry Creditors |
20,000 |
||||||
|
Stock |
39,500 |
Bills Payable |
25,500 |
||||||
|
Machinery |
48,000 |
Ashok’s Current A/c (Investment) |
40,000 |
||||||
|
Investment |
42,000 |
Babu’s Current A/c (Machinery) |
45,000 |
||||||
|
Freehold property |
50,500 |
Chetan’s Current A/c |
55,000 |
||||||
|
Bank: |
(Free hold property) |
||||||||
|
Sundry Creditors |
18,600 |
Bank: |
|||||||
|
Bills payable |
25,500 |
Sundry Debtors |
56,500 |
||||||
|
Expenses |
3,000 |
47,100 |
Stock |
36,500 |
|||||
|
Profit Transferred to |
Unrecorded computer |
9,000 |
1,02,000 |
||||||
|
Ashok’s Current A/c |
1,200 |
||||||||
|
Babu’s Current A/c |
800 |
||||||||
|
Chetan’s Current A/c |
400 |
2,400 |
|||||||
|
2,87,500 |
2,87,500 |
||||||||
|
Partners’ Current Account |
||||||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
||||||||
|
Particulars |
Ashok |
Babu |
Chetan |
Particulars |
Ashok |
Babu |
Chetan |
|||
|
Realisation |
40,000 |
45,000 |
55,000 |
Balance b/d |
10,000 |
5,000 |
3,000 |
|||
|
(Assets taken) |
Realisation (Profit) |
1,200 |
800 |
400 |
||||||
|
Ashok’s Capital A/c |
28,800 |
|||||||||
|
Babu’s Capital A/c |
39200 |
|||||||||
|
Chetan’s Capital A/c |
51600 |
|||||||||
|
40,000 |
45,000 |
55,000 |
40,000 |
45,000 |
55,000 |
|||||
|
Partners’ Capital Account |
||||||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
||||||||
|
Particulars |
Ashok |
Babu |
Chetan |
Particulars |
Ashok |
Babu |
Chetan |
|||
|
Ashok’s Current |
28,800 |
Balance b/d |
70,000 |
55,000 |
27,000 |
|||||
|
Babu’s Current |
39200 |
Bank |
24,600 |
|||||||
|
Chetan’s Current |
51600 |
|||||||||
|
Bank |
41,200 |
15,800 |
||||||||
|
70,000 |
55,000 |
51,600 |
70,000 |
55,000 |
51,600 |
|||||
|
Babu’s Loan A/c |
|||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||
|
Particulars |
Amount |
Particulars |
Amount |
||
|
Cash A/c |
30,000 |
Balance b/d |
30,000 |
||
|
30,000 |
30,000 |
||||
|
Bank Account |
||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|||
|
Balance b/d |
7,500 |
Realisation (Payment of Expenses |
47,100 |
|||
|
Realisation (Assets realised ) |
102,000 |
and Liabilities) |
||||
|
Chetan’s Capital A/c |
24,600 |
Babu’s Loan |
30,000 |
|||
|
Ashok’s Capital A/c |
41,200 |
|||||
|
Babu’s Capital A/c |
15,800 |
|||||
|
1,34,100 |
1,34,100 |
|||||
Note: As per the solution, profit on realisation is Rs 2,400. However, the answer provided in the book is Rs 1,200
Q24: The following is the Balance sheet of Tanu and Manu, who shares profit and losses in the ratio of 5:3, On December 31,2012:
|
Balance Sheet of Tanu and Manu as on December 31, 2012
|
|
||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
||
|
Sundry Creditors |
|
62,000 |
Cash at Bank |
16,000 |
|
|
Bills Payable |
|
32,000 |
Sundry Debtors |
55,000 |
|
|
Bank Loan |
|
50,000 |
Stock |
75,000 |
|
|
Reserve fund |
|
16,000 |
Motor car |
90,000 |
|
|
Capital: |
|
|
Machinery |
45,000 |
|
|
Tanu |
1,10,000 |
|
Investment |
70,000 |
|
|
Manu |
90,000 |
2,00,000 |
Fixtures |
9,000 |
|
|
|
|
3,60,000 |
|
3,60,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
On the above date the firm is dissolved and the following agreement was made: Tanu agree to pay the bank loan and took away the sundry debtors. Sundry creditors accepts stock and paid Rs 10,000 to the firm. Machinery is taken over by Manu for Rs 40,000 and agreed to pay of bills payable at a discount of 5%.. Motor car was taken over by Tanu for Rs 60,000. Investment realised Rs 76,000 and fixtures Rs 4,000. The expenses of dissolution amounted to Rs 2,200.
Prepare Realisation Account, Bank Account and Partners Capital Accounts.
Answer:
|
Books of Tanu and Manu
Realisation Account |
|||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||
|
Sundry Debtors |
55,000 |
Sundry Creditors |
62,000 |
||||
|
Stock |
75,000 |
Bills Payable |
32,000 |
||||
|
Motor Car |
90,000 |
Bank Loan |
50,000 |
||||
|
Machinery |
45,000 |
Tanu’s Capital A/c: |
|||||
|
Investment |
70,000 |
Sundry Debtors |
55,000 |
||||
|
Fixtures |
9,000 |
Motor Car |
60,000 |
1,15,000 |
|||
|
Manu’s Capital A/c (Bills Payable) |
30,400 |
Bank: |
|||||
|
Bank (Expenses) |
2,200 |
Stock |
10,000 |
||||
|
Tanu’s Capital A/c (Bank Loan) |
50000 |
Investment |
76,000 |
||||
|
Fixtures |
4,000 |
90,000 |
|||||
|
Manu’s Capital (Machinery) |
40,000 |
||||||
|
Loss transferred to |
|||||||
|
Manu’s Capital A/c |
23,500 |
||||||
|
Manu’s Capital A/c |
14,100 |
37,600 |
|||||
|
4,26,600 |
4,26,600 |
||||||
|
Partners’ Capital Account |
||||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
||||||
|
Particulars |
Tanu |
Manu |
Particulars |
Tanu |
Manu |
|||
|
Realisation (Assets taken) |
1,15,000 |
40,000 |
Balance b/d |
1,10,000 |
90,000 |
|||
|
Realisation (Loss) |
23,500 |
14,100 |
Realisation (Liabilities) |
50,000 |
30,400 |
|||
|
Bank |
31,500 |
72,300 |
Reserve Fund |
10,000 |
6,000 |
|||
|
1,70,000 |
1,26,400 |
1,70,000 |
1,26,400 |
|||||
|
Bank Account |
||||||
|
Dr. |
|
Cr. |
||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|||
|
Balance b/d |
16,000 |
Realisation (Expenses) |
2,200 |
|||
|
Realisation (Assets) |
90,000 |
Tanu’s Capital A/c |
31,500 |
|||
|
Manu’s Capital A/c |
72,300 |
|||||
|
1,06,000 |
1,06,000 |
|||||