Short answers : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 422
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Financial Accounting Part-2 Chapter 2 – Financial Statements
Q1 :Why is it necessary to record the adjusting entries in the preparation of final accounts?
Answer : It is extremely important to record the adjusting entries in the preparation of final accounts.
1. This is done in order to assess the true net profit or net loss of the business organisation.
2. It helps us record those adjustments which were left or omitted and were not recorded in the accounts.
3. It assists us to separate all the financial transactions into a year-wise category. The financial statements include only those entries which belong to the current year. It rules out the previous and forthcoming years’ entries which are the basis for accrual basis of accounting.
4. Further, it provides us the room for making various provisions which are made at the end of the year, after assessing the entire year’s performance
Q2 :What is meant by closing stock? Show its treatment in final accounts.
Answer :
Closing stock implies the value of unsold goods at the end of an accounting period. The valuation of closing stock is done on the basis of its cost price or the realisable value, whichever of the two is lesser.
Example: If a good with the cost price of Rs 20,000 is purchased at the end of an accounting period and its realisable value is Rs 30,000, then the closing stock will be valued at Rs 20,000 not at Rs 30,000.
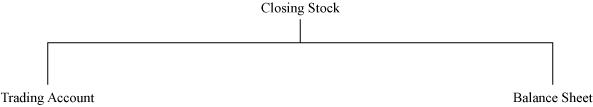
Treatment of closing stock
If closing stock is given in the adjustment, then there will be two postings.
|
Trading Account |
Balance Sheet |
||||||||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||||||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount |
Particulars |
Amount |
Liabilities |
Amount |
Assets |
Amount |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Closing Stock |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
If closing stock is given in the trial balance, then it needs to be shown only in the assets side of the Balance Sheet.
Q3 :Write short notes on
(a) Outstanding expenses
(b) Prepaid expenses
(c) Income received in advance
(d) Accrued income
Answer :
(a) Outstanding Expenses: These refer to those expenses which belong to and are incurred in the current accounting period but are left unpaid. In other words, we can say that the services in exchange of these payments have been realised but the payments are not made. For example, if Rs 1000 wages are outstanding, then this means that labour worth Rs 1,000 has been used but has not been paid for till the end of the year.
(b) Prepaid Expenses: These refer to those expenses for which the benefits have not been realised but the payments have already been made in advance. These are basically the advance payments for the next year, which are made in the current accounting period.
Example: Prepaid insurance premium of Rs 1,000 means that the payment of Rs 1,000 is made in advance for the next accounting period.
(c) Income Received in Advance: This refers to the income received whose actual realisation of benefits will occur in the next accounting period. These are also called unearned incomes.
Example: Commission of Rs 1,200 for the year 2011-12 is received in 2010-11. This commission does not belong to the current year as it is related with the work to be done in the next accounting year i.e., 2011-12.
(d) Accrued Income: This refers to those incomes which have been earned during an accounting period but have not been actually realised in the current period. These are also called earned incomes.
Q4 :Give the performa of income statement and balance in vertical form.
Answer :
|
Income statement for the period ended——— |
|||
|
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Amount Rs |
|
Sales (Gross) |
|
|
|
|
Less: Returns |
|
|
|
|
|
Net Sales |
|
|
|
Cost of goods sold |
|
|
|
|
|
Opening Stock |
|
|
|
|
Purchases |
|
|
|
|
Less: Returns |
|
|
|
|
Carriage Inwards |
|
|
|
|
Wages |
|
|
|
|
Cost of Goods Available for Sale |
|
|
|
Less: Closing Stock |
|
|
|
|
Gross Profit |
|
|
|
|
Operating Expenses |
|
|
|
|
(a) Selling Expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
Advertising |
|
|
|
|
Discount |
|
|
|
|
Allowances |
|
|
|
|
Bad-Debts and Provisions |
|
|
|
|
Carriage Outwards |
|
|
|
|
Total Selling Expenses |
|
|
|
(b) General and Administration Expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
Salaries |
|
|
|
|
Rent and Rates |
|
|
|
|
Insurance |
|
|
|
|
Depreciation |
|
|
|
|
Postage |
|
|
|
|
Repairs |
|
|
|
|
General Expenses |
|
|
|
|
Total Operating Expenses |
|
|
|
|
Net Income from Operations (Operating |
|
|
|
Other Income (Non-operating gains) |
|
|
|
|
|
Interest Earned |
|
|
|
|
Commission Earned |
|
|
|
|
Profit on Sale of Fixed Assets |
|
|
|
Less: Deductions |
|
|
|
|
|
Interest Paid |
|
|
|
|
Loss by Fire |
|
|
|
|
Net Non-operating Gains |
|
|
|
|
Net Income (Net profit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income statement for the period ended ——– |
|||
|
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Amount Rs |
|
Current Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
Cash in Hand |
|
|
|
|
Cash at Bank |
|
|
|
|
Bills Receivable |
|
|
|
|
Accrued Income |
|
|
|
|
Debtors |
|
|
|
|
Stock |
|
|
|
Prepaid Expenses |
|
|
|
|
Total Current Assets |
|
|
|
|
 Less: Current |
|
|
|
|
|
Bank Overdraft |
|
|
|
|
Outstanding Expenses |
|
|
|
|
Bills Payable |
|
|
|
|
Trade Creditors |
|
|
|
|
Income Received in Advance |
|
|
|
|
Total Current Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
Net Working Capital |
|
|
|
|
(Current assets and Current liabilities) |
|
|
|
 Fixed Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
Furniture and Fixtures |
|
|
|
|
Patents |
|
|
|
|
Plants and Machinery |
|
|
|
|
Building |
|
|
|
|
Land |
|
|
|
|
Goodwill |
|
|
|
|
Total Fixed Assets |
|
|
|
|
Total Assets (After paying current |
|
|
|
 Capital Employed |
|
|
|
|
|
Long-term Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
Loan |
|
|
|
|
Mortgage |
|
|
|
|
Total Long-term Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
Net Assets (being the difference between |
|
|
|
 Capital (Proprietor) |
|
|
|
|
|
 Capital in the Beginning |
|
|
|
 Add: Capital Introduced During |
|
|
|
|
|
 Interest on Capital, Salary, etc. |
|
|
|
|
 Profit for the Current Year |
|
|
|
 Less: Drawings During the Current |
|
|
|
|
|
 Interest on Drawings |
|
|
|
|
 Loss for the Current Year |
|
|
|
|
 Total Capital of the Proprietor at the End |
|
|
Q5 :Why is it necessary to create a provision for doubtful-debts at the time of preparation of final accounts?
Answer : The provision for doubtful-debts is created with the motive of minimising the effect of actual loss caused by the bad-debts. The actual figure of the current year’s bad-debts will be known in the next year with the realisation of debtors. At that point of time, it will be known as to how many of the debtors have become bad. Thus, instead of waiting for the realisation of debtors, we create a provision for doubtful-debts in order to cover the expected future loss associated with the debtors becoming bad.
Q6 :What adjusting entries would you record for the following?
(a) Depreciation
(b) Discount on debtors
(c) Interest on capital
(d) Manager’s commission
Answer :
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount |
Particulars |
Amount |
Liabilities |
Amount |
Assets |
Amount |
|||
|
Depreciation |
Assets |
|||||||||
|
Less: Depreciation |
||||||||||
<

|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount |
Particulars |
Amount |
Liabilities |
Amount |
Assets |
Amount |
|||
|
Discount on Debtors |
Debtors |
|||||||||
|
Less: New Provision |
||||||||||
|
Less: Further Bad Debts |
||||||||||
|
Less: Discount on Debtors |
||||||||||

|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount |
Particulars |
Amount |
Liabilities |
Amount |
Assets |
Amount |
||||
|
Interest on Capital |
Capital |
||||||||||
|
Add: Interest on Capital |
|||||||||||
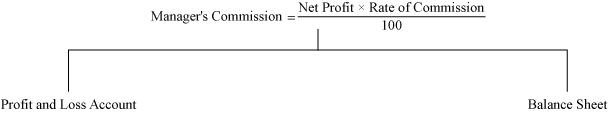
(d) Manager’s commission
There are two cases in manager’s commission.
Case 1: Manager’s commission based on profits before charging the manager’s commission.
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount |
Particulars |
Amount |
Liabilities |
Amount |
Assets |
Amount |
|||
|
Manager’s Commission |
Outstanding Manager’s |
|||||||||
|
Commission |
||||||||||
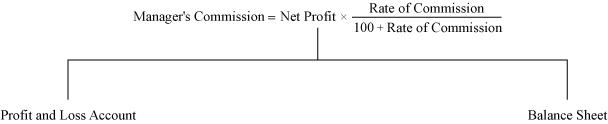
Case 2: Manager’s commission based on profits after charging the manager’s commission.
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount |
Particulars |
Amount |
Liabilities |
Amount |
Assets |
Amount |
|||
|
Net Profit before |
Outstanding Manager’s |
|||||||||
|
Manager’s Commission |
Commission |
|||||||||
|
O/S Manager’s Commission |
||||||||||
|
Net Profit after |
||||||||||
|
Manager’s Commission |
||||||||||
Q7 :What do you mean by provision for discount on debtors?
Answer : The discount is allowed to those debtors who are ready to pay a huge amount in one shot. It is given in order to encourage them to repay the debt. The provision for discount on debtors is created on good debtors. The amount of good debtors is calculated by deducting the amount of Bad Debts, further Bad Debts and new provision for Doubtful Debts. The required percentage of the good debtors is calculated and the provision for discount on debtors is deducted from the Debtors’ amount in the Assets side of a Balance Sheet. As it is a loss for the business, it is shown in the Debit side of the Profit and Loss Account.
Q8 : Give the journal entries for the following adjustments:
(a) Outstanding salary at Rs 3,500.
(b) Rent unpaid for one month at Rs 6,000 per annum.
(c) Insurance prepaid for a quarter at Rs 16,000 per annum.
(d) Purchase of furniture costing Rs 7,000 entered in the purchases book.
Answer :
|
S. No. |
Particulars |
L.F. |
Debit Rs |
Credit Rs |
|||
|
a) |
Salaries A/c Dr. |
3,500 |
|||||
|
To Outstanding Salaries |
3,500 |
||||||
|
(Salaries of Rs 3,500 is |
|||||||
|
b) |
Rent A/c Dr. |
500 |
|||||
|
To Outstanding Rent |
500 |
||||||
|
(Rent unpaid for one month at |
6000 |
) |
|||||
|
12 |
|||||||
|
c) |
Prepaid Insurance A/c |
4,000 |
|||||
|
To Insurance A/c |
4,000 |
||||||
|
(Insurance paid in advance |
|||||||
|
d) |
Furniture A/c Dr. |
7,000 |
|||||
|
To Purchases A/c |
7,000 |
||||||
|
(Furniture was wrongly now rectified) |
|||||||
Long answers : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 423
Q1 : What are adjusting entries? Why are they necessary for preparing the final accounts?
Answer : Adjusting entries are the entries of those adjustments which are given outside the trial balance and which help us reflect the true financial position i.e., profit or loss of an organisation. According to the double-entry system, all the adjustments given outside the Trial Balance are posted at two places. The adjusting entries are necessary they enable us to post and take into account those items which are omitted or entered with the wrong amount and/or recorded under wrong heads.
The treatment of adjusting entries is necessary.
(i) It helps us assess the true financial position of an organisation based on accrual basis of accounting.
(ii) It helps us know the actual figure of profit or loss.
(iii) It records the omitted entries and rectifies the errors made.
(iv) It helps in providing depreciation and making different provisions, such as Bad Debts and depreciation.
Q2 :What is meant by provision for doubtful-debts? How are the relevant accounts prepared and what journal entries are recorded in the final accounts? How is the amount for provision for doubtful-debts calculated?
Answer :
The provision for doubtful-debts is provided after deducting the amount of bad-debts from the debtors. The provision for doubtful-debts is provided because of the rationale that the actual amount of bad-debts will only be known in the next year, when the amount of debtors will get realised. Thus, it will only then be known as to how many of the debtors have become bad. Thus, in order to bridge-up the expected future loss, we create a provision for doubtful-debts.
For the provision for doubtful-debts, we prepare debtors account and provision for doubtful-debts account. For recording bad-debts, the following journal entry is passed.
|
Profit and Loss A/c |
Dr. |
|
|
To Provision for Bad and Doubtful Debts A/c |
||
Example: An extract from a Trial Balance as on December 31, 2010.
|
Debtors |
10,500 |
|
Provision for Doubtful Debts |
1,000 |
|
Bad Debts Account |
1,500 |
Adjustment:
(i) Further bad-debts amount to Rs 500.
(ii) Create a provision for doubtful-debts at 5% on debtors.
Explanation
The provision for Doubtful Debt as on January 01, 2010 was Rs 1,000 and the Bad Debts during the year were Rs 1,500. In addition to this, there was a further Bad Debt of Rs 500 which was known at the end of the year i.e., December 31, 2010. Now we need to create a provision for Doubtful Debts at 5% on debtors.
|
Profit and Loss A/c |
||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Amount |
Particulars |
Amount |
|||
|
Bad Debts |
1,500 |
|||||
|
Add: Further Bad Debts |
500 |
|||||
|
Add: New Provision for Doubtful Debts |
500 |
|||||
|
Less: Old Provision (given in Trial |
1,000 |
1,500 |
||||
|
Balance Sheet |
|||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount |
Assets |
Amount |
||
|
Debtors |
10,500 |
||||
|
Less: |
500 |
||||
|
10,000 |
|||||
|
Less: |
500 |
9,500 |
|||
The amount of provision for Doubtful Debts is calculated by debiting the amount of further Bad Debts from debtors and calculating the given percentage of provision on remaining debtors. This provision is added to the Bad Debts amount in the profit and loss account and deducted from debtors in the assets side of a Balance Sheet.
Q3 : Show the treatment of prepaid expenses, depreciation and closing stock at the time of preparation of final accounts when they are given
(a) inside the Trial Balance
(b) outside the Trial Balance
Answer :
(i) Prepaid expenses
(a) When given inside the Trial Balance: It will be posted only in the Assets side of the Balance Sheet.
|
Balance Sheet |
||
|
Assets |
Amount |
|
|
Prepaid Expenses |
|
|
When given outside the Trial Balance:
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount |
Particulars |
Amount |
Liabilities |
Amount |
Assets |
Amount |
||||
|
Concerned Expenses |
Prepaid Expenses |
||||||||||
|
Less: Prepaid Expenses |
|||||||||||
Depreciation
(a) If depreciation is given inside the Trial Balance, then it can be shown in the Debit side of the Profit and Loss A/c. It means that this depreciation amount has already been deducted from the concerned assets in the Balance Sheet.
|
Profit and Loss Account |
||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||
|
Particulars |
Amount |
Particulars |
Amount |
|
|
Depreciation |
||||
(b) If depreciation is given outside the Trial Balance, i.e. in the adjustments, then it is shown in the debit side of the Profit and Loss Account and deducted from the concerned assets in the Assets side of Balance Sheet.

|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount |
Particulars |
Amount |
Liabilities |
Amount |
Assets |
Amount |
|||
|
Depreciation on Concerned Assets |
Concerned Assets |
|||||||||
|
Less: Depreciation |
||||||||||
Closing stock
(a) The closing stock is valued at cost price or realisable value, whichever of the two is lesser. If given inside the Trial Balance, then it will be posted only in the Assets side of the Balance Sheet.
|
Balance Sheet |
|||
|
Liabilities |
Amount |
Assets |
Amount |
|
Closing Stock |
|||
(b) If the closing stock is given outside the Trial Balance then, it needs to be posted at two places.
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount |
Particulars |
Amount |
Liabilities |
Amount |
Assets |
Amount |
||
|
Closing Stock |
|||||||||
|
Closing Stock |
|||||||||
Numerical questions : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 423
Q1 : Prepare a trading and profit and loss account for the year ending December 31, 2005. from the balances extracted of M/s Rahul Sons. Also prepare a balance sheet at the end of the year.
|
Account Title |
Amount Rs |
Account Title |
Amount Rs |
|
Stock |
50,000 |
Sales |
1,80,000 |
|
Wages |
3,000 |
Purchases return |
2,000 |
|
Salary |
8,000 |
Discount received |
500 |
|
Purchases |
1,75,000 |
Provision for doubtful |
2,500 |
|
Sales return |
3,000 |
Capital |
3,00,000 |
|
Sundry Debtors |
82,000 |
Bills payable |
22,000 |
|
Discount allowed |
1,000 |
Commission received |
4,000 |
|
Insurance |
3,200 |
Rent |
6,000 |
|
Rent Rates and |
4,300 |
Loan |
34,800 |
|
Fixtures and |
20,000 |
||
|
Trade expenses |
1,500 |
||
|
Bad debts |
2,000 |
||
|
Drawings |
32,000 |
||
|
Repair and renewals |
1,600 |
||
|
Travelling expenses |
4,200 |
||
|
Postage |
300 |
||
|
Telegram expenses |
200 |
||
|
Legal fees |
500 |
||
|
Bills receivable |
50,000 |
||
|
Building |
1,10,000 |
||
|
5,51,800 |
5,51,800 |
Adjustments
1. Commission received in advance Rs 1,000.
2. Rent receivable Rs 2,000.
3. Salary outstanding Rs 1,000 and insurance prepaid Rs 800.
4. Further bad debts Rs 1,000 and provision for doubtful debts @ 5% on debtors and discount on debtors @ 2%.
5. Closing stock Rs 32,000.
6. Depreciation on building @ 6% p.a.
Answer :
|
Books of M/s. Rahul Sons. Trading Account for the year ending December 31, 2010 |
|||||||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||||||
|
Opening Stock |
50,000 |
Sales |
1,80,000 |
||||||||
|
Purchases |
1,75,000 |
Less: Sales Returns |
3,000 |
1,77,000 |
|||||||
|
Less: Purchase Returns |
2,000 |
1,73,000 |
Closing Stock |
32,000 |
|||||||
|
Wages |
3,000 |
Gross Loss |
17,000 |
||||||||
|
2,26,000 |
2,26,000 |
||||||||||
|
Profit and Loss Account for the year ending December 31, 2010 |
|||||||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||||||
|
Gross Loss |
17,000 |
Discount Received |
500 |
||||||||
|
Salary |
8,000 |
Commission Received |
4,000 |
||||||||
|
Add: Outstanding Salary |
1,000 |
9,000 |
Less: Advance Commission |
1,000 |
3,000 |
||||||
|
Discount Allowed |
1,000 |
||||||||||
|
Insurance |
3,200 |
Rent |
6,000 |
||||||||
|
Less: Insurance Prepaid |
800 |
2,400 |
Add: Rent Receivable |
2,000 |
8,000 |
||||||
|
Rent Rates and Taxes |
4,300 |
||||||||||
|
Trade Expenses |
1,500 |
Net Loss |
43,189 |
||||||||
|
Bad-Debts |
2,000 |
||||||||||
|
Add: Further Bad-Debts |
1,000 |
||||||||||
|
Add: New Provision |
4,050 |
||||||||||
|
Less: Old Provision |
2,500 |
4,550 |
|||||||||
|
Discount on Debtors |
1,539 |
||||||||||
|
Postage |
300 |
||||||||||
|
Telegram Expenses |
200 |
||||||||||
|
Depreciation on Building |
6,600 |
||||||||||
|
Repair and Renewals |
1,600 |
||||||||||
|
Travelling Expenses |
4,200 |
||||||||||
|
Legal Fees |
500 |
||||||||||
|
54,689 |
54,689 |
||||||||||
|
Balance Sheet for the year ending December 31, 2010 |
||||||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
|||||
|
Capital |
3,00,000 |
Debtors |
82,000 |
|||||
|
Less: Net Loss |
43,189 |
Less: Further Bad-Debts |
1,000 |
|||||
|
Less: Drawings |
32,000 |
2,24,811 |
Less: New Provision |
4,050 |
||||
|
Bills Payable |
22,000 |
Less: Discount on Debtors (on Rs 76,950) |
1,539 |
75,411 |
||||
|
Loan |
34,800 |
B/R |
50,000 |
|||||
|
Advance Commission |
1,000 |
Buildings |
1,10,000 |
|||||
|
Outstanding Salary |
1,000 |
Less: 6% Depreciation |
6,600 |
1,03,400 |
||||
|
Rent Receivable |
2,000 |
|||||||
|
Prepaid Insurance |
800 |
|||||||
|
Closing Stock |
32,000 |
|||||||
|
Furniture and Fittings |
20,000 |
|||||||
|
2,83,611 |
2,83,611 |
|||||||
Q2 : Prepare a trading and profit and loss account of M/s Green Club Ltd. for the year ending December 31, 2010. from the following figures taken from his trial balance :
|
Account Title |
Amount Rs |
Account Title |
Amount Rs |
|
Opening stock |
35,000 |
Sales |
2,50,000 |
|
Purchases |
1,25,000 |
Purchase return |
6,000 |
|
Return inwards |
25,000 |
Creditors |
10,000 |
|
Postage and Telegram |
600 |
Bills payable |
20,000 |
|
Salary |
12,300 |
Discount |
1,000 |
|
Wages |
3,000 |
Provision for bad |
4,500 |
|
Rent and Rates |
1,000 |
Interest received |
5,400 |
|
Packing and Transport |
500 |
Capital |
75,000 |
|
General expense |
400 |
||
|
Insurance |
4,000 |
||
|
Debtors |
50,000 |
||
|
Cash in hand |
20,000 |
||
|
Cash at bank |
40,000 |
||
|
Machinery |
20,000 |
||
|
Lighting and Heating |
5,000 |
||
|
Discount |
3,500 |
||
|
Bad debts |
3,500 |
||
|
Investment |
23,100 |
||
|
3,71,900 |
3,71,900 |
Adjustments
1. Depreciation charged on machinery @ 5% p.a.
2. Further bad debts Rs 1,500, discount on debtors @ 5% and make a provision on debtors @ 6%.
3. Wages prepaid Rs 1,000.
4. Interest on investment @ 5% p.a.
5. Closing stock 10,000.
Answer:
|
Trading Account for the year ending December 31, 2010 |
|||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||
|
Opening Stock |
35,000 |
Sales |
2,50,000 |
||||
|
Purchases |
1,25,000 |
Less: Sales Returns |
(25,000) |
2,25,000 |
|||
|
Less: Purchase Returns |
(6,000) |
1,19,000 |
Closing Stock |
10,000 |
|||
|
Wages |
3,000 |
||||||
|
Less: Prepaid Wages |
(1,000) |
2,000 |
|||||
|
Gross Profit |
79,000 |
||||||
|
2,35,000 |
2,35,000 |
||||||
|
Profit and Loss Account for the year ending December 31, 2010 |
|||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||
|
Bad Debts |
3,500 |
Gross Profit |
79,000 |
||||
|
Add: Further Bad-debts |
1,500 |
Interest on Accrued Investment |
1,155 |
||||
|
Add: New Provision |
2,910 |
Discount |
1,000 |
||||
|
Less: Old Provision |
4,500 |
3,410 |
Interest Received |
5,400 |
|||
|
Discount on Debtors |
2,280 |
||||||
|
Postage and Telegram |
600 |
||||||
|
Salary |
12,300 |
||||||
|
Rent and Rates |
1,000 |
||||||
|
Packing and Transport |
500 |
||||||
|
General Expenses |
400 |
||||||
|
Insurance |
4,000 |
||||||
|
Discount |
3,500 |
||||||
|
Depreciation on Machinery |
1,000 |
||||||
|
Lighting and Heating |
5,000 |
||||||
|
Net Profit |
52,565 |
||||||
|
86,555 |
86,555 |
||||||
|
Balance Sheet as on December 31, 2010 |
|||||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
||||
|
Creditors |
10,000 |
Cash in Hand |
20,000 |
||||
|
Bills Payable |
20,000 |
Cash at Bank |
40,000 |
||||
|
Capital |
75,000 |
||||||
|
Add: Net Profit |
52,565 |
1,27,565 |
Debtors |
50,000 |
|||
|
Less: Further Bad-Debts |
1,500 |
||||||
|
Less New Provision |
2,910 |
||||||
|
Less: Discount on Debtors |
2,280 |
43,310 |
|||||
|
Investment |
23,100 |
||||||
|
Add: Interest on Investment |
1,155 |
24,255 |
|||||
|
Machinery |
20,000 |
||||||
|
Less: Depreciation |
1,000 |
19,000 |
|||||
|
Prepaid Wages |
1,000 |
||||||
|
Closing Stock |
10,000 |
||||||
|
1,57,565 |
1,57,565 |
||||||
Q3 : The following balances has been extracted from the trial of M/s Runway Shine Ltd. Prepare a trading and profit and loss account and a balance sheet as on December 31, 2010.
|
Account Title |
Amount Rs |
Account Title |
Amount Rs |
|
Purchases |
1,50,000 |
Sales |
2,50,000 |
|
Opening stock |
50,000 |
Return outwards |
4,500 |
|
Return inwards |
2,000 |
Interest received |
3,500 |
|
Carriage inwards |
4,500 |
Discount received |
400 |
|
Cash in hand |
77,800 |
Creditors |
1,25,000 |
|
Cash at bank |
60,800 |
Bill payable |
6,040 |
|
Wages |
2,400 |
Capital |
1,00,000 |
|
Printing and |
4,500 |
||
|
Discount |
400 |
||
|
Bad debts |
1,500 |
||
|
Insurance |
2,500 |
||
|
Investment |
32,000 |
||
|
Debtors |
53,000 |
||
|
Bills receivable |
20,000 |
||
|
Postage and Telegraph |
400 |
||
|
Commission |
200 |
||
|
Interest |
1,000 |
||
|
Repair |
440 |
||
|
Lighting Charges |
500 |
||
|
Telephone charges |
100 |
||
|
Carriage outward |
400 |
||
|
Motor car |
25,000 |
||
|
4,89,440 |
4,89,440 |
Adjustments
1. Further bad debts Rs 1,000. Discount on debtors Rs 500 and make a provision on debtors @ 5%.
2. Interest received on investment @ 5%.
3. Wages and interest outstanding Rs 100 and Rs 200 respectively.
4. Depreciation charged on motor car @ 5% p.a.
5. Closing Stock Rs 32,500.
Answer :
|
Trading Account |
|||||||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||||||
|
Opening Stock |
50,000 |
Sales |
2,50,000 |
||||||||
|
Purchases |
1,50,000 |
Less: Return Inwards |
2,000 |
2,48,000 |
|||||||
|
Less: Return Outwards |
4,500 |
1,45,500 |
Closing Stock |
32,500 |
|||||||
|
Carriage Inwards |
4,500 |
||||||||||
|
Wages |
2,400 |
||||||||||
|
Add: Outstanding Wages |
100 |
2,500 |
|||||||||
|
Gross Profit |
78,000 |
||||||||||
|
2,80,500 |
2,80,500 |
||||||||||
|
Profit and Loss Account |
|||||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||||
|
Carriage Outward |
400 |
Gross Profit |
78,000 |
||||||
|
Printing and Stationery |
4,500 |
Interest Received |
3,500 |
||||||
|
Discount |
400 |
Discount Received |
400 |
||||||
|
Bad Debts |
1,500 |
Interest Received on Investment |
1,600 |
||||||
|
Add: Further Bad Debts |
1,000 |
||||||||
|
Add: New Provision |
2,600 |
5,100 |
|||||||
|
Discount on Debtors |
500 |
||||||||
|
Insurance |
2,500 |
||||||||
|
Postage and Telegraph |
400 |
||||||||
|
Commission |
200 |
||||||||
|
Interest |
1,000 |
||||||||
|
Add: Outstanding Interest |
200 |
1,200 |
|||||||
|
Repair |
440 |
||||||||
|
Lighting Charges |
500 |
||||||||
|
Telephone Charges |
100 |
||||||||
|
Depreciation on Motor Car |
1,250 |
||||||||
|
Net Profit |
66,010 |
||||||||
|
83,500 |
83,500 |
||||||||
|
Balance Sheet |
|||||||||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
||||||||
|
Creditors |
1,25,000 |
Cash in Hand |
77,800 |
||||||||
|
Add: Interest Received |
1,600 |
79,400 |
|||||||||
|
Bills Payable |
6,040 |
Cash at Bank |
60,800 |
||||||||
|
Capital |
1,00,000 |
Investment |
32,000 |
||||||||
|
Add: Net Profit |
66,010 |
1,66,010 |
Debtors |
53,000 |
|||||||
|
Less: Further Bad Debts |
1,000 |
||||||||||
|
Outstanding Interest |
100 |
Less: New Provision |
2,600 |
||||||||
|
Outstanding Wages |
200 |
Less: Discount on Debtors |
500 |
48,900 |
|||||||
|
Motor Car |
25,000 |
||||||||||
|
Less: Depreciation |
1,250 |
23,750 |
|||||||||
|
Bills Receivable |
20,000 |
||||||||||
|
Closing Stock |
32,500 |
||||||||||
|
2,97,350 |
2,97,350 |
||||||||||
Q4 :The following balances have been extracted from the trial of M/s Haryana Chemical Ltd. You are required to prepare a trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet as on December 31, 2005 from the given information.
|
Account Title |
Amount Rs |
Account Title |
Amount Rs |
|
Opening stock |
50,000 |
Sales |
3,50,000 |
|
Purchases |
1,25,500 |
Purchases return |
2,500 |
|
Sales return |
2,000 |
Creditors |
25,000 |
|
Cash in hand |
21,200 |
Rent |
5,000 |
|
Cash at bank |
12,000 |
Interest |
2,000 |
|
Carriage |
100 |
Bills payable |
1,71,700 |
|
Free hold land |
3,20,000 |
Capital |
3,00,000 |
|
Patents |
1,20,000 |
||
|
General Expenses |
2,000 |
||
|
Sundry Debtors |
32,500 |
||
|
Building |
86,000 |
||
|
Machinery |
34,500 |
||
|
Insurance |
12,400 |
||
|
Drawings |
10,000 |
||
|
Motor vehicle |
10,500 |
||
|
Bad debts |
2,000 |
||
|
Light and Water |
1,200 |
||
|
Trade expenses |
2,000 |
||
|
Power |
3,900 |
||
|
Salary and Wages |
5,400 |
||
|
Loan a 15% |
3,000 |
||
|
8,56,200 |
8,56,200 |
Adjustments
1. Closing stock was valued at the end of the year Rs 40,000.
2. Salary amounting Rs 500 and trade expense Rs 300 are due.
3. Depreciation charged on building and machinery are @ 4% and @ 5% respectively.
4. Make a provision of @ 5% on sundry debtors.
Answer :
|
Trading Account |
||||||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|||||||
|
Opening Stock |
50,000 |
Sales |
3,50,000 |
|||||||
|
Purchases |
1,25,500 |
Less: Return |
2,000 |
3,48,000 |
||||||
|
Less: Return Outwards |
2,500 |
1,23,000 |
Closing Stock |
40,000 |
||||||
|
Carriage |
100 |
|||||||||
|
Power |
3,900 |
|||||||||
|
Gross Profit |
2,11,000 |
|||||||||
|
3,88,000 |
3,88,000 |
|||||||||
|
Profit and Loss Account |
|||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||
|
General Expenses |
2,000 |
Gross Profit |
2,11,000 |
||||
|
Insurance |
12,400 |
Rent |
5,000 |
||||
|
Bad Debts |
2,000 |
Interest |
2,000 |
||||
|
Add: Provision for Bad Debts |
1,625 |
3,625 |
Accrued Interest on Loan |
150 |
|||
|
Light and Water |
1,200 |
||||||
|
Trade Expenses |
2,000 |
||||||
|
Add: Outstanding Trade Expenses |
300 |
2,300 |
|||||
|
Salary and Wages |
5,400 |
||||||
|
Add: Outstanding Salary |
500 |
5,900 |
|||||
|
Depreciation on Building |
3,440 |
||||||
|
Depreciation on Machinery |
1,725 |
||||||
|
Net Profit |
1,85,560 |
||||||
|
2,18,150 |
2,18,150 |
||||||
|
Balance Sheet |
|||||||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
||||||
|
Capital |
3,00,000 |
Cash in Hand |
21,200 |
||||||
|
Add: Net Profit |
1,85,560 |
Cash at Bank |
12,000 |
||||||
|
Less: Drawings |
10,000 |
4,75,560 |
Freehold Land |
3,20,000 |
|||||
|
Creditors |
25,000 |
Patents |
1,20,000 |
||||||
|
Bills Payable |
1,71,700 |
Sundry Debtors |
32,500 |
||||||
|
Outstanding Trade Expenses |
300 |
Less: Provision for Bad Debts |
1,625 |
30,875 |
|||||
|
Outstanding Salary |
500 |
||||||||
|
Building |
86,000 |
||||||||
|
Less: Depreciation |
3,440 |
82,560 |
|||||||
|
Machinery |
34,500 |
||||||||
|
Less: Depreciation |
1,725 |
32,775 |
|||||||
|
Motor Vehicle |
10,500 |
||||||||
|
Loan |
3,000 |
||||||||
|
Add: Interest on Loan |
150 |
3,150 |
|||||||
|
Closing Stock |
40,000 |
||||||||
|
6,73,060 |
6,73,060 |
||||||||
Working Note
In the question, the loan given by us bears an interest of 15% p.a. and interest is unpaid from 01-9-2010 to 31-12-2010. Thus, interest for loan is outstanding for four months and is calculated as follows:
Interest on loan = 3000 × 15⁄100 × 4⁄12 = Rs 150
Q5 : From the following information prepare trading and profit and loss account of M/s Indian sports house for the year ending December 31, 2011.
|
Account Title |
Amount Rs |
Account Title |
Amount Rs |
|
Drawings |
20,000 |
Capital |
2,00,000 |
|
Sundry debtors |
80,000 |
Return outwards |
2,000 |
|
Bad debts |
1,000 |
Bank overdraft |
12,000 |
|
Trade Expenses |
2,400 |
Provision for bad debts |
4,000 |
|
Printing and Stationery |
2,000 |
Sundry creditors |
60,000 |
|
Rent Rates and Taxes |
5,000 |
Bills payable |
15,400 |
|
Freight |
4,000 |
Sales |
2,76,000 |
|
Return inwards |
7,000 |
||
|
Opening stock |
25,000 |
||
|
Purchases |
1,80,000 |
||
|
Furniture and Fixture |
20,000 |
||
|
Plant and Machinery |
1,00,000 |
||
|
Bills receivable |
14,000 |
||
|
Wages |
10,000 |
||
|
Cash in hand |
6,000 |
||
|
Discount allowed |
2,000 |
||
|
Investments |
40,000 |
||
|
Motor car |
51,000 |
||
|
5,69,400 |
5,69,400 |
Adjustments
1. Closing stock was Rs 45,000.
2. Provision for doubtful debts is to be maintained @ 2% on debtors.
3. Depreciation charged on : furniture and fixture @ 5%, plant and Machinery @ 6% and motor car @ 10%.
4. A Machine of Rs 30,000 was purchased on July 01, 2005.
5. The manager is entitle to a commission of @ 10% of the net profit after charging such commission.
Answer :
|
Trading Account |
|||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||
|
Opening Stock |
25,000 |
Sales |
2,76,000 |
||||
|
Purchases |
1,80,000 |
Less: Return Inwards |
7,000 |
2,69,000 |
|||
|
Less: Return Outwards |
2,000 |
1,78,000 |
Closing Stock |
45,000 |
|||
|
Wages |
10,000 |
||||||
|
Freight |
4,000 |
||||||
|
Gross Profit |
97,000 |
||||||
|
3,14,000 |
3,14,000 |
||||||
|
Profit and Loss Account |
|||||||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||||||
|
Trade Expenses |
2,400 |
Gross Profit |
97,000 |
||||||||
|
Printing and Stationery |
2,000 |
Old Provision for Bad Debts |
4,000 |
||||||||
|
Rent Rates and Taxes |
5,000 |
Less: Bad Debts |
1,000 |
||||||||
|
Discount Allowed |
2,000 |
Less: New Provision |
1,600 |
1,400 |
|||||||
|
Depreciation on Motor Car |
5,100 |
||||||||||
|
Depreciation on Furniture and Fixtures |
1,000 |
||||||||||
|
*Depreciation on P & M of Rs 70,000 |
4,200 |
||||||||||
|
**Depreciation on P & M of Rs 30,000 |
900 |
||||||||||
|
Net Profit Before Manager’s Commission |
75,800 |
||||||||||
|
1,02,400 |
1,02,400 |
||||||||||
|
Manager’s Commission |
6,891 |
||||||||||
|
Net Profit After Commission |
68,909 |
Balance b/d |
75,800 |
||||||||
|
75,800 |
75,800 |
||||||||||
|
Balance Sheet |
||||||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
|||||
|
Capital |
2,00,000 |
Cash in Hand |
6,000 |
|||||
|
Add: Net Profit |
68,909 |
Sundry Debtors |
80,000 |
|||||
|
Less: Drawings |
20,000 |
2,48,909 |
Less: New Provision |
1,600 |
78,400 |
|||
|
O/S Manager’s Commission |
6,891 |
Furniture and Fixtures |
20,000 |
|||||
|
Bank Overdraft |
12,000 |
Less: Depreciation |
1,000 |
19,000 |
||||
|
Creditors |
60,000 |
|||||||
|
Bills Payable |
15,400 |
Plant and Machinery |
1,00,000 |
|||||
|
Less: Depreciation 1* |
4,200 |
|||||||
|
Less: Depreciation 2** |
900 |
94,900 |
||||||
|
Bills Receivable |
14,000 |
|||||||
|
Investments |
40,000 |
|||||||
|
Motor Car |
51000 |
|||||||
|
Less: Depreciation |
5100 |
45,900 |
||||||
|
Closing Stock |
45,000 |
|||||||
|
3,43,200 |
3,43,200 |
|||||||
Working Notes
1. Manager’s Commission
|
= Net Profit before commission × |
10 |
||
|
110 |
|||
|
= 75,800 × |
10 |
||
|
110 |
|||
|
= Rs 6,891 |
|||
2. Out of the machinery of Rs 1,00,000, Rs 30,000 worth of machinery was purchased on 01/July/2011. Therefore, the depreciation on this machinery will be for 6 months at 6% p.a.
|
*Depreciation on machinery (30,000) = |
30,000 × |
6 |
× |
6 |
= Rs 900 |
|
12 |
100 |
**The rest of the machinery of Rs 70,000 will bear depreciation at 6% p.a.
Depreciation on machinery (70,000) =
70,000 ×
6
= Rs 900
12
Note: As per our solution Gross Profit is Rs 97,000, however, as per book it is Rs 1,01,000.
Q6 : Prepare the trading and profit and loss account and a balance sheet of M/s Shine Ltd. from the following particulars.
Answer:
|
Account |
Amount Rs |
Account |
Amount Rs |
|
Sundry debtors |
1,00,000 |
Bills payable |
85,550 |
|
Bad debts |
3,000 |
Sundry creditors |
25,000 |
|
Trade expenses |
2,500 |
Provision for bad |
1,500 |
|
Printing and |
5,000 |
Return outwards |
4,500 |
|
Rent, Rates and |
3,450 |
Capital |
2,50,000 |
|
Freight |
2,250 |
Discount received |
3,500 |
|
Sales return |
6,000 |
Interest received |
11,260 |
|
Motor car |
25,000 |
Sales |
1,00,000 |
|
Opening stock |
75,550 |
||
|
Furniture and |
15,500 |
||
|
Purchases |
75,000 |
||
|
Drawings |
13,560 |
||
|
Investments |
65,500 |
||
|
Cash in hand |
36,000 |
||
|
Cash in bank |
53,000 |
||
|
4,81,310 |
4,81,310 |
Adjustments
1. Closing stock was valued Rs 35,000.
2. Depreciation charged on furniture and fixture @ 5%.
3. Further bad debts Rs 1,000. Make a provision for bad debts @ 5% on sundry debtors.
4. Depreciation charged on motor car @ 10%.
5. Interest on drawing @ 6%.
6. Rent, rates and taxes was outstanding Rs 200.
7. Discount on debtors 2%.
Answer :
|
Trading Account |
|||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||
|
Opening Stock |
75,550 |
Sales |
1,00,000 |
||||
|
Purchases |
75,000 |
Less: Sales Inwards |
6,000 |
94,000 |
|||
|
Less: Return Outwards |
4,500 |
70,500 |
Closing Stock |
35,000 |
|||
|
Freight |
2,250 | ||||||
|
Gross Loss |
19,300 |
||||||
|
1,48,300 |
1,48,300 |
||||||
|
Profit and Loss Account |
||||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|||||
|
Gross Loss |
19,300 |
Discount |
3,500 |
|||||
|
Bad Debts |
3,000 |
Interest Received |
11,260 |
|||||
|
Add: Further Bad-Debts |
1,000 |
Interest on Drawings |
814 |
|||||
|
Add: New Provision |
4,950 |
Net Loss |
27,482 |
|||||
|
Less: Old Provision |
1,500 |
7,450 |
||||||
|
Discount on Debtors |
1,881 |
|||||||
|
Trade Expenses |
2,500 |
|||||||
|
Printing and Stationery |
5,000 |
|||||||
|
Rent, Rates and Taxes |
3,450 |
|||||||
|
Add: O/S Rent, Rates and Taxes |
200 |
3,650 |
||||||
|
Depreciation on Furniture |
775 |
|||||||
|
Depreciation on Motor Car |
2,500 |
|||||||
|
43,056 |
43,056 |
|||||||
|
Balance Sheet |
|||||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
||||
|
Bills Payable |
85,550 |
Sundry Debtors |
100,000 |
||||
|
Sundry Creditors |
25,000 |
Less: Further Debts |
1,000 |
||||
|
Capital |
2,50,000 |
Less: New Provision |
4,950 |
||||
|
Less: Net Loss |
27,482 |
Less: Discount on Debtors |
1,881 |
92,169 |
|||
|
Less: Drawings |
13,560 |
||||||
|
Less: Interest on Drawings |
814 |
Motor Car |
25,000 |
||||
|
2,08,144 |
Less: Depreciation |
2,500 |
22,500 |
||||
|
Outstanding Rent, Rates and Taxes |
200 |
Furniture and Fixtures |
15,500 |
||||
|
Less: Depreciation |
775 |
14,725 |
|||||
|
Investments |
65,500 |
||||||
|
Cash in Hand |
36,000 |
||||||
|
Cash in Bank |
53,000 |
||||||
|
Closing Stock |
35,000 |
||||||
|
3,18,894 |
3,18,894 |
||||||
Note: In NCERT book, the Gross Loss is Rs 17,050, the Net Loss is Rs 27,344 and the Total of Balance Sheet is Rs 3,19,032. However, as per the solution Net Loss and the Total of the Balance Sheet are Rs 27,482 and Rs 3,18,894 respectively.
Q7 : Following balances have been extracted from the trial balance of M/s Keshav Electronics Ltd. You are required to prepare the trading and profit and loss account and a balance sheet as on December 31, 2011.
|
Account Title |
Amount Rs |
Account Title |
Amount Rs |
|
Opening stock |
2,26,000 |
Sales |
6,80,000 |
|
Purchases |
4,40,000 |
Return outwards |
15,000 |
|
Drawings |
75,000 |
Creditors |
50,000 |
|
Buildings |
1,00,000 |
Bills payable |
63,700 |
|
Motor van |
30,000 |
Interest received |
20,000 |
|
Freight inwards |
3,400 |
Capital |
3,50,000 |
|
Sales return |
10,000 |
||
|
Trade expense |
3,300 |
||
|
Heat and Power |
8,000 |
||
|
Salary and Wages |
5,000 |
||
|
Legal expense |
3,000 |
||
|
Postage and Telegram |
1,000 |
||
|
Bad debts |
6,500 |
||
|
Cash in hand |
79,000 |
||
|
Cash at bank |
98,000 |
||
|
Sundry debtors |
25,000 |
||
|
Investments |
40,000 |
||
|
Insurance |
3,500 |
||
|
Machinery |
22,000 |
||
|
11,78,700 |
11,78,700 |
The following additional information is available :
1. Stock on December 31, 2005 was Rs 30,000.
2. Depreciation is to be charged on building at 5% and motor van at 10%.
3. Provision for doubtful debts is to be maintained at 5% on Sundry Debtors.
4. Unexpired insurance was Rs 600.
5. The Manager is entitled to a commission @ 5% on net profit before charging such commission.
Stock on December 31, 2011 was Rs 30,000
Answer :
|
Trading Account |
||||||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|||||||
|
Opening Stock |
2,26,000 |
Sales |
6,80,000 |
|||||||
|
Purchases |
4,40,000 |
Less: Sales Return |
10,000 |
6,70,000 |
||||||
|
Less: Returns Outwards |
15,000 |
4,25,000 |
Closing Stock |
30,000 |
||||||
|
Freight Inwards |
3,400 |
|||||||||
|
Heat and Power |
8,000 |
|||||||||
|
Gross Profit |
37,600 |
|||||||||
|
7,00,000 |
7,00,000 |
|||||||||
|
Profit and Loss Account |
|||||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||||
|
Trade Expenses |
3,300 |
Gross Profit |
37,600 |
||||||
|
Salary and Wages |
5,000 |
Interest Received |
20,000 |
||||||
|
Legal Expenses |
3,000 |
||||||||
|
Postage and Telegram |
1,000 |
||||||||
|
Bad Debts |
6,500 |
||||||||
|
Add: New Provision |
1,250 |
7,750 |
|||||||
|
Depreciation on Building |
5,000 |
||||||||
|
Depreciation on Motor Van |
3,000 |
||||||||
|
Insurance |
3,500 |
||||||||
|
Less: Unexpired Insurance |
600 |
2,900 |
|||||||
|
Net Profit |
26,650 |
||||||||
|
57,600 |
57,600 |
||||||||
|
Manager’s Commission Payable |
1,269 |
Balance b/d |
26,650 |
||||||
|
Net Profit after Commission |
25,381 |
||||||||
|
26,650 |
26,650 |
||||||||
|
Balance Sheet |
||||||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
|||||
|
Capital |
3,50,000 |
Cash in Hand |
79,000 |
|||||
|
Add: Net Profit |
25,381 |
Cash at Bank |
98,000 |
|||||
|
Less: Drawings |
75,000 |
3,00,381 |
Buildings |
1,00,000 |
||||
|
Creditors |
50,000 |
Less: Depreciation |
5,000 |
95,000 |
||||
|
Bills Payable |
63,700 |
|||||||
|
Manager’s Commission Payable |
1,269 |
Motor Van |
30,000 |
|||||
|
Less: Depreciation |
3,000 |
27,000 |
||||||
|
Sundry Debtors |
25,000 |
|||||||
|
Less: New Provision |
1,250 |
23,750 |
||||||
|
Investments |
40,000 |
|||||||
|
Machinery |
22,000 |
|||||||
|
Unexpired Insurance |
600 |
|||||||
|
Closing Stock |
30,000 |
|||||||
|
4,15,350 |
4,15,350 |
|||||||
Q8 : From the following balances extracted from the books of Raga Ltd. Prepare a trading and profit and loss account for the year ended December 31, 2011 and a balance sheet as on that date.
Answer:
|
Account Title |
Amount Rs |
Account Title |
Amount Rs |
|
Drawings |
20,000 |
Sales |
2,20,000 |
|
Land and Buildings |
12,000 |
Capital |
1,01,110 |
|
Plant and Machinery |
40,000 |
Discount |
1,260 |
|
Carriage inwards |
100 |
Apprentice premium |
5,230 |
|
Wages |
500 |
Bills payable |
1,28,870 |
|
Salary |
2,000 |
Purchases return |
10,000 |
|
Sales return |
200 |
||
|
Bank charges |
200 |
||
|
Coal, Gas and Water |
1,200 |
||
|
Purchases |
1,50,000 |
||
|
Trade Expenses |
3,800 |
||
|
Stock (Opening) |
76,800 |
||
|
Cash at bank |
50,000 |
||
|
Rates and Taxes |
870 |
||
|
Bills receivable |
24,500 |
||
|
Sundry debtors |
54,300 |
||
|
Cash in hand |
30,000 |
||
|
4,66,470 |
4,66,470 |
The additional information is as under:
1. Closing stock was valued at the end of the year Rs, 20,000.
2. Depreciation on plant and machinery charged at 5% and land and building at 10%.
3. Discount on debtors at 3%.
4. Make a provision at 5% on debtors for doubtful debts.
5. Salary outstanding was Rs 100 and Wages prepaid was Rs 40.
6. The manager is entitled a commission of 5% on net profit after charging such commission.
Answers:
|
Trading Account |
|||||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||||
|
Opening Stock |
76,800 |
Sales |
2,20,000 |
||||||
|
Purchases |
1,50,000 |
Less: Sales Return |
200 |
2,19,800 |
|||||
|
Less: Purchases Return |
10,000 |
1,40,000 |
Closing Stock |
20,000 |
|||||
|
Carriage Inwards |
100 |
||||||||
|
Wages |
500 |
||||||||
|
Less: Prepaid |
40 |
460 |
|||||||
|
Coal, Gas and Water |
1,200 |
||||||||
|
Gross Profit |
21,240 |
||||||||
|
2,39,800 |
2,39,800 |
||||||||
|
Profit and Loss Account |
|||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||
|
Salary |
2,000 |
Gross Profit |
21,240 |
||
|
Add: Outstanding Salary |
100 |
2,100 |
Discount |
1,260 |
|
|
Bank Charges |
200 |
Apprentice Premium |
5,230 |
||
|
Trade Expenses |
3,800 |
||||
|
Rates and Taxes |
870 |
||||
|
Depreciation on Plant and Machinery |
2,000 |
||||
|
Depreciation on Land and Building |
1,200 |
||||
|
Provision for Doubtful Debts |
2,715 |
||||
|
Discount on Debtors |
1,548 |
||||
|
Net Profit |
13,297 |
||||
|
27,730 |
27,730 |
||||
|
Manager’s Commission |
633 |
Balance b/d |
13,297 |
||
|
Net Profit after Commission |
12,664 |
||||
|
13,297 |
13,297 |
||||
|
Balance Sheet |
||||||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
|||||
|
Capital |
1,01,110 |
Cash at Bank |
50,000 |
|||||
|
Add: Net Profit |
12,664 |
Land and Building |
12,000 |
|||||
|
Less: Drawings |
20,000 |
93,774 |
Less: Depreciation |
1,200 |
10,800 |
|||
|
Plant and Machinery |
40,000 |
|||||||
|
Bills Payable |
1,28,870 |
Less: Depreciation |
2,000 |
38,000 |
||||
|
Outstanding Salary |
100 |
Bills Receivable |
24,500 |
|||||
|
Outstanding Manager’s Commission |
633 |
Sundry Debtors |
54,300 |
|||||
|
Less: New Provision |
2,715 |
|||||||
|
Less: Discount on Debtors |
1,548 |
50,037 |
||||||
|
Cash in Hand |
30,000 |
|||||||
|
Closing Stock |
20,000 |
|||||||
|
Prepaid Wages |
40 |
|||||||
|
2,23,377 |
2,23,377 |
|||||||
Q9 :From the following balances of M/s Jyoti Exports, prepare trading and profit and loss account for the year ended March 31, 2012 and balance sheet as on this date.
|
Account Title |
Debit Amount Rs |
Account Title |
Credit Amount Rs |
|
Sundry debtors |
9,600 |
Sundry creditors |
2,500 |
|
Opening stock |
22,800 |
Sales |
72,670 |
|
Purchases |
34,800 |
Purchases returns |
2,430 |
|
Carriage inwards |
450 |
Bills payable |
15,600 |
|
Wages |
1,770 |
Capital |
42,000 |
|
Office rent |
820 |
||
|
Insurance |
1,440 |
||
|
Factory rent |
390 |
||
|
Cleaning charges |
940 |
||
|
Salary |
1,590 |
||
|
Building |
24,000 |
||
|
Plant and Machinery |
3,600 |
||
|
Cash in hand |
2,160 |
||
|
Gas and Water |
240 |
||
|
Octroi |
60 |
||
|
Furniture |
20,540 |
||
|
Patents |
10,000 |
||
|
1,35,200 |
1,35,200 |
Closing stock Rs 10,000.
1. To provision for doubtful debts is to be maintained at 5 per cent on sundry debtors.
2. Wages amounting to Rs 500 and salary amounting to Rs 350 are outstanding.
3. Factory rent prepaid Rs 100.
4. Depreciation charged on Plant and Machinery @ 5% and Building @ 10%.
5. Outstanding insurance Rs 100.
Answer:
|
Trading Account |
|||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||
|
Opening Stock |
22,800 |
Sales |
72,670 |
||||
|
Purchases |
34,800 |
Closing Stock |
10,000 |
||||
|
Less: Purchases Return |
2,430 |
32,370 |
|||||
|
Carriage Inwards |
450 |
||||||
|
Wages |
1,770 |
||||||
|
Add: Outstanding Wages |
500 |
2,270 |
|||||
|
Factory Rent |
390 |
||||||
|
Less: Prepaid Rent |
100 |
290 |
|||||
|
Gas and Water |
240 |
||||||
|
Octroi |
60 |
||||||
|
Cleaning Charges |
940 |
||||||
|
Gross Profit |
23,250 |
||||||
|
82,670 |
82,670 |
||||||
|
Profit and Loss Account |
||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|||
|
Office Rent |
820 |
Gross Profit |
23,250 |
|||
|
Insurance |
1,440 |
|||||
|
Add: Outstanding Insurance |
100 |
1,540 |
||||
|
Depreciation on Plant and Machinery |
180 |
|||||
|
Salary |
1,590 |
|||||
|
Add: Outstanding Salary |
350 |
1,940 |
||||
|
Provision for Doubtful Debts |
480 |
|||||
|
Depreciation on Building |
2,400 |
|||||
|
Net Profit |
15,890 |
|||||
|
23,250 |
23,250 |
|||||
|
Balance Sheet |
|||||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
||||
|
Capital |
42,000 |
Sundry Debtors |
9,600 |
||||
|
Add: Net Profit |
15,890 |
57,890 |
Less: New Provision |
480 |
9,120 |
||
|
Sundry Creditors |
2,500 |
Building |
24,000 |
||||
|
Bills Payable |
15,600 |
Less: Depreciation |
2,400 |
21,600 |
|||
|
Outstanding Salary |
350 |
Plant and Machinery |
3,600 |
||||
|
Outstanding Wages |
500 |
Less: Depreciation |
180 |
3,420 |
|||
|
Outstanding Insurance |
100 |
Cash in Hand |
2,160 |
||||
|
Furniture |
20,540 |
||||||
|
Patents |
10,000 |
||||||
|
Closing Stock |
10,000 |
||||||
|
Prepaid Factory Rent |
100 |
||||||
|
76,940 |
76,940 |
||||||
Note: As per solution Net Profit is Rs 15,890 and Total of the Balance Sheet is Rs 76,940. However, NCERT shows Net Profit Rs 16,370 and Total of the Balance Sheet Rs 63,530.
Q10 : The following balances have been extracted from the books of M/s Green House for the year ended December 31, 2010 prepare trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet as on this date.
|
Account Title |
Amount Rs |
Account Title |
Amount Rs |
|
Purchases |
80,000 |
Capital |
2,10,000 |
|
Bank balance |
11,000 |
Bills payable |
6,500 |
|
Wages |
34,000 |
Sales |
2,00,000 |
|
Debtors |
70,300 |
Creditors |
50,000 |
|
Cash in hand |
1,200 |
Return outwards |
4,000 |
|
Legal expenses |
4,000 |
||
|
Building |
60,000 |
||
|
Machinery |
120,000 |
||
|
Bills receivable |
7,000 |
||
|
Office expenses |
3,000 |
||
|
Opening stock |
45,000 |
||
|
Gas and fuel |
2,700 |
||
|
Freight and Carriage |
3,500 |
||
|
Factory lighting |
5,000 |
||
|
Office furniture |
5,000 |
||
|
Patent right |
18,800 |
||
|
4,70,500 |
4,70,500 |
adjustments :
(a) Machinery is depreciated at 10% and buildings depreciated at 6%.
(b) Interest on capital @ 4%.
(c) Outstanding wages Rs 50.
(d) Closing stock Rs 50,000.
Answer:
|
Trading Account |
|||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||
|
Opening Stock |
45,000 |
Sales |
2,00,000 |
||
|
Purchases |
80,000 |
Closing Stock |
50,000 |
||
|
Less: Return Outwards |
4,000 |
76,000 |
|||
|
Wages |
34,000 |
||||
|
Add: Wages Outstanding |
50 |
34,050 |
|||
|
Gas and Fuel |
2,700 |
||||
|
Freight and Carriage |
3,500 |
||||
|
Factory Lighting |
5,000 |
||||
|
Gross Profit |
83,750 |
||||
|
2,50,000 |
2,50,000 |
||||
|
Profit and Loss Account |
|||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||
|
To Legal Expenses |
4,000 |
By Gross Profit |
83,750 |
||
|
To Office Expenses |
3,000 |
||||
|
To Depreciation on Machine |
12,000 |
||||
|
To Depreciation on Building |
3,600 |
||||
|
To Interest on Capital |
8,400 |
||||
|
To Net Profit* |
52,750 |
||||
|
83,750 |
83,750 |
||||
|
Balance Sheet |
|||||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
||||
|
Capital |
2,10,000 |
Bank Balance |
11,000 |
||||
|
Add: Interest on Capital |
8,400 |
Debtors |
70,300 |
||||
|
Add: Net profit |
52,750 |
2,71,150 |
Cash in Hand |
1,200 |
|||
|
Building |
60,000 |
||||||
|
Bills Payable |
6,500 |
Less: Depreciation |
3,600 |
56,400 |
|||
|
Creditors |
50,000 |
Machinery |
1,20,000 |
||||
|
Outstanding Wages |
50 |
Less: Depreciation |
12,000 |
1,08,000 |
|||
|
Bills Receivable |
7,000 |
||||||
|
Patent Right |
18,800 |
||||||
|
Office Furniture |
5,000 |
||||||
|
Closing Stock |
50,000 |
||||||
|
3,27,700 |
3,27,700 |
||||||
Note: As per our solution, total of Balance Sheet is Rs 3,27,700, however, as per book it is Rs 3,19,250.
Q11 : From the following balances extracted from the book of M/s Manju Chawla on March 31, 2010. You are requested to prepare the trading and profit and loss account and a balance sheet as on this date.
|
Account Title |
Amount Rs |
Amount Rs |
|
Opening stock |
10,000 |
|
|
Purchases and Sales |
40,000 |
80,000 |
|
Returns |
200 |
600 |
|
Wages |
6,000 |
|
|
Dock and cleaning charges |
4,000 |
|
|
Lighting |
500 |
|
|
Misc. Income |
6,000 |
|
|
Rent |
2,000 |
|
|
Capital |
40,000 |
|
|
Drawings |
2,000 |
|
|
Debtors and Creditors |
6,000 |
7,000 |
|
Cash |
3,000 |
|
|
Investment |
6,000 |
|
|
Patent |
4,000 |
|
|
Land and Machinery |
43,000 |
|
|
Donations and Charity |
600 |
|
|
Sales tax collected |
1,000 |
|
|
Furniture |
11,300 |
|
|
1,36,600 |
1,36,600 |
Closing stock was Rs 2,000.
(a) Interest on drawings @ 7% and interest on capital @ 5%.
(b) Land and Machinery is depreciated at 5%.
(c) Interest on investment @ 6%.
(d) Unexpired rent Rs 100.
(e) Charge 5% depreciation on furniture.
Answer:
|
Trading Account |
||||||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|||||||
|
Opening Stock |
10,000 |
Sales |
80,000 |
|||||||
|
Purchases |
40,000 |
Less: Sales Return |
200 |
79,800 |
||||||
|
Less: Purchases Return |
600 |
39,400 |
Closing Stock |
2,000 |
||||||
|
Wages |
6,000 |
|||||||||
|
Dock and Cleaning Charges |
4,000 |
|||||||||
|
Gross Profit |
22,400 |
|||||||||
|
81,800 |
81,800 |
|||||||||
|
Profit and Loss Account |
||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|||
|
Lighting |
500 |
Gross Profit |
22,400 |
|||
|
Donations and Charity |
600 |
Miscellaneous Income |
6,000 |
|||
|
Interest on Capital |
2,000 |
Rent |
2,000 |
|||
|
Depreciation on Furniture |
565 |
Less: Unearned Rent |
100 |
1,900 |
||
|
Depreciation on Land and Machinery |
2,150 |
Interest on Drawings |
140 |
|||
|
Net Profit |
24,985 |
Interest on Investment |
360 |
|||
|
30,800 |
30,800 |
|||||
|
Balance Sheet |
||||||||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
|||||||
|
Capital |
40,000 |
Debtors |
6,000 |
|||||||
|
Add: Interest on Capital |
2,000 |
Cash |
3,000 |
|||||||
|
Add: Net Profit |
24,985 |
Investment |
6,000 |
|||||||
|
Less: Drawings |
2,000 |
Add: Interest on Investment |
360 |
6,360 |
||||||
|
Less: Interest on Drawings |
140 |
64,845 |
Patent |
4,000 |
||||||
|
Creditors |
7,000 |
Land and Machinery |
43,000 |
|||||||
|
Sales Tax Collected |
1,000 |
Less: Depreciation |
2,150 |
40,850 |
||||||
|
Unearned Rent |
100 |
|||||||||
|
Furniture |
11,300 |
|||||||||
|
Less: Depreciation |
565 |
10,735 |
||||||||
|
Closing Stock |
2,000 |
|||||||||
|
72,945 |
72,945 |
|||||||||
Q12 : The following balances were extracted from the books of M/s Panchsheel Garments on December 31, 2010.
|
Account Title |
Debit Amount Rs |
Account Title |
Credit Amount Rs |
|
Opening stock |
16,000 |
Sales |
1,12,000 |
|
Purchases |
67,600 |
Return outwards |
3,200 |
|
Return Inwards |
4,600 |
Discount |
1,400 |
|
Carriage inwards |
1,400 |
Bank overdraft |
10,000 |
|
General expenses |
2,400 |
Commission |
1,800 |
|
Insurance |
4,000 |
Creditors |
16,000 |
|
Scooter expenses |
200 |
Capital |
50,000 |
|
Salary |
8,800 |
||
|
Cash in hand |
4,000 |
||
|
Scooter |
8,000 |
||
|
Furniture |
5,200 |
||
|
Buildings |
65,000 |
||
|
Debtors |
6,000 |
||
|
Wages |
1,200 |
||
|
1,94,400 |
1,94,400 |
Prepare the trading and profit and loss account for the year ended December, 31 and a balance sheet as on that date.
(a) Unexpired insurance Rs 1,000.
(b) Salary due but not paid Rs 1,800.
(c) Wages outstanding Rs 200.
(d) Interest on capital 5%.
(e) Scooter is depreciated @ 5%.
(f) Furniture is depreciated Rs @ 10%.
Answer:
|
Trading Account |
||||||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|||||||
|
Opening Stock |
16,000 |
Sales |
1,12,000 |
|||||||
|
Purchases |
67,600 |
Less: Return Inwards |
4,600 |
1,07,400 |
||||||
|
Less: Return Outwards |
3,200 |
64,400 |
Closing Stock |
15,000 |
||||||
|
Carriage Inwards |
1,400 |
|||||||||
|
Wages |
1,200 |
|||||||||
|
Add: Outstanding Wages |
200 |
1,400 |
||||||||
|
Gross Profit |
39,200 |
|||||||||
|
1,22,400 |
1,22,400 |
|||||||||
|
Trading Account |
||||||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|||||||
|
Opening Stock |
16,000 |
Sales |
1,12,000 |
|||||||
|
Purchases |
67,600 |
Less: Return Inwards |
4,600 |
1,07,400 |
||||||
|
Less: Return Outwards |
3,200 |
64,400 |
Closing Stock |
15,000 |
||||||
|
Carriage Inwards |
1,400 |
|||||||||
|
Wages |
1,200 |
|||||||||
|
Add: Outstanding Wages |
200 |
1,400 |
||||||||
|
Gross Profit |
39,200 |
|||||||||
|
1,22,400 |
1,22,400 |
|||||||||
|
Balance Sheet |
|||||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
||||
|
Capital |
50,000 |
Cash in Hand |
4,000 |
||||
|
Add: Interest on Capital |
2,500 |
Scooter |
8,000 |
||||
|
Add: Net Profit |
22,780 |
75,280 |
Less: Depreciation |
400 |
7,600 |
||
|
Bank Overdraft |
10,000 |
Furniture |
5,200 |
||||
|
Creditors |
16,000 |
Less: Depreciation |
520 |
4,680 |
|||
|
Outstanding Salary |
1,800 |
Buildings |
65,000 |
||||
|
Outstanding Wages |
200 |
Debtors |
6,000 |
||||
|
Unexpired Insurance |
1,000 |
||||||
|
Closing Stock |
15,000 |
||||||
|
1,03,280 |
1,03,280 |
||||||
Q13 :Prepare the trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet of M/s Control Device India on December 31, 2012 from the following balance as on that date.
|
Account Title |
Debit Amount Rs |
Credit Amount Rs |
|
Drawings and Capital |
19,530 |
67,500 |
|
Purchase and Sales |
45,000 |
1,12,500 |
|
Salary and Commission |
25,470 |
1,575 |
|
Carriage |
2,700 |
|
|
Plant and Machinery |
27,000 |
|
|
Furniture |
6,750 |
|
|
Opening stock |
42,300 |
|
|
Insurance premium |
2,700 |
|
|
Interest |
7,425 |
|
|
Bank overdraft |
24,660 |
|
|
Rent and Taxes |
2,160 |
|
|
Wages |
11,215 |
|
|
Returns |
2,385 |
1,440 |
|
Carriage outwards |
1,485 |
|
|
Debtors and Creditors |
36,000 |
58,500 |
|
General expenses |
6,975 |
|
|
Octroi |
530 |
|
|
Investment |
41,400 |
|
|
2,73,600 |
2,73,600 |
Closing stock was valued Rs 20,000.
(a) Interest on capital @ 10%.
(b) Interest on drawings @ 5%.
(c) Wages outstanding Rs 50.
(d) Outstanding salary Rs 20.
(e) Provide a depreciation @ 5% on plant and machinery.
(f) Make a 5% provision on debtors.
Answer:
|
Trading Account |
||||||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|||||||
|
Opening Stock |
42,300 |
Sales |
1,12,500 |
|||||||
|
Purchases |
45,000 |
Less: Sales Return |
2,385 |
1,10,115 |
||||||
|
Less: Purchases Return |
1,440 |
43,560 |
Closing Stock |
20,000 |
||||||
|
Carriage |
2,700 |
|||||||||
|
Wages |
11,215 |
|||||||||
|
Add: Outstanding Wages |
50 |
11,265 |
||||||||
|
Octroi |
530 |
|||||||||
|
Gross Profit |
29,760 |
|||||||||
|
1,30,115 |
1,30,115 |
|||||||||
|
Profit and Loss Account |
|||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||
|
Salary |
25,470 |
Gross Profit |
29,760 |
||||
|
Add: Outstanding Salary |
20 |
25,490 |
Commission |
1,575 |
|||
|
Insurance Premium |
2,700 |
Interest |
7,425 |
||||
|
Rent and Taxes |
2,160 |
Interest on Drawings |
977 |
||||
|
Carriage Outwards |
1,485 |
Net Loss |
8,973 |
||||
|
General Expenses |
6,975 |
||||||
|
Interest on Capital |
6,750 |
||||||
|
Depreciation on P & M |
1,350 |
||||||
|
Provision on Debtors |
1,800 |
||||||
|
48,710 |
48,710 |
||||||
|
Balance Sheet |
|||||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
||||
|
Capital |
67,500 |
Plant and Machinery |
27,000 |
||||
|
Add: Interest on Capital |
6,750 |
Less: Depreciation |
1,350 |
25,650 |
|||
|
Less: Net Loss |
8,973 |
Furniture |
6,750 |
||||
|
Less: Drawings |
19,530 |
Debtors |
36,000 |
||||
|
Less: Interest on Drawings |
977 |
44,770 |
Less: New Provision |
1,800 |
34,200 |
||
|
Bank Overdraft |
24,660 |
Investment |
41,400 |
||||
|
Creditors |
58,500 |
Closing Stock |
20,000 |
||||
|
Outstanding Wages |
50 |
||||||
|
Salary Outstanding |
20 |
||||||
|
1,28,000 |
1,28,000 |
||||||
Q14 : The following balances appeared in the trial balance of M/s Kapil Traders as on March 31, 2006
|
Rs |
|
|
Sundry debtors |
30,500 |
|
Bad debts |
500 |
|
Provision for doubtful debts |
2,000 |
The partners of the firm agreed to records the following adjustments in the books of the Firm: Further bad debts Rs.300. Maintain provision for bad debts 10%. Show the following adjustments in the bad debts account, provision account, debtors account, profit and loss account and balance sheet.
Answer :
|
Profit and Loss Account |
||||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|||||
|
Bad Debts |
500 |
|||||||
|
Add: Further Bad Debts |
300 |
|||||||
|
Add: New Provision |
3,020 |
|||||||
|
Less: Old Provision |
2,000 |
1,820 |
||||||
|
Balance Sheet |
|||||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
||||
|
Debtors |
30,500 |
||||||
|
Less: Further Bad Debts |
300 |
||||||
|
Less: New Provision |
3,020 |
27,180 |
|||||
|
Debtors Account |
||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Date |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|
|
2012 |
2012 |
|||||
|
March 31 |
Balance b/d |
30,500 |
March 31 |
Further Bad Debts |
300 |
|
|
March 31 |
Provision for Doubtful Debts |
3,020 |
||||
|
March 31 |
Balance c/d |
27,180 |
||||
|
30,500 |
30,500 |
|||||
|
Bad Debts Account |
||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Date |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|
|
2012 |
2012 |
|||||
|
March 31 |
Balance b/d |
500 |
March 31 |
Provision for Doubtful Debts |
800 |
|
|
(As per the Trial Balance) |
||||||
|
March 31 |
Sundry Debtors |
300 |
||||
|
800 |
800 |
|||||
|
Provision for Doubtful Debts Account |
||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Date |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|
|
2012 |
2011 |
|||||
|
March 31 |
Bad Debt |
800 |
April 01 |
Balance b/d (Old Provision) |
2,000 |
|
|
April 01 |
Profit and Loss |
1,820 |
||||
|
(Balancing figure) |
||||||
|
March 31 |
Balance b/d |
3,020 |
||||
|
(New Provision) |
||||||
|
3,820 |
3,820 |
|||||
Q15 : Prepare the bad debts account, provision for account, profit and loss account and balance sheet from the following information as on December 31, 2011
|
Rs |
|
|
Debtors |
80,000 |
|
Bad debts |
2,000 |
|
Provision for doubtful debts |
5,000 |
Adjustments
Bad Debts Rs 500 Provision on Debtors @ 3%.
|
Profit and Loss Account |
|||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
||||||
|
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
||||
|
Bad Debts |
2,000 |
Old Provision for Doubtful Debts |
5,000 |
||||
|
Add: Further Bad Debts |
500 |
||||||
|
Add: New Provision for Bad Debts |
2,385 |
4,885 |
|||||
|
Balancing figure |
115 |
||||||
|
5,000 |
5,000 |
||||||
|
Balance Sheet |
||||||
|
Liabilities |
Amount Rs |
Assets |
Amount Rs |
|||
|
Debtors |
80,000 |
|||||
|
Less: Further Bad Debts |
500 |
|||||
|
Less: New Provision on Debtors |
2,385 |
77,115 |
||||
|
77,115 |
||||||
|
Bad Debts Account |
||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Date |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|
|
2011 |
2011 |
|||||
|
Dec.31 |
Balance b/d |
2,000 |
Dec.31 |
Provision for Doubtful Debts |
2,500 |
|
|
(as per the Trial Balance) |
||||||
|
Dec.31 |
Sundry Debtors |
500 |
||||
|
2,500 |
2,500 |
|||||
|
Provision for Doubtful Debts Account |
||||||
|
Dr. |
Cr. |
|||||
|
Date |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
Date |
Particulars |
Amount Rs |
|
|
2011 |
2011 |
|||||
|
Dec.31 |
Bad Debts |
2,500 |
Jan.01 |
Balance b/d (Old Provision) |
5,000 |
|
|
Dec.31 |
Balance b/d |
2,385 |
||||
|
(New Provision) |
||||||
|
Dec.31 |
Profit and Loss |
115* |
||||
|
(Balancing Figure) |
||||||
|
5,000 |
5,000 |
|||||
strong>Note: In this case, the old provision exceeds the sum total of Bad debts and the New Provision. Thus, the balancing figure is Rs 115 and is calculated as Rs 2,500 + Rs 2,385 – Rs 5,000 = Rs (115)