Exercise 12.1 : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 271
Q1 :A point is on the x-axis. What are its y-coordinates and z-coordinates?
Answer :
If a point is on the x-axis, then its y-coordinates and z-coordinates are zero.
NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 12 – Introduction to Three Dimensional Geometry
Q2 :A point is in the XZ-plane. What can you say about its y-coordinate?
Answer :
If a point is in the XZ plane, then its y-coordinate is zero.
Q3 :Name the octants in which the following points lie:
(1, 2, 3), (4, -2, 3), (4, -2, -5), (4, 2, -5), (-4, 2, -5), (-4, 2, 5),
(-3, -1, 6), (2, -4, -7)
Answer :
The x-coordinate, y-coordinate, and z-coordinate of point (1, 2, 3) are all positive. Therefore, this point lies in octant I.
The x-coordinate, y-coordinate, and z-coordinate of point (4, -2, 3) are positive, negative, and positive respectively. Therefore, this point lies in octant IV.
The x-coordinate, y-coordinate, and z-coordinate of point (4, -2, -5) are positive, negative, and negative respectively. Therefore, this point lies in octant VIII.
The x-coordinate, y-coordinate, and z-coordinate of point (4, 2, -5) are positive, positive, and negative respectively. Therefore, this point lies in octant V.
The x-coordinate, y-coordinate, and z-coordinate of point (-4, 2, -5) are negative, positive, and negative respectively. Therefore, this point lies in octant VI.
The x-coordinate, y-coordinate, and z-coordinate of point (-4, 2, 5) are negative, positive, and positive respectively. Therefore, this point lies in octant II.
The x-coordinate, y-coordinate, and z-coordinate of point (-3, -1, 6) are negative, negative, and positive respectively. Therefore, this point lies in octant III.
The x-coordinate, y-coordinate, and z-coordinate of point (2, -4, -7) are positive, negative, and negative respectively. Therefore, this point lies in octant VIII.
Q4 :Fill in the blanks:
Answer :
(i) The x-axis and y-axis taken together determine a plane known as ![]()
(ii) The coordinates of points in the XY-plane are of the form ![]()
(iii) Coordinate planes divide the space into octants ![]()
Exercise 12.2 : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 273
Q1 :Find the distance between the following pairs of points:
(i) (2, 3, 5) and (4, 3, 1) (ii) (-3, 7, 2) and (2, 4, -1)
(iii) (-1, 3, -4) and (1, -3, 4) (iv) (2, -1, 3) and (-2, 1, 3)
Answer :
The distance between points P(x1, y1, z1) and P(x2, y2, z2) is given by
![]()
(i) Distance between points (2, 3, 5) and (4, 3, 1)
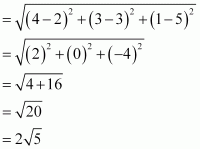
(ii) Distance between points (-3, 7, 2) and (2, 4, -1)
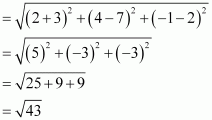
(iii) Distance between points (-1, 3, -4) and (1, -3, 4)
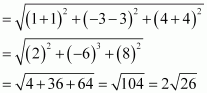
(iv) Distance between points (2, -1, 3) and (-2, 1, 3)
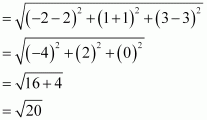
Q2 :Show that the points (-2, 3, 5), (1, 2, 3) and (7, 0, -1) are collinear.
Answer :
Let points (-, 3, 5), (1, 2, 3), and (7, 0,-1) be denoted by P, Q, and R respectively.
Points P, Q, and R are collinear if they lie on a line.
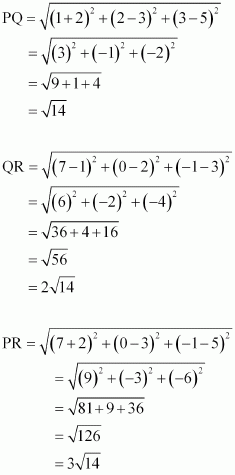
Here, PQ + QR![]() = PR
= PR
Hence, points P(-2, 3, 5), Q(1, 2, 3), and R(7, 0, -1) are collinear.
Q3 :Verify the following:
(i) (0, 7, -10), (1, 6, -6) and (4, 9, -6) are the vertices of an isosceles triangle.
(ii) (0, 7, 10), (-1, 6, 6) and (-4, 9, 6) are the vertices of a right angled triangle.
(iii) (-1, 2, 1), (1, -2, 5), (4, -7, 8) and (2, -3, 4) are the vertices of a parallelogram.
Answer :
(i) Let points (0, 7, -10), (1, 6, -6), and (4, 9, -6) be denoted by A, B, and C respectively.
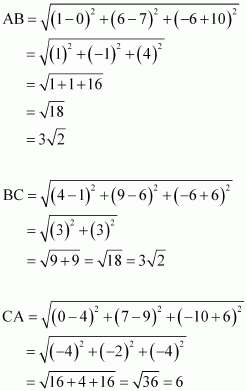
Here, AB = BC ≠ CA
Thus, the given points are the vertices of an isosceles triangle.
(ii) Let (0, 7, 10), (-1, 6, 6), and (-4, 9, 6) be denoted by A, B, and C respectively.
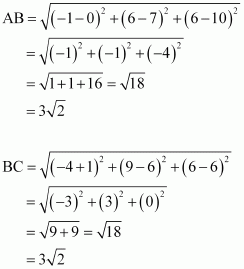
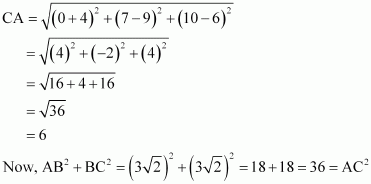
Therefore, by Pythagoras theorem, ABC is a right triangle.
Hence, the given points are the vertices of a right-angled triangle.
(iii) Let (-1, 2, 1), (1, -2, 5), (4, -7, 8), and (2, -3, 4) be denoted by A, B, C, and D respectively.
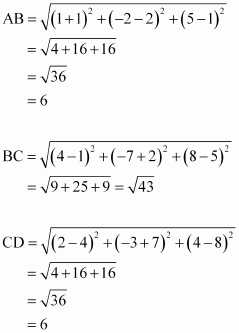
Here, AB = CD = 6, BC = AD = ![]()
Hence, the opposite sides of quadrilateral ABCD , whose vertices are taken in order, are equal.
Therefore, ABCD is a parallelogram.
Hence, the given points are the vertices of a parallelogram.
Q4 :Find the equation of the set of points which are equidistant from the points (1, 2, 3) and (3, 2, -1).
Answer :
Let P (x, y, z) be the point that is equidistant from points A(1, 2, 3) and B(3, 2,
1).
Accordingly, PA = PB
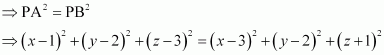
⇒ x2 – 2x + 1 + y2 – 4y + 4 + z2 – 6z + 9 = x2 – 6x + 9 + y2 – 4y + 4 + z2 + 2z + 1
⇒ -2x -4y – 6z + 14 = -6x – 4y + 2z + 14
⇒ – 2x – 6z + 6x – 2z = 0
⇒ 4x – 8z = 0
⇒ x – 2z = 0
Thus, the required equation is x – 2z = 0.
Q5 :Find the equation of the set of points P, the sum of whose distances from A (4, 0, 0) and B (-4, 0, 0) is equal to 10.
Answer :
Let the coordinates of P be (x, y, z).
The coordinates of points A and B are (4, 0, 0) and (-4, 0, 0) respectively.
It is given that PA + PB = 10.
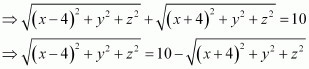
On squaring both sides, we obtain
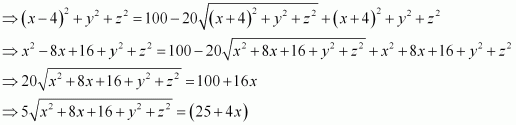
On squaring both sides again, we obtain
25 (x2 + 8x + 16 + y2 + z2) = 625 + 16x2 + 200x
⇒ 25x2 + 200x + 400 + 25y2 + 25z2 = 625 + 16x2 + 200x
⇒ 9x2 + 25y2 + 25z2 – 225 = 0
Thus, the required equation is 9x2 + 25y2 + 25z2 – 225 = 0.
Exercise 12.3 : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 277
Q1 :Find the coordinates of the point which divides the line segment joining the points (-2, 3, 5) and (1, -4, 6) in the ratio (i) 2:3 internally, (ii) 2:3 externally.
Answer :
(i) The coordinates of point R that divides the line segment joining points P (x1, y1, z1) and Q (x2, y2, z2) internally in the ratio m: n are
![]()
Let R (x, y, z) be the point that divides the line segment joining points(-2, 3, 5) and (1, -4, 6) internally in the ratio 2:3
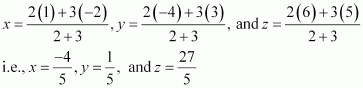
Thus, the coordinates of the required point are ![]()
(ii) The coordinates of point R that divides the line segment joining points P (x1, y1, z1) and Q (x2, y2, z2) externally in the ratio m: n are
![]()
Let R (x, y, z) be the point that divides the line segment joining points(-2, 3, 5) and (1, -4, 6) externally in the ratio 2:3
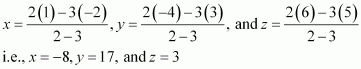
Thus, the coordinates of the required point are (-8, 17, 3).
Q2 :Given that P (3, 2, -4), Q (5, 4, -6) and R (9, 8, -10) are collinear. Find the ratio in which Q divides PR.
Answer :
Let point Q (5, 4, -6) divide the line segment joining points P (3, 2, -4) and R (9, 8, -10) in the ratio k:1.
Therefore, by section formula,
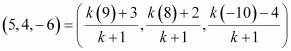
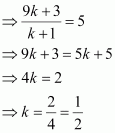
Thus, point Q divides PR in the ratio 1:2.
Q3 :Find the ratio in which the YZ-plane divides the line segment formed by joining the points (-2, 4, 7) and (3, -5, 8).
Answer :
Let the YZ planedivide the line segment joining points (-2, 4, 7) and (3, -5, 8) in the ratio k:1.
Hence, by section formula, the coordinates of point of intersection are given by
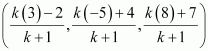
On the YZ plane, the x-coordinate of any point is zero.
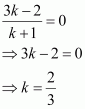
Thus, the YZ plane divides the line segment formed by joining the given points in the ratio 2:3.
Q4 :Using section formula, show that the points A (2, -3, 4), B (-1, 2, 1) and ![]() are collinear.
are collinear.
Answer :
The given points are A (2, -3, 4), B (-1, 2, 1), and ![]()
Let P be a point that divides AB in the ratio k:1.
Hence, by section formula, the coordinates of P are given by
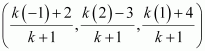
Now, we find the value of k at which point P coincides with point C.
By taking ![]() , we obtain k = 2.
, we obtain k = 2.
For k = 2, the coordinates of point P are ![]()
i.e. ![]() is a point that divides AB externally in the ratio 2:1 and is the same as point P.
is a point that divides AB externally in the ratio 2:1 and is the same as point P.
Hence, points A, B, and C are collinear.
Q5 :Find the coordinates of the points which trisect the line segment joining the points P (4, 2, -6) and Q (10, -16, 6).
Answer :
Let A and B be the points that trisect the line segment joining points P (4, 2, -6) and Q (10, -16, 6)
![]()
Point A divides PQ in the ratio 1:2. Therefore, by section formula, the coordinates of point A are given by
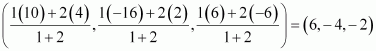
Point B divides PQ in the ratio 2:1. Therefore, by section formula, the coordinates of point B are given by
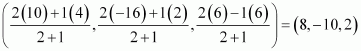
Thus, (6, -4, -2) and (8, -10, 2) are the points that trisect the line segment joining points P (4, 2, -6) and Q (10, -16, 6).
Exercise Miscellaneous : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 278
Q1 :Three vertices of a parallelogram ABCD are A (3, -1, 2), B (1, 2, -4) and C (-1, 1, 2). Find the coordinates of the fourth vertex.
Answer :
The three vertices of a parallelogram ABCD are given as A (3, -1, 2), B (1, 2, -4), and C (-1, 1, 2). Let the coordinates of the fourth vertex be D (x, y, z).
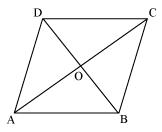
We know that the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
Therefore, in parallelogram ABCD, AC and BD bisect each other.
∴ Mid-point of AC = Mid-point of BD
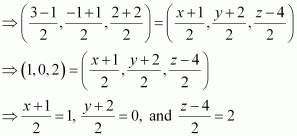
⇒ x = 1, y = -2, and z = 8
Thus, the coordinates of the fourth vertex are (1, -2, 8).
Q2 :Find the lengths of the medians of the triangle with vertices A (0, 0, 6), B (0, 4, 0) and (6, 0, 0).
Answer :
Let AD, BE, and CF be the medians of the given triangle ABC.
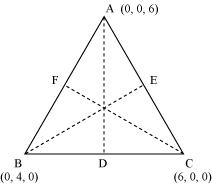
Since AD is the median, D is the mid-point of BC.
∴ Coordinates of point D = ![]() = (3, 2, 0)
= (3, 2, 0)
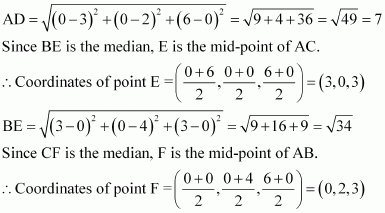
![]()
Thus, the lengths of the medians of ΔABC are ![]()
Q3 :If the origin is the centroid of the triangle PQR with vertices P (2a, 2, 6), Q (-4, 3b, -10) and R (8, 14, 2c), then find the values of a, b and c.
Answer :
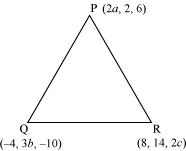
It is known that the coordinates of the centroid of the triangle, whose vertices are (x1, y1, z1), (x2, y2, z2) and (x3, y3, z3), are ![]()
Therefore, coordinates of the centroid of ΔPQR
![]()
It is given that origin is the centroid of ΔPQR.
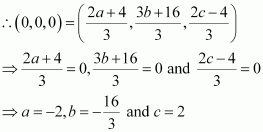
Thus, the respective values of a, b, and c are ![]()
Q4 :Find the coordinates of a point on y-axis which are at a distance of ![]() from the point P (3, -2, 5).
from the point P (3, -2, 5).
Answer :
If a point is on the y-axis, then x-coordinate and the z-coordinate of the point are zero.
Let A (0, b, 0) be the point on the y-axis at a distance of ![]() from point P (3, -2, 5).
from point P (3, -2, 5).
Accordingly,
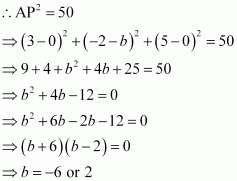
Thus, the coordinates of the required points are (0, 2, 0) and (0, -6, 0).
Q5 :A point R with x-coordinate 4 lies on the line segment joining the points P (2, -3, 4) and Q (8, 0, 10). Find the coordinates of the point R.
[Hint suppose R divides PQ in the ratio k: 1. The coordinates of the point R are given by ![]()
Answer :
The coordinates of points P and Q are given as P (2, -3, 4) and Q (8, 0, 10).
Let R divide line segment PQ in the ratio k:1.
Hence, by section formula, the coordinates of point R are given by
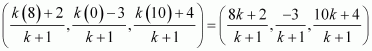
It is given that the x-coordinate of point R is 4.
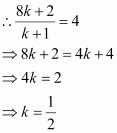
Therefore, the coordinates of point R are 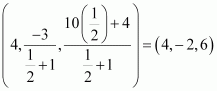
Q6 :If A and B be the points (3, 4, 5) and (-1, 3, -7), respectively, find the equation of the set of points P such that PA2 + PB2 = k2, where k is a constant.
Answer :
The coordinates of points A and B are given as (3, 4, 5) and (-1, 3, -7) respectively.
Let the coordinates of point P be (x, y, z).
On using distance formula, we obtain
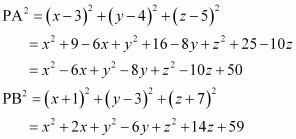
Now, if PA2 + PB2 = k2, then
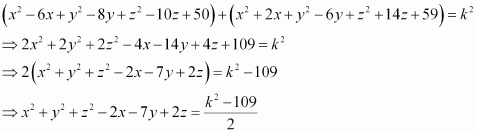
Thus, the required equation is ![]()