Exercise 4.1 : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 94
NCERT Solution for Class 11 Maths Chapter 4 Principle of Mathematical Induction
Q1 :Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction for all n ∈ N:![]()
Answer:
Let the given statement be P(n), i.e.,![]()
For n = 1, we have
P(1): 1 =![]() , which is true.
, which is true.
Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
![]() We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
Consider
1 + 3 + 32 + … + 3k-1 + 3(k+1) – 1
= (1 + 3 + 32 +… + 3k-1) + 3k
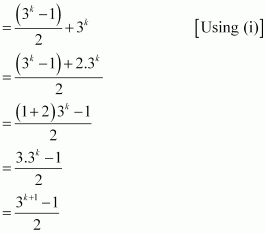
Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, by the principle of mathematical induction, statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n.
Q2 :Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction for all n ∈ N:
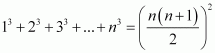
Answer :
Let the given statement be P(n), i.e.,
P(n):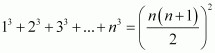 For n = 1, we have
For n = 1, we have
P(1): 13 = 1 =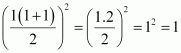 , which is true.
, which is true.
Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
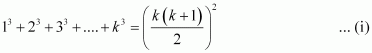
We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
Consider
13 + 23 + 33 + … + k3 + (k + 1)3
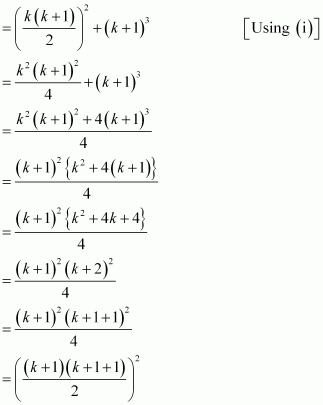 = (13 + 23 + 33 + …. + k3) + (k + 1)3
= (13 + 23 + 33 + …. + k3) + (k + 1)3
Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, by the principle of mathematical induction, statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n.
Q3 :Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction for all n ∈ N:
![]()
Answer :
Let the given statement be P(n), i.e.,
P(n): ![]() For n = 1, we have
For n = 1, we have
P(1): 1 =![]() which is true.
which is true.
Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
![]() We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
Consider
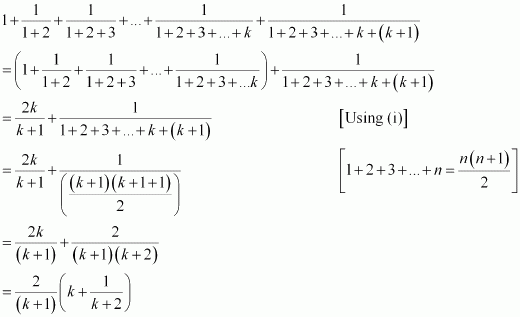 Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, by the principle of mathematical induction, statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n.
Q4 :Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction for all n ∈ N: 1.2.3 + 2.3.4 + … + n(n + 1) (n + 2) =![]()
Answer :
Let the given statement be P(n), i.e.,
P(n): 1.2.3 + 2.3.4 + … + n(n + 1) (n + 2) =![]() For n = 1, we have
For n = 1, we have
P(1): 1.2.3 = 6 =![]() , which is true.
, which is true.
Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
1.2.3 + 2.3.4 + … + k(k + 1) (k + 2) = ![]() We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
Consider
1.2.3 + 2.3.4 + … + k(k + 1) (k + 2) + (k + 1) (k + 2) (k + 3)
= {1.2.3 + 2.3.4 + … + k(k + 1) (k + 2)} + (k + 1) (k + 2) (k + 3)
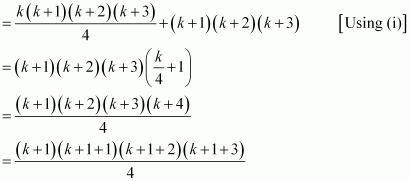 Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, by the principle of mathematical induction, statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n.
Q5 :Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction for all n ∈ N:
![]()
Answer :
Let the given statement be P(n), i.e.,
P(n) :![]() For n = 1, we have
For n = 1, we have
P(1): 1.3 = 3=![]() , which is true.
, which is true.
Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
![]() We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
Consider
1.3 + 2.32 + 3.33 + … + k3k+ (k + 1) 3k+1
= (1.3 + 2.32 + 3.33 + …+ k.3k) + (k + 1) 3k+1
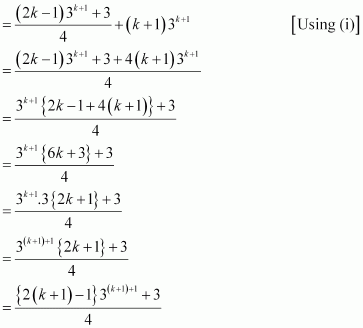 Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, by the principle of mathematical induction, statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n.
Q6 :Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction for all n ∈ N:
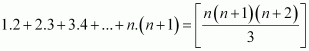
Answer :
Let the given statement be P(n), i.e.,
P(n):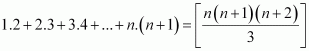 For n = 1, we have
For n = 1, we have
P(1): ![]() , which is true.
, which is true.
Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
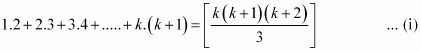 We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
Consider
1.2 + 2.3 + 3.4 + … + k.(k + 1) + (k + 1).(k + 2)
= [1.2 + 2.3 + 3.4 + … + k.(k + 1)] + (k + 1).(k + 2)
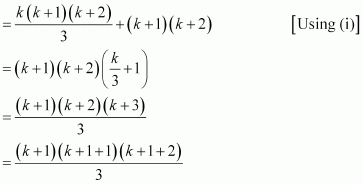 Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, by the principle of mathematical induction, statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n.
Q7 :Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction for all n ∈ N:
![]()
Answer :
Let the given statement be P(n), i.e.,
P(n):![]() For n = 1, we have
For n = 1, we have
![]()
, which is true.
Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
![]() We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
Consider
(1.3 + 3.5 + 5.7 + … + (2k -1) (2k + 1) + {2(k + 1) -1}{2(k + 1) + 1}
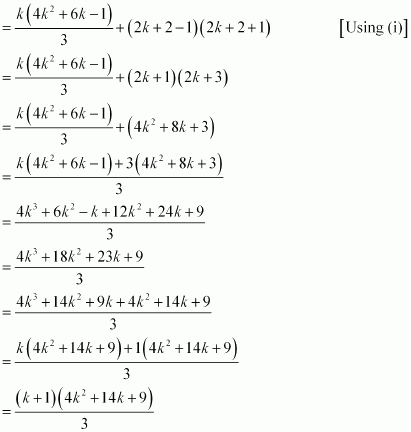 Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, by the principle of mathematical induction, statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n.
Q8 :Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction for all n ∈ N: 1.2 + 2.22 + 3.22 + … + n.2n = (n – 1) 2n+1 + 2
Answer :
Let the given statement be P(n), i.e.,
P(n): 1.2 + 2.22 + 3.22 + … + n.2n = (n – 1) 2n+1 + 2
For n = 1, we have
P(1): 1.2 = 2 = (1 – 1) 21+1 + 2 = 0 + 2 = 2, which is true.
Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
1.2 + 2.22 + 3.22 + … + k.2k = (k – 1) 2k+1 + 2 … (i)
We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
Consider
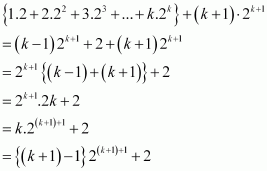 Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, by the principle of mathematical induction, statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n.
Q9 :Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction for all n ∈ N:
![]()
Answer :
Let the given statement be P(n), i.e.,
P(n):![]() For n = 1, we have
For n = 1, we have
P(1):![]() , which is true.
, which is true.
Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
![]() We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
Consider
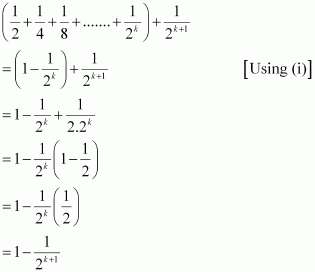 Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, by the principle of mathematical induction, statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n.
Q10 :Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction for all n ∈ N:
![]()
Answer :
Let the given statement be P(n), i.e.,
P(n):![]() For n = 1, we have
For n = 1, we have
![]() , which is true.
, which is true.
Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
![]()
We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
Consider
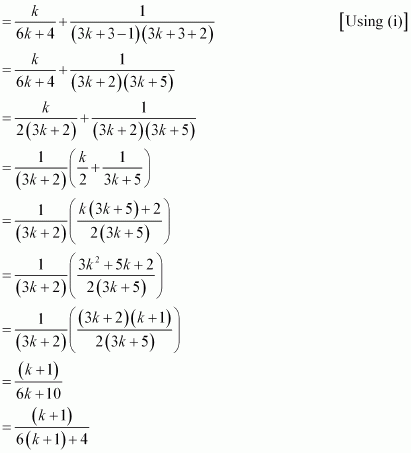 Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, by the principle of mathematical induction, statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n.
Q11 :Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction for all n ∈ N:
![]()
Answer :
Let the given statement be P(n), i.e.,
P(n):![]() For n = 1, we have
For n = 1, we have
![]()
, which is true.
Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
![]() We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
Consider
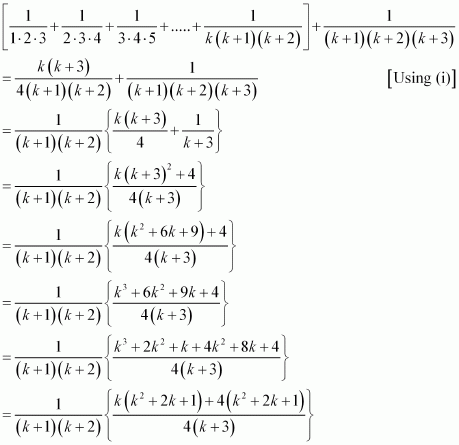 Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, by the principle of mathematical induction, statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n.
Q12 :Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction for all n ∈ N:
![]()
Answer :
Let the given statement be P(n), i.e.,
![]() For n = 1, we have
For n = 1, we have
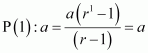 , which is true.
, which is true.
Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
![]() We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
Consider
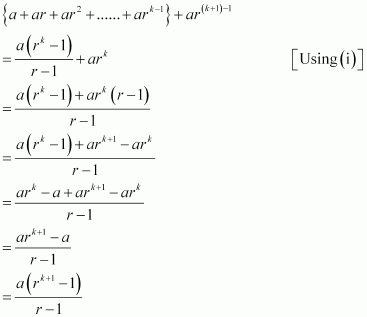 Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, by the principle of mathematical induction, statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n.
Q13 :Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction for all n ∈ N:
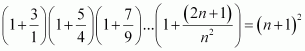
Answer :
Let the given statement be P(n), i.e.,
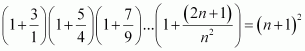 For n = 1, we have
For n = 1, we have
![]() Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
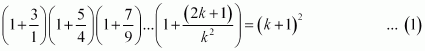 We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
Consider
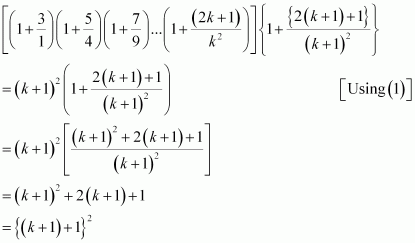 Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, by the principle of mathematical induction, statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n.
Q14 :Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction for all n ∈ N:
![]()
Answer :
Let the given statement be P(n), i.e.,
![]() For n = 1, we have
For n = 1, we have
![]() , which is true.
, which is true.
Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
![]() We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
Consider
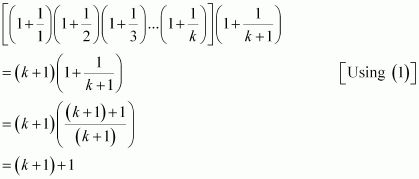 Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, by the principle of mathematical induction, statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n.
Q15 :Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction for all n ∈ N:
![]()
Answer :
Let the given statement be P(n), i.e.,
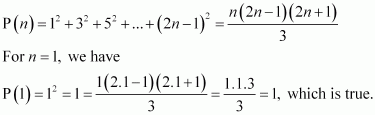 Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
![]() We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
Consider
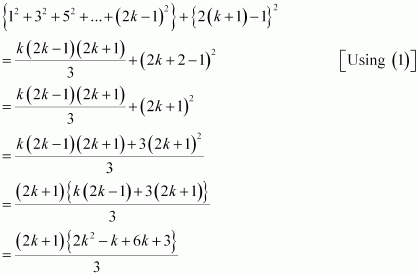 Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, by the principle of mathematical induction, statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n.
Q16 :Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction for all n ∈ N:
![]()
Answer :
Let the given statement be P(n), i.e.,
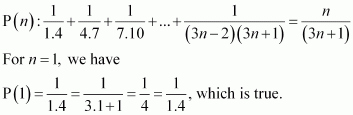 Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
![]() We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
Consider
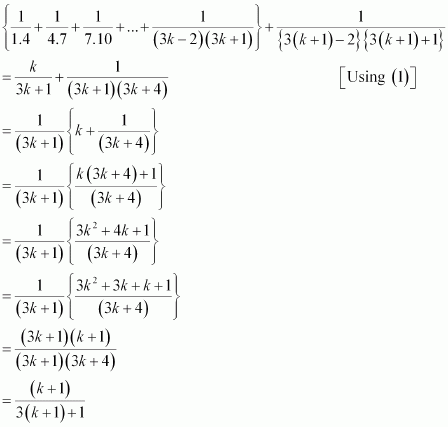 Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, by the principle of mathematical induction, statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n.
Q17 :Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction for all n ∈ N:
![]()
Answer :
Let the given statement be P(n), i.e.,
![]() For n = 1, we have
For n = 1, we have
![]() , which is true.
, which is true.
Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
![]() We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true.
Consider
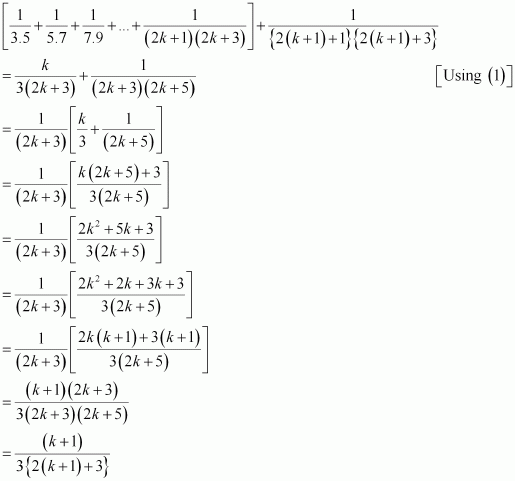 Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, by the principle of mathematical induction, statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n.
Q18 :Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction for all n ∈ N:
![]()
Answer :
Let the given statement be P(n), i.e.,
![]() It can be noted that P(n) is true for n = 1 since
It can be noted that P(n) is true for n = 1 since ![]() Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
![]() We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Consider
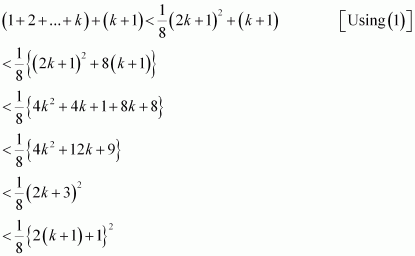 Hence,
Hence,![]() Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, by the principle of mathematical induction, statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n.
Q19 :Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction for all n ∈ N: n (n + 1) (n + 5) is a multiple of 3.
Answer :
Let the given statement be P(n), i.e.,
P(n): n (n + 1) (n + 5), which is a multiple of 3.
It can be noted that P(n) is true for n = 1 since 1 (1 + 1) (1 + 5) = 12, which is a multiple of 3.
Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
k (k + 1) (k + 5) is a multiple of 3.
∴k (k + 1) (k + 5) = 3m, where m ∈ N … (1)
We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Consider
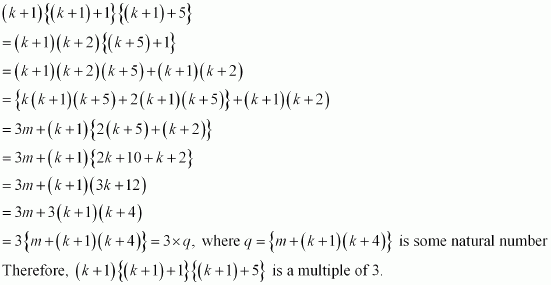 Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, by the principle of mathematical induction, statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n.
Q20 :Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction for all n ∈ N: 102n – 1 + 1 is divisible by 11.
Answer :
Let the given statement be P(n), i.e.,
P(n): 102n 1 + 1 is divisible by 11.
It can be observed that P(n) is true for n = 1 since P(1) = 102.1-1 + 1 = 11, which is divisible by 11.
Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
102k-1 + 1 is divisible by 11.
∴102-1 + 1 = 11m, where m ∈ N … (1)
We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Consider
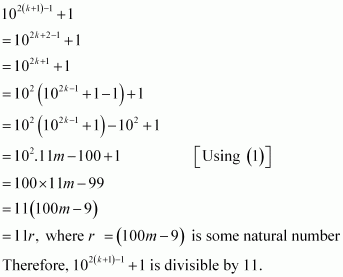 Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, by the principle of mathematical induction, statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n.
Q21 :Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction for all n ∈ N: x2n – y2n is divisible by x + y.
Answer :
Let the given statement be P(n), i.e.,
P(n): x2n – y2n is divisible by x + y.
It can be observed that P(n) is true for n = 1.
This is so because x2×1 – y2 ×1 = x2 – y2 = (x + y) (x – y) is divisible by (x + y).
Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
x2k – y2k is divisible by x + y.
∴x2k – y2k = m (x + y), where m ∈ N … (1)
We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Consider
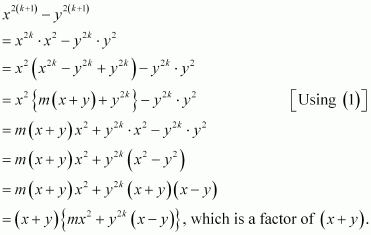 Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, by the principle of mathematical induction, statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n.
Q22 :Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction for all n ∈ N: 32n+2 – 8n – 9 is divisible by 8.
Answer :
Let the given statement be P(n), i.e.,
P(n): 32n + 2 – 8n – 9 is divisible by 8.
It can be observed that P(n) is true for n = 1 since 32 ×1 + 2- 8 × 1 – 9 = 64, which is divisible by 8.
Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
32k+ 2 – 8k – 9 is divisible by 8.
∴32k+ 2 – 8k – 9 = 8m; where m ∈ N … (1)
We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Consider
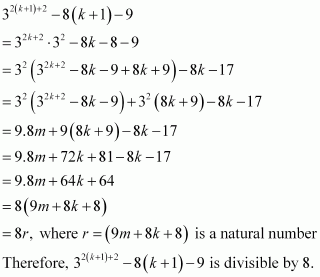 Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, by the principle of mathematical induction, statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n.
Q23 :Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction for all n ∈ N: 41n – 14n is a multiple of 27.
Answer :
Let the given statement be P(n), i.e.,
P(n):41n – 14n is a multiple of 27.
It can be observed that P(n) is true for n = 1 since , which is a multiple of 27.
Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
41k – 14k is a multiple of 27
∴41k – 14k = 27m, where m ∈ N … (1)
We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Consider
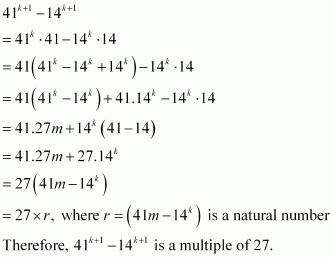 Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, by the principle of mathematical induction, statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n.
Q24 :Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction for all n ∈ N(2n +7) < (n + 3)2
Answer :
Let the given statement be P(n), i.e.,
P(n): (2n +7) < (n + 3)2
It can be observed that P(n) is true for n = 1 since 2.1 + 7 = 9 < (1 + 3)2 = 16, which is true.
Let P(k) be true for some positive integer k, i.e.,
(2k + 7) < (k + 3)2 … (1)
We shall now prove that P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Consider
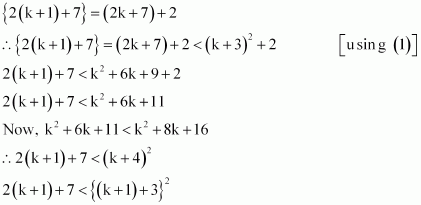 Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Thus, P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, by the principle of mathematical induction, statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n.