Exercise : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 105
Q1 : Tick the most suitable answer in question 1 and 2.
In addition to the rock particles, the soil contains
(i) air and water
(ii) water and plants
(iii) minerals, organic matter, air and water
(iv) water, air and plants
Answer :
In addition to the rock particles, the soil contains
(i) air and water
(ii) water and plants
(iii) minerals, organic matter, air and water (correct)
(iv) water, air and plants
Q2 : The water holding capacity is the highest in
(i) sandy soil
(ii) clayey soil
(iii) loamy soil
(iv) mixture of sand and loam
Answer :
The water holding capacity is the highest in
(i) sandy soil
(ii) clayey soil (correct)
(iii) loamy soil
(iv) mixture of sand and loam
Q3 : Match the items in Column I with those in Column II:
|
Column I |
Column II |
||
| (i) | A home for living organisms | (a) | Large particles |
| (ii) | Upper layer of the soil | (b) | All kinds of soil |
| (iii) | Sandy soil | (c) | Dark in colour |
| (iv) | Middle layer of the soil | (d) | Small particles and packed tight |
| (v) | Clayey soil | (e) | Lesser amount of humus |
Answer :
|
Column I |
Column II |
||
| (i) | A home for living organisms | (b) | All kinds of soil |
| (ii) | Upper layer of the soil | (c) | Dark in colour |
| (iii) | Sandy soil | (a) | Large particles |
| (iv) | Middle layer of the soil | (e) | Lesser amount of humus |
| (v) | Clayey soil | (d) | Small particles and packed tight |
Q4 : Explain how soil is formed.
Answer :
Soil is formed through the process of weathering. Weathering is a process of physical breakdown and chemical decomposition of rocks and minerals near or at the surface of the earth. This physical and chemical decomposition is primarily done by wind, water, and climate. As a result of these processes, large rock pieces are converted into smaller pieces and eventually to soil.
Q5 : How is clayey soil useful for crops?
Answer :
Due to the very small size of the particles of clayey soil, particles are packed tightly and therefore can retain water. Clayey soil is also rich in organic matter. For growing crops such as wheat, gram, and paddy, the soil that is good at retaining water and rich in organic matter is suitable. Therefore, clayey soils having these characteristics are useful for such kind of crops.
Q6 : List the differences between clayey soil and sandy soil.
Answer :
|
Clayey soil |
Sandy soil |
||
|
1. |
The proportion of fine particles is higher. |
1. |
The proportion of large particles is higher. |
|
2. |
Particles are packed tightly. |
2. |
Particles are loosely packed. |
|
3. |
It can hold good amount of water. |
3. |
It’s ability to retain water is low. |
|
4. |
Water cannot drain quickly. |
4. |
Water can drain quickly. |
|
5. |
It is heavy in weight. |
5. |
It is light in weight. |
|
6. |
Less air is trapped between the particles. |
6. |
More air is trapped between the particles. |
|
7. |
It is rich in humus. |
7. |
It is notrich in humus. |
Q7 : Sketch the cross section of soil and label the various layers.
Answer :
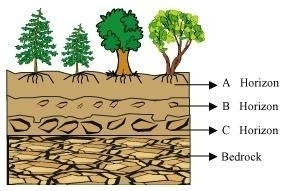
Soil profile
Q8 : Razia conducted an experiment in the field related to the rate of percolation. She observed that it took 40 min for 200 mL of water to percolate through the soil sample. Calculate the rate of percolation.
Answer :
Given amount of water = 200 mL
Percolation time = 40 min
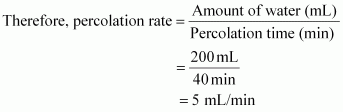
Q10 : Solve the following crossword puzzle with the clues given:
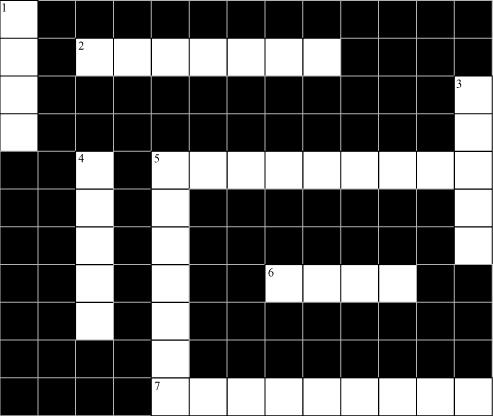
Across
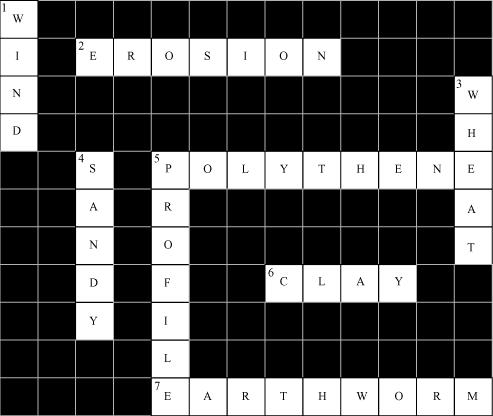
2. Plantation prevents it.
5. Use should be banned to avoid soil pollution.
6. Type of soil used for making pottery.
7. Living organism in the soil.
Down
- In desert soil erosion occurs through.
- Clay and loam are suitable for cereals like.
- This type of soil can hold very little water.
- Collective name for layers of soil.
Answer :
Exercise : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 106
Q9 : Explain how soil pollution and soil erosion could be prevented.
Answer :
Prevention of soil pollution:
The persistent build-up of toxic compounds in the soil is defined as soil pollution. To prevent soil pollution, its causes must be controlled.
(i) Plastics and polythene bags destroy the fertility of soil. Hence, they should be disposed properly and if possible, their use should be avoided.
(ii) Some waste products from industries and homes pollute soil. These pollutants should be treated chemically to make them harmless before they are disposed.
(iii) Other pollutants of soil include pesticides and insecticides. Therefore, excessive use of these substances should be avoided.
Prevention of soil erosion:
Removal of the upper fertile layer of the soil (top soil) by strong wind and flowing water is known as soil erosion. Roots of plants bind the soil firmly and prevent soil erosion. Absence of plants leads to soil erosion. Therefore, soil erosion can be prevented by planting trees and checking indiscriminate cutting of trees.