Exercise : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 141
Q1 : Fill in the blanks:
(a) Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of parent is called ________.
(b) A flower may have either male or female reproductive parts. Such a flower is called _________.
(c) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same or of another flower of the same kind is known as _________.
(d) The fusion of male and female gametes is termed as __________.
(e) Seed dispersal takes place by means of _________, _________ and _________.
Answer :
(a) Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of parent is called __vegetative propagation__.
(b) A flower may have either male or female reproductive parts. Such a flower is called __unisexual__.
(c) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same or of another flower of the same kind is known as__pollination__.
(d) The fusion of male and female gametes is termed as __fertilisation__.
(e) Seed dispersal takes place by means of __wind__, __water__ and __animals__.
Q2 : Describe the different methods of asexual reproduction. Give examples.
Answer :
The various modes of asexual reproduction in plants are as follows:
(i)Vegetative propagation: It is the ability of a plant to produce new plants from roots, stems, leaves, and buds. Vegetative propagation is divided into two types.
• Natural vegetative propagation: This type of vegetative propagation occurs easily in nature and involves simple vegetative parts. Potato plant sprouting from an eye is a common example.
• Artificial vegetative propagation: This type of vegetative propagation is performed manually and generally occurs in laboratory conditions. The formation of a complete plant from a stem cutting of rose is a common example of this method.
(ii) Budding:It involves the formation of a new individual from a bulb-like projection called a bud. The bud grows and gets detached from the parent to form a new individual. It is commonly observed in yeast.
(iii)Fragmentation:It is a form of asexual reproduction where a new organism is formed from the fragments of the parent body. It is the only mode of asexual reproduction in Spirogyra.
(iv)Spore formation:Many non-flowering plants reproduce through spore formation. Spores are tiny cells protected by a thick wall. Fungi such as bread moulds reproduce asexually using this method.
Q3 : Explain what you understand by sexual reproduction.
Answer :
Sexual reproduction is a process which involves production of seeds. It requires two parents. Most plants reproduce sexually with the help of flowers. The main function of a flower is to reproduce and therefore develop new seeds that can grow into new plants
Q4 : State the main difference between asexual and sexual reproduction.
Answer :
Differences between sexual and asexual reproduction:
|
Asexual reproduction |
Sexual reproduction |
|
It requires only one parent. |
It requires two parents. |
|
In asexual reproduction, newly developed plants are |
In sexual reproduction, newly developed plants are not |
|
Special reproductive parts are not required for asexual |
Flower is the reproductive part of a plant which contains the sexual organs of a plant. These are important for sexual reproduction. |
|
Examples are yeast, rose, jasmine, potato, etc. |
Examples are flowering plants, such as Hibiscus, |
Q5 : Explain the difference between self-pollination and cross-pollination.
Answer :
Differences between self-pollination and cross-pollination:
|
Self-pollination |
Cross-pollination |
|
It involves the transfer of pollen from the stamen to the |
It involves the transfer of pollen from the stamen of one |
|
It occurs only in bisexual flowers. |
It occurs in both unisexual and bisexual flowers. |
Q6 : How does the process of fertilisation take place in flowers?
Answer :
When pollen lands on stigma, it germinates and gives rise to a pollen tube that passes through the style and reaches the ovary of a pistil. When the pollen tube reaches an ovule, it releases the male gametes. A male gamete fuses with a female gamete in the ovule. This process is known as fertilisation. The cell which is formed after the fusion of a male and a female gamete is known as zygote. This zygote divides several times in order to form the embryo present inside the seed.
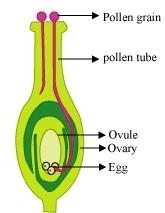
Process of fertilisation
Q7 : Describe the various ways by which seeds are dispersed.
Answer :
Seed dispersal occurs by the following agencies.
(a)Dispersal by animals – There are many ways by which birds and animals can disperse seeds. For example, birds and animals can eat the fruits and excrete the seeds away from the parent plant. Some seeds have barbs or other structures that get attached to the animal’s body and are carried to new sites. Some fruits have hooks on them which cling to fur or clothes.
(b)Dispersal by wind – Seeds that get dispersed by wind are usually smaller in size or they have wings or hair-like structures. For example, winged seeds of drumsticks, hairy fruit of sunflower, etc. are dispersed by wind.
(c)Dispersal by water – Many aquatic plants or plants that live near water has seeds that can float and are carried away by water. For example, coconuts can float and are dispersed by water.
(d) Dispersal by explosion – Sometimes the seeds are dispersed by the bursting of fruits with sudden jerks. The seeds get scattered or distributed far from the parent plant. Examples of such plants are castor and balsam.
Q8 : Match items in Column I with those in Column II:
|
Column I |
Column II |
||
|
(a) |
Bud |
(i) |
Maple |
|
(b) |
Eyes |
(ii) |
Spirogyra |
|
(c) |
Fragmentation |
(iii) |
Yeast |
|
(d) |
Wings |
(iv) |
Bread mould |
|
(e) |
Spores |
(v) |
Potato |
|
(vi) |
Rose |
Answer :
|
Column I |
Column II |
||
|
(a) |
Bud |
(iii) |
Yeast |
|
(b) |
Eyes |
(v) |
Potato |
|
(c) |
Fragmentation |
(ii) |
Spirogyra |
|
(d) |
Wings |
(i) |
Maple |
|
(e) |
Spores |
(iv) |
Bread mould |
Q9 : Tick (∠Å¡ ) the correct answer:
(a) The reproductive part of a plant is the
(i) leaf
(ii) stem
(iii) root
(iv) flower
(b) The process of fusion of the male and female gametes is called
(i) fertilisation
(ii) pollination
(iii) reproduction
(iv) seed formation
(c) Mature ovary forms the
(i) seed
(ii) stamen
(iii) pistil
(iv) fruit
(d) A spore producing plant is
(i) rose
(ii) bread mould
(iii) potato
(iv) ginger
(e) Bryophyllum can reproduce by its
(i) stem
(ii) leaves
(iii) roots
(iv) flower
Answer :
(a) The reproductive part of a plant is the
(i) leaf
(ii) stem
(iii) root
(iv) flower ∠Å¡
(b) The process of fusion of the male and female gametes is called
(i) fertilisation ∠Å¡
(ii) pollination
(iii) reproduction
(iv) seed formation
(c) Mature ovary forms the
(i) seed
(ii) stamen
(iii) pistil
(iv) fruit ∠Å¡
(d) A spore producing plant is
(i) rose
(ii) bread mould ∠Å¡
(iii) potato
(iv) ginger
(e) Bryophyllum can reproduce by its
(i) stem
(ii) leaves ∠Å¡
(iii) roots
(iv) flower