Exercise : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 9
Q1 : Why do organisms need to take food?
Answer :
All living organisms require food to survive. It gives them energy to perform various activities. All activities such as playing, running, walking, studying, etc. require energy. The various components present in our food such as carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals provide energy to our body. These are also important for growth and development of the body.
Q2 : Distinguish between a parasite and a saprotroph.
Answer :
|
Parasite |
Saprotroph |
|
The organism that grows on the body of another organism |
The organism that obtains nutrients from the dead or |
|
Examples of parasites are Cuscuta and orchids. |
Examples of saprotrophs are fungi and some bacteria. |
Q3 : How would you test the presence of starch in leaves?
Answer :
Experiment to test the presence of starch in leaves:
Take two healthy green potted plants of the same type. Keep one potted plant in a dark room for one or two days in order to remove all the starch from the leaves. Keep the other plant in sunlight. Now, take one leaf from each potted plant and put a few drops of iodine solution on them. Then note down the observation.

Plants kept in light and dark conditions
No blue black colour will be observed on the leaves of the plant kept in the dark room. This indicates the absence of starch. Blue black colour will be observed on the leaves of the plant kept in sunlight. This indicates the presence of starch.
Q4 : Give a brief description of the process of synthesis of food in green plants.
Answer :
Photosynthesis is defined as the process in which the chlorophyll-containing plant cells synthesise food in the form of carbohydrates, using carbon dioxide and water in the presence of solar energy.
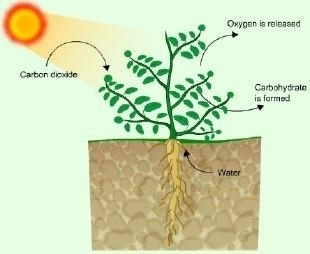
Photosynthesis
Sources of raw materials required for photosynthesis:
(a) Water is taken in from the roots of the plant and is transported to the leaves.
(b) Carbon dioxide from the air enters the leaves through the tiny pores called stomata and diffuses to the cells containing chlorophyll.
(c) Solar energy is used to break water into hydrogen and oxygen. This hydrogen is combined with carbon dioxide to form food for the plants, which is ultimately used by the animals as well.
Thus, photosynthesis can be represented by the following equation.
![]()
Q5 : Show with the help of a sketch that the plants are the ultimate source of food.
Answer :
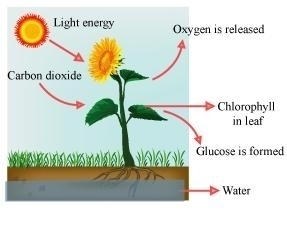
Photosynthesis
Q6 : Fill in the blanks:
(a) Green plants are called __________ since they synthesise their own food.
(b) The food synthesised by the plants is stored as __________.
(c) In photosynthesis solar energy is captured by the pigment called ___________.
(d) During photosynthesis plants take in ___________and release ___________.
Answer :
(a) Green plants are called __autotrophs__ since they synthesise their own food.
(b) The food synthesised by the plants is stored as __starch__.
(c) In photosynthesis solar energy is captured by the pigment called chlorophyll__.
(d) During photosynthesis plants take in __carbon dioxide__ and release __oxygen__.
Q7 : Name the following:
(i) A parasitic plant with yellow, slender and tubular stem.
(ii) A plant that has both autotrophic and heterotrophic mode of nutrition.
(iii) The pores through which leaves exchange gases.
Answer :
(i) Cuscuta
(ii) Pitcher plant
(iii) Stomata
Q8 : Tick the correct answer:
(a)Amarbel is an example of
(i) autotroph
(ii) parasite
(iii) saprotroph
(iv) host
(b)The plant which traps and feeds on insects is
(i) Cuscuta
(ii) china rose
(iii) pitcher plant
(iv) rose
Answer :
(a)Amarbel is an example of
(i) autotroph
(ii) parasite
(iii) saprotroph
(iv) host
(b)The plant which traps and feeds on insects is
(i) Cuscuta
(ii) China rose
(iii) pitcher plant
(iv) rose
Q9 : Match the items given in Column I with those in Column II:
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
Chlorophyll |
Bacteria |
|
Nitrogen |
Heterotrophs |
|
Amarbel |
Pitcher plant |
|
Animals |
Leaf |
|
Insects |
Parasite |
Answer :
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
Chlorophyll |
Leaf |
|
Nitrogen |
Bacteria |
|
Amarbel |
Parasite |
|
Animals |
Heterotrophs |
|
Insects |
Pitcher plant |
Q10 : Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false:
(i) Carbon dioxide is released during photosynthesis. (T/F)
(ii) Plants which synthesise their food themselves are called saprotrophs. (T/F)
(iii) The product of photosynthesis is not a protein. (T/F)
(iv) Solar energy is converted into chemical energy during photosynthesis. (T/F)
Answer :
(i) Carbon dioxide is released during photosynthesis. (F)
(ii) Plants which synthesise their food themselves are called saprotrophs. (F)
(iii) The product of photosynthesis is not a protein. (T)
(iv) Solar energy is converted into chemical energy during photosynthesis. (T)
Exercise : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 10
Q11 : Choose the correct option from the following:
Which part of the plant takes in carbon dioxide from the air for photosynthesis?
(i) Root hair
(ii) Stomata
(iii) Leaf veins
(iv) Sepals
Answer :
(ii) Stomata
Q12 : Choose the correct option from the following:
Plants take carbon dioxide from the atmosphere mainly through their:
(i) roots
(ii) stem
(iii) flowers
(iv) leaves
Answer :
(iv) leaves