NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 – Real Numbers
Exercise 1.1 : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 7
Q1 : Use Euclid’s division algorithm to find the HCF of:
![]()
Answer :
(i) 135 and 225
Since 225 > 135, we apply the division lemma to 225 and 135 to obtain
225 = 135 x 1 + 90
Since remainder 90 ≠ 0, we apply the division lemma to 135 and 90 to obtain
135 = 90 x 1 + 45
We consider the new divisor 90 and new remainder 45, and apply the division lemma to obtain
90 = 2 x 45 + 0
Since the remainder is zero, the process stops.
Since the divisor at this stage is 45,
Therefore, the HCF of 135 and 225 is 45.
(ii)196 and 38220
Since 38220 > 196, we apply the division lemma to 38220 and 196 to obtain
38220 = 196 x 195 + 0
Since the remainder is zero, the process stops.
Since the divisor at this stage is 196,
Therefore, HCF of 196 and 38220 is 196.
(iii)867 and 255
Since 867 > 255, we apply the division lemma to 867 and 255 to obtain
867 = 255 x 3 + 102
Since remainder 102 ≠ 0, we apply the division lemma to 255 and 102 to obtain
255 = 102 x 2 + 51
We consider the new divisor 102 and new remainder 51, and apply the division lemma to obtain
102 = 51 x 2 + 0
Since the remainder is zero, the process stops.
Since the divisor at this stage is 51,
Therefore, HCF of 867 and 255 is 51.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers
Q2 : Show that any positive odd integer is of the form![]() , or
, or![]() , or
, or ![]() , where q is some integer.
, where q is some integer.
Answer :
Let a be any positive integer and b = 6. Then, by Euclid’s algorithm,
a = 6q + rfor some integer q ≤ 0, and r = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 because 0 ≤ r < 6.
Therefore, a = 6q or 6q + 1 or 6q + 2 or 6q + 3 or 6q + 4 or 6q + 5
Also, 6q + 1 = 2 x 3q + 1 = 2k1 + 1, where k1 is a positive integer
6q + 3 = (6q + 2) + 1 = 2 (3q + 1) + 1 = 2k2 + 1, where k2 is an integer
6q + 5 = (6q + 4) + 1 = 2 (3q + 2) + 1 = 2k3 + 1, where k3 is an integer
Clearly, 6q + 1, 6q + 3, 6q + 5 are of the form 2k + 1, where k is an integer.
Therefore, 6q + 1, 6q + 3, 6q + 5 are not exactly divisible by 2. Hence, these expressions of numbers are odd numbers.
And therefore, any odd integer can be expressed in the form 6q + 1, or 6q + 3,
or 6q + 5
Q3 : An army contingent of 616 members is to march behind an army band of 32 members in a parade. The two groups are to march in the same number of columns. What is the maximum number of columns in which they can march?
Answer :
HCF (616, 32) will give the maximum number of columns in which they can march.
We can use Euclid’s algorithm to find the HCF.
616 = 32 x 19 + 8
32 = 8 x 4 + 0
The HCF (616, 32) is 8.
Therefore, they can march in 8 columns each.
Q4 : Use Euclid’s division lemma to show that the square of any positive integer is either of form 3m or 3m + 1 for some integer m.
[Hint: Let x be any positive integer then it is of the form 3q, 3q + 1 or 3q + 2. Now square each of these and show that they can be rewritten in the form 3m or 3m + 1.]
Answer :
Let a be any positive integer and b = 3.
Then a = 3q + r for some integer q ≥ 0
And r = 0, 1, 2 because 0 ≤ r < 3
Therefore, a = 3q or 3q + 1 or 3q + 2
Or,

Where k1, k2, and k3 are some positive integers
Hence, it can be said that the square of any positive integer is either of the form 3m or 3m + 1.
Q5 : Use Euclid’s division lemma to show that the cube of any positive integer is of the form 9m, 9m + 1 or 9m + 8.
Answer :
Let a be any positive integer and b = 3
a = 3q + r, where q ≥ 0 and 0 ≤ r < 3
![]()
Therefore, every number can be represented as these three forms. There are three cases.
Case 1: When a = 3q,
![]()
Where m is an integer such that m =![]()
Case 2: When a = 3q + 1,
a3 = (3q +1)3
a3= 27q3 + 27q2 + 9q + 1
a3 = 9(3q3 + 3q2 + q) + 1
a3 = 9m + 1
Where m is an integer such that m = (3q3 + 3q2 + q)
Case 3: When a = 3q + 2,
a3 = (3q +2)3
a3= 27q3 + 54q2 + 36q + 8
a3 = 9(3q3 + 6q2 + 4q) + 8
a3 = 9m + 8
Where m is an integer such that m = (3q3 + 6q2 + 4q)
Therefore, the cube of any positive integer is of the form 9m, 9m + 1,
or 9m + 8.
Exercise 1.2 : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 11
Q1 : Express each number as product of its prime factors:
![]()
Answer :
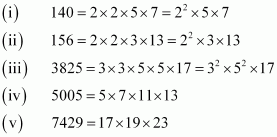
Q2 : Find the LCM and HCF of the following pairs of integers and verify that LCM × HCF = product of the two numbers.
![]()
Answer :
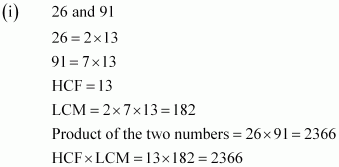
Hence, product of two numbers = HCF × LCM
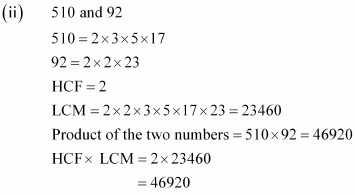
Hence, product of two numbers = HCF × LCM
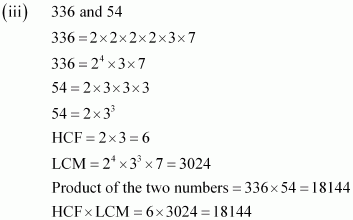
Hence, product of two numbers = HCF × LCM
Q3 : Find the LCM and HCF of the following integers by applying the prime factorisation method.
![]()
Answer :
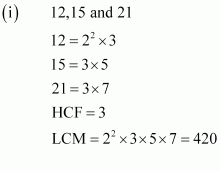
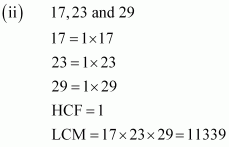
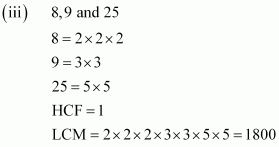
Q4 : Given that HCF (306, 657) = 9, find LCM (306, 657).
Answer :
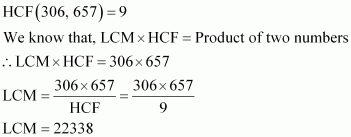
Q5 : Check whether 6n can end with the digit 0 for any natural number n.
Answer :
If any number ends with the digit 0, it should be divisible by 10 or in other words, it will also be divisible by 2 and 5 as 10 = 2 x 5
Prime factorisation of 6n = (2 x 3)n
It can be observed that 5 is not in the prime factorisation of 6n.
Hence, for any value of n, 6n will not be divisible by 5.
Therefore, 6n cannot end with the digit 0 for any natural number n.
Q6 : Explain why 7 x 11 x 13 + 13 and 7 x 6 x 5 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 1 + 5 are composite numbers.
Answer :
Numbers are of two types – prime and composite. Prime numbers can be divided by 1 and only itself, whereas composite numbers have factors other than 1 and itself.
It can be observed that
7 x 11 x 13 + 13 = 13 x (7 x 11 + 1) = 13 x (77 + 1)
= 13 x 78
= 13 x 13 x 6
The given expression has 6 and 13 as its factors. Therefore, it is a composite number.
7 x 6 x 5 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 1 + 5 = 5 x (7 x 6 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 1 + 1)
= 5 x (1008 + 1)
= 5 x 1009
1009 cannot be factorised further. Therefore, the given expression has 5 and 1009 as its factors. Hence, it is a composite number.
Q7 : There is a circular path around a sports field. Sonia takes 18 minutes to drive one round of the field, while Ravi takes 12 minutes for the same. Suppose they both start at the same point and at the same time, and go in the same direction. After how many minutes will they meet again at the starting point?
Answer :
It can be observed that Ravi takes lesser time than Sonia for completing 1 round of the circular path. As they are going in the same direction, they will meet again at the same time when Ravi will have completed 1 round of that circular path with respect to Sonia. And the total time taken for completing this 1 round of circular path will be the LCM of time taken by Sonia and Ravi for completing 1 round of circular path respectively i.e., LCM of 18 minutes and 12 minutes.
18 = 2 x 3 x 3
And, 12 = 2 x 2 x 3
LCM of 12 and 18 = 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 = 36
Therefore, Ravi and Sonia will meet together at the starting pointafter 36 minutes.
Exercise 1.3 : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 14
Q1 : Prove that![]() is irrational.
is irrational.
Answer :
Let![]() is a rational number. Therefore, we can find two integers a, b (b ≠ 0) such that
is a rational number. Therefore, we can find two integers a, b (b ≠ 0) such that![]() Let a and b have a common factor other than 1. Then we can divide them by the common factor, and assume that a and b are co-prime.
Let a and b have a common factor other than 1. Then we can divide them by the common factor, and assume that a and b are co-prime.
![]()
Therefore, a2 is divisible by 5 and it can be said that a is divisible by 5.
Let a = 5k, where k is an integer
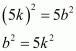 This means that b2 is divisible by 5 and hence, b is divisible by 5.
This means that b2 is divisible by 5 and hence, b is divisible by 5.
This implies that a and b have 5 as a common factor.
And this is a contradiction to the fact that a and b are co-prime.
Hence,![]() cannot be expressed as
cannot be expressed as![]() or it can be said that
or it can be said that
![]() is irrational.
is irrational.
Q2 : Prove that![]() is irrational.
is irrational.
Answer :
Let![]() is rational.
is rational.
Therefore, we can find two integers a, b (b ≠ 0) such that
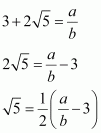
Since a and b are integers, ![]() will also be rational and therefore,
will also be rational and therefore,![]() is rational.
is rational.
This contradicts the fact that ![]() is irrational. Hence, our assumption that
is irrational. Hence, our assumption that![]() is rational is false. Therefore,
is rational is false. Therefore, ![]() is irrational.
is irrational.
Q3 : Prove that the following are irrationals:
![]()
Answer :
![]()
Let ![]() is rational.
is rational.
Therefore, we can find two integers a, b (b ≠ 0) such that
![]()
![]()
![]() is rational as a and b are integers.
is rational as a and b are integers.
Therefore,![]() is rational which contradicts to the fact that
is rational which contradicts to the fact that![]() is irrational.
is irrational.
Hence, our assumption is false and![]() is irrational.
is irrational.
![]()
Let ![]() is rational.
is rational.
Therefore, we can find two integers a, b (b ≠ 0) such that
![]() for some integers a and b
for some integers a and b
![]()
![]() is rational as a and b are integers.
is rational as a and b are integers.
Therefore, ![]() should be rational.
should be rational.
This contradicts the fact that ![]() is irrational. Therefore, our assumption that
is irrational. Therefore, our assumption that![]() is rational is false. Hence,
is rational is false. Hence,![]() is irrational.
is irrational.
![]()
Let ![]() be rational.
be rational.
Therefore, we can find two integers a, b (b ≠ 0) such that
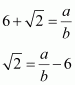 Since a and b are integers,
Since a and b are integers, ![]() is also rational and hence,
is also rational and hence, ![]() should be rational. This contradicts the fact that
should be rational. This contradicts the fact that![]() is irrational. Therefore, our assumption is false and hence,
is irrational. Therefore, our assumption is false and hence,![]() is irrational.
is irrational.
Exercise 1.4 : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 17
Q1 : Without actually performing the long division, state whether the following rational numbers will have a terminating decimal expansion or a non-terminating repeating decimal expansion:
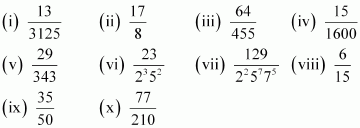
Answer :
(i)![]()
![]()
The denominator is of the form 5m.
Hence, the decimal expansion of![]() is terminating.
is terminating.
(ii)![]()
The denominator is of the form 2m.
Hence, the decimal expansion ![]() of is terminating.
of is terminating.
(iii)![]()
455 = 5 × 7 × 13
Since the denominator is not in the form 2m × 5n, and it also contains 7 and 13 as its factors, its decimal expansion will be non-terminating repeating.
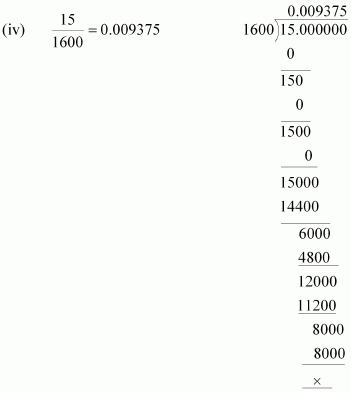
(iv)![]()
1600 = 26 × 52
The denominator is of the form 2m ×5n.
Hence, the decimal expansion of![]() is terminating.
is terminating.
(v)![]()
![]()
Since the denominator is not in the form 2m × 5n, and it has 7 as its factor, the decimal expansion of ![]() is non-terminating repeating.
is non-terminating repeating.
(vi)![]() The denominator is of the form 2m × 5n.
The denominator is of the form 2m × 5n.
Hence, the decimal expansion of ![]() is terminating.
is terminating.
(vii)![]()
Since the denominator is not of the form 2m × 5n, and it also has 7 as its factor, the decimal expansion of ![]() is non-terminating repeating.
is non-terminating repeating.
(viii)![]() The denominator is of the form 5n.
The denominator is of the form 5n.
Hence, the decimal expansion of![]() is terminating.
is terminating.
(ix)![]()
![]()
The denominator is of the form 2m × 5n.
Hence, the decimal expansion of![]() is terminating.
is terminating.
(x)![]()
![]()
Since the denominator is not of the form 2m 5n,and it also has 3 as its factors,the decimal expansion of![]() is non-terminating repeating.
is non-terminating repeating.
Q2 : Write down the decimal expansions of those rational numbers in Question 1 above which have terminating decimal expansions.
Answer :

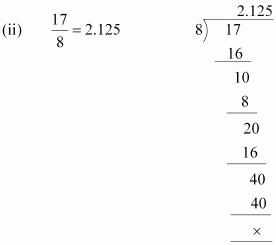
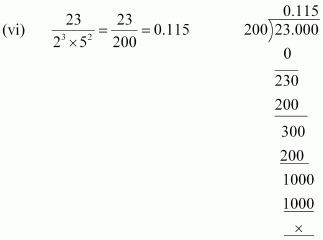
(viii)![]()
![]()
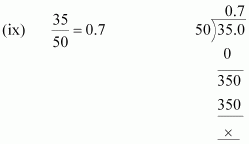
Q3 : The following real numbers have decimal expansions as given below. In each case, decide whether they are rational or not. If they are rational, and of the form ![]() , what can you say about the prime factor of q?
, what can you say about the prime factor of q?
(i) 43.123456789 (ii) 0.120120012000120000… (iii)![]()
(i) 43.123456789
Since this number has a terminating decimal expansion, it is a rational number of the form ![]() and q is of the form
and q is of the form![]()
i.e., the prime factors of q will be either 2 or 5 or both.
(ii) 0.120120012000120000 …
The decimal expansion is neither terminating nor recurring. Therefore, the given number is an irrational number.
(iii)![]()
Since the decimal expansion is non-terminating recurring, the given number is a rational number of the form![]() and q is not of the form
and q is not of the form ![]() i.e., the prime factors of q will also have a factor other than 2 or 5.
i.e., the prime factors of q will also have a factor other than 2 or 5.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths All Chapters
- Chapter 1 – Real Numbers
- Chapter 2 – Polynomials
- Chapter 3 – Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Chapter 4 – Quadratic Equations
- Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions
- Chapter 6 – Triangles
- Chapter 7 – Coordinate Geometry
- Chapter 8 – Introduction to Trigonometry
- Chapter 9 – Some Applications of Trigonometry
- Chapter 10 – Circles
- Chapter 11 – Constructions
- Chapter 12 – Areas Related to Circles
- Chapter 13 – Surface Areas and Volumes
- Chapter 14 – Statistics
- Chapter 15 – Probability