Coordinate Geometry Class 9
Exercise 3.1 : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 53
Q1 : How will you describe the position of a table lamp on your study table to another person?
Answer :
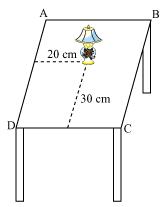
Consider that the lamp is placed on the table. Choose two adjacent edges, DC and AD. Then, draw perpendiculars on the edges DC and AD from the position of lamp and measure the lengths of these perpendiculars. Let the length of these perpendiculars be 30 cm and 20 cm respectively. Now, the position of the lamp from the left edge (AD) is 20 cm and from the lower edge (DC) is 30 cm. This can also be written as (20, 30), where 20 represents the perpendicular distance of the lamp from edge AD and 30 represents the perpendicular distance of the lamp from edge DC.
Q2 : (Street Plan): A city has two main roads which cross each other at the centre of the city. These two roads are along the North-South direction and East-West direction.
All the other streets of the city run parallel to these roads and are 200 m apart. There are about 5 streets in each direction. Using 1 cm = 100 m, draw a model of the city on your notebook Represent the roads/streets by single lines.
There are many cross-streets in your model. A particular cross-street is made by two streets, one running in the North-South direction and another in the East-West direction. Each cross street is referred to in the following manner: If the 2nd street running in the North-South direction and 5th in the East-West direction meet at some crossing, then we will call this cross-street (2, 5). Using this convention, find:
(i) How many cross – streets can be referred to as (4, 3).
(ii) How many cross – streets can be referred to as (3, 4).
Answer :
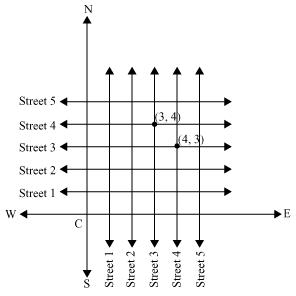
Both the cross-streets are marked in the above figure. It can be observed that there is only one cross-street which can be referred as (4, 3), and again, only one which can be referred as (3, 4).
Exercise 3.2 : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 60
Q1 : Write the answer of each of the following questions:
(i) What is the name of horizontal and the vertical lines drawn to determine the position of any point in the Cartesian plane?
(ii) What is the name of each part of the plane formed by these two lines?
(iii) Write the name of the point where these two lines intersect.
Answer :
(i) The name of horizontal lines and vertical lines drawn to determine the position of any point in the Cartesian plane is x-axis and y-axis respectively.
(ii) The name of each part of the plane formed by these two lines, x-axis and y-axis, is quadrant (one-fourth part).
(iii) The name of the point where these two lines intersect is the origin.
Q2 : See the given figure, and write the following:
(i) The coordinates of B.
(ii) The coordinates of C.
(iii) The point identified by the coordinates(-3,-5).
(iv) The point identified by the coordinates(2,-4).
(v) The abscissa of the point D.
(vi) The ordinate of the point H.
(vii) The coordinates of the point L.
(viii) The coordinates of the point M
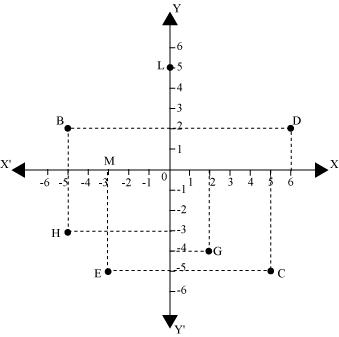
Answer :
(i) The x-coordinate and the y-coordinate of point B are -5 and 2 respectively. Therefore, the coordinates of point B are (-5, 2).
(ii) The x-coordinate and the y-coordinate of point C are 5 and -5 respectively. Therefore, the coordinates of point C are (5, -5).
(iii) The point whose x-coordinate and y-coordinate are -3 and -5 respectively is point E.
(iv) The point whose x-coordinate and y-coordinate are 2 and -4 respectively is point G.
(v) The x-coordinate of point D is 6. Therefore, the abscissa of point D is 6.
(vi) The y-coordinate of point H is -3. Therefore, the ordinate of point H is -3.
(vii) The x-coordinate and the y-coordinate of point L are 0 and 5 respectively. Therefore, the coordinates of point L are (0, 5).
(viii) The x-coordinate and the y-coordinate of point M are -3 and 0 respectively. Therefore, the coordinates of point M is (-3, 0).
Exercise 3.3 : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 65
Q1 : In which quadrant or on which axis do each of the points(-2,4),(3,-1),(-1,0),(1,2) and (-3,-5) lie? Verify your answer by locating them on the Cartesian plane.
Answer :
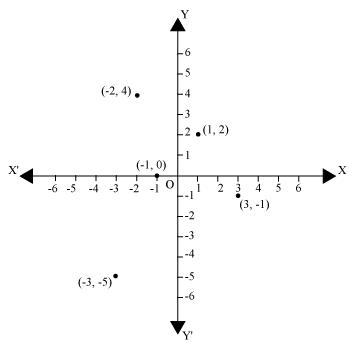
The point (-2,4) lies in the IInd quadrant in the Cartesian plane because for point(-2,4), x-coordinate is negative and y-coordinate is positive.
Again, the point(3,-1) lies in the IVth quadrant in the Cartesian plane because for point(3,-1), x-coordinate is positive and y-coordinate is negative.
The point(-1,0) lies on negative x-axis because for point(-1,0) , the value of y-coordinate is zero and the value of x-coordinate is negative.
The point(1,2) lies in the Ist quadrant as for point(1,2) , both x and y are positive.
The point (-3,-5)lies in the IIIrd quadrant in the Cartesian plane because for point(-3,-5) , both x and y are negative.
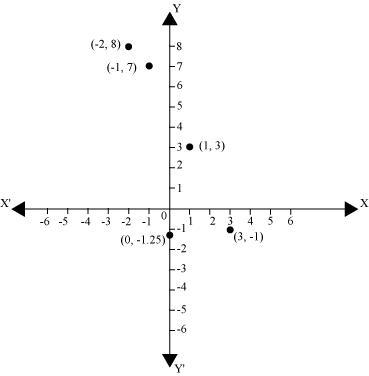
Q2 : Plot the point (x, y) given in the following table on the plane, choosing suitable units of distance on the axis.
|
x |
– 2 |
– 1 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
|
y |
8 |
7 |
1.25 |
3 |
– 1 |
Answer :
The given points can be plotted on the Cartesian plane as follows.