Exercise 10.1 : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 157
Q1 : For each of the given solid, the two views are given. Match for each solid the corresponding top and front views.

Answer :
The given solids, matched to their respective side view and top view, are as follows.
Object Side view Top view

Q2 : For each of the given solid, the three views are given. Identify for each solid the corresponding top, front and side views.

Answer :
(a)

(i) Front (ii) Side (iii) Top
(b)

(i) Side (ii) Front (iii) Top
(c)

(i) Front (ii) Side (iii) Top
(d)
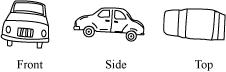
(i) Front (ii) Side (iii) Top
Q3 : For each given solid, identify the top view, front view and side view.
(a)

(b)

(c)

(d)

(e)

Answer :
(a)

(i) Top (ii) Front/Side (iii) Side/Front
(b)

(i) Side (ii) Front (iii) Top
(c)

(i) Top (ii) Side (iii) Front
(d)

(i) Side (ii) Front (iii) Top
(e)

(i) Front/Side (ii) Top (iii) Side/Front
Q4 : Draw the front view, side view and top view of the given objects.
 |
 |
| (a) A military tent | (b) A table |
 |
 |
| (c) A nut | (d) A hexagonal block |
 |
 |
| (e) A dice | (f) A solid |
Answer :
(a)
| A military tent | |
| Front View |  |
| Top View |  |
| Side View |  |
(b)
| A table | |
| Front View |  |
| Top View |  |
| Side View |  |
(c)
| A nut | |
| Front View |  |
| Top View |  |
| Side View |  |
(d)
| A hexagonal block | |
| Front View |  |
| Top View |  |
| Side View |  |
(e)
| A dice | |
| Front View |  |
| Top View |  |
| Side View |  |
(f)
| A solid | |
| Front View |  |
| Top View |  |
| Side View |  |
Exercise 10.2 : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 163
Q1 : Look at the given map of a city.

Answer the following.
(a) Colour the map as follows: Blue – water plant, red – fire station, orange – library, yellow – schools, green – park, pink – college, purple – hospital, brown – cemetery.
(b) Mark a green ‘X’ at the intersection of Road ‘C’ and Nehru Road, Green ‘Y’ at the intersection of Gandhi Road and Road A.
(c) In red, draw a short street route from library to the bus depot.
(d) Which is further east, the city park or the market?
(e) Which is further south, the Primary School or the Sr. Secondary School?
Answer :
(a) The given map coloured in the required way is as follows.

(b)The marks can be put at the given points as follows.

(c) The shortest route from the library to bus depot is represented by red colour.

(d) Between the Market and the City Park, the City Park is further east.
(e) Between the Primary School and the Sr. Secondary School, the Sr. Secondary School is further south.
Exercise 10.3 : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 166
Q1 : Can a polyhedron have for its faces
(i) 3 triangles? (ii) 4 triangles?
(iii) a square and four triangles?
Answer :
(i) No, such a polyhedron is not possible. A polyhedron has minimum 4 faces.
(ii) Yes, a triangular pyramid has 4 triangular faces.

(iii) Yes, a square pyramid has a square face and 4 triangular faces.

Q2 : Is it possible to have a polyhedron with any given number of faces? (Hint: Think of a pyramid).
Answer :
A polyhedron has a minimum of 4 faces.
Q3 : Which are prisms among the following?
(i)![]()
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
Answer :
(i) It is not a polyhedron as it has a curved surface. Therefore, it will not be a prism also.
(ii) It is a prism.
(iii) It is not a prism. It is a pyramid.
(iv) It is a prism.
Q4 : (i) How are prisms and cylinders alike?
(ii) How are pyramids and cones alike?
Answer :
(i) A cylinder can be thought of as a circular prism i.e., a prism that has a circle as its base.
(ii) A cone can be thought of as a circular pyramid i.e., a pyramid that has a circle as its base.
Q5 : Is a square prism same as a cube? Explain.
Answer :
A square prism has a square as its base. However, its height is not necessarily same as the side of the square. Thus, a square prism can also be a cuboid.
Q6 : Verify Euler’s formula for these solids.
(i)

(ii)

Answer :
(i) Number of faces = F = 7
Number of vertices = V = 10
Number of edges = E = 15
We have, F + V – E = 7 + 10 – 15 = 17 – 15 = 2
Hence, Euler’s formula is verified.
(ii) Number of faces = F = 9
Number of vertices = V = 9
Number of edges = E = 16
F + V – E = 9 + 9 – 16 = 18 – 16 = 2
Hence, Euler’s formula is verified.
Q7 : Using Euler’s formula, find the unknown.
| Faces | ? | 5 | 20 |
| Vertices | 6 | ? | 12 |
| Edges | 12 | 9 | ? |
Answer :
By Euler’s formula, we have
F + V – E = 2
(i) F + 6 – 12 = 2
F – 6 = 2
F = 8
(ii) 5 + V – 9 = 2
V – 4 = 2
V = 6
(iii) 20 + 12 – E = 2
32 – E = 2
E = 30
Thus, the table can be completed as
| Faces | 8 | 5 | 20 |
| Vertices | 6 | 6 | 12 |
| Edges | 12 | 9 |
Q8 : Can a polyhedron have 10 faces, 20 edges and 15 vertices?Answer :
Number of faces = F = 10
Number of edges = E = 20
Number of vertices = V = 15
Any polyhedron satisfies Euler’s Formula, according to which, F + V – E = 2
For the given polygon,
F + V – E = 10 + 15 – 20 = 25 – 20 = 5 ≠ 2
Since Euler’s formula is not satisfied, such a polyhedron is not possible.