Answer the following Question
Question-1
Fill in the blanks: ,
(a)……. was a word used for large landowners in TamiL
(b)The ‘gramabhojaka’ often got his land cultivated by the…………………..
(c)Ploughmen were known as ………….. in Tamil .
(d)Most ‘grihapatis’ were………….
Answer:
(a) ‘Vellalar’ (b) slaves and workers
(c) ‘uzhavar’ (d) smaller.
Question-2
Describe the Junctions of the ‘gramabhojaka’. Why do you think he was powerful?
Answer:
The ‘gramabhojaka’ was the largest landowner. He had slaves and he hired workers to cultivate the land. He was powerful since the king entrusted him with the important job of collecting taxes from the villagers. His other functions were those of a policeman and judge.
Question-3
List the crafts persons who would have been present in both villages and cities.
Answer:
Craftsman like the carpenters, weavers, potters, etc. were presumably present in both villages and cities.
Question-4
Choose the correct answer:
(a)Ring wells were used for:
1.bathing 2.washing clothes
3.irrigation 4. drainage.
(b)Punch marked coins were made of:
1.Silver 2.gold
3.tin 4.ivory.
(c)Mathura was an important:
1.village 2.port
3.religious centre 4.forested area.
(d)‘Shrenis’ were associations of:
1.rulers 2.crafts persons
3.farmers 4.herders.
Answer:
(a)drainage
(b)silver
(c)religious centre
(d)crafts persons.
Question-5
Which of the iron tools shown on page 87 (of the NCERT textbook) would have been important for agriculture? What would the other tools have been used for?
Answer:
The iron tools shown on page 87 are: sickle, tongs, and axe. The ones that would have been used for agriculture were—sickle and axe.
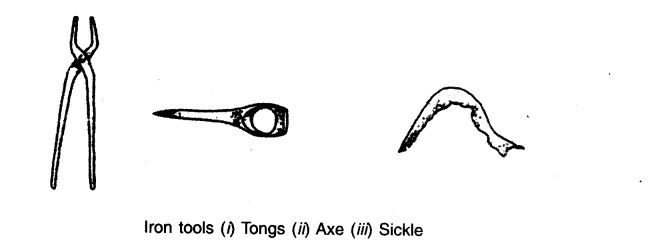
Tongs would have been used to hold things without actually touching them.
Question-6
Compare the drainage system in your locality with that of the cities mentioned in the lesson. What similarities and differences do you notice?
Answer:
The drainage system in our localities is well-planned. The same system was adopted in the times mentioned in the lesson. Both the systems are found to be similar in many ways. The only difference that we find in the modem and the past systems is that the past system was made of mud, bricks and thatch. They could not survive for long. They were not well-maintained, but today we have well-maintained and developed drainage system. It is made of solid materials. It tests long.
Question-7
If you have seen crafts persons at work, describe in a short paragraph what they do.
[Hint. How do they get the raw materials, what kind of equipment do they use, how do they work, what happens to the finished product.]
Answer:
I have seen crafts persons like weavers, blacksmiths, goldsmiths in villages and cities. Weavers are mostly seen in villages. I saw them running their spinning wheel or handmill. First they collect the cotton balls, they weave thread and then they weave clothes. After that they sell it in the market.
Question-8
List (he Junctions performed by men and women who live in your city and village. In what ways are these similar to those performed by people who lived in Mathura? In what ways are they different?
Answer:
In the city I live, I see men and women working to feed their families. Mostly men work in offices and other establishments. Women also work in offices these days. In a city like Mathura, people worked to provide food items to the city- folks because it was located at the intersection of two major trade and travel routes. Life of people of our cities and that in Mathura was in no way much different.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct option to complete the statements given below:
(i) The use of iron in the Indian Subcontinent began about .
(a) 2000 years ago (b) a million years ago
(c) 3000 years ago (d) 500 years ago.
(ii) VeUalar was the term used for
(a) Large landowners (b) Small farmers
(c) Common people (d) Slaves.
(iii) Gram bhqjaka was a powerful man. He also worked as a
(a) Judge (b) Policemen
(c) Councillor (d) Both (a) and (b).
(iv) Mathura is an important centre for worship of
(a) Lord Rama (b) Lord Krishna
(c) Lord Vishnu (d) Both (a) and (b).
(v) Between 2200 and 1900 years ago, Arikamedu was a
(a) Coastal settlement (b) Monastery
(c) Religious place (d) None of the above.
Answer: (i)—(c), (ii)—(a), (iii)—(d), (iv)—(b), (v)—(a).
FILL IN THE BLANKS
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words to complete each sentence.
(i) The post of gram bhojaka was …………….
(ii)There were independent farmers also who were known as ……………………
(iii)……. literature was popular in Tamil Nadu.
(iv) The Jatakas were stories preserved by …………………
(v) The associations of crafts persons and merchants were known as ……………………….
(vi) Stamped red-glazed pottery was known as ………………. ware.
Answer: (i) hereditary (ii)grihpatis
(iiij Sangam (iv)Buddhist monks
(v) shrenis (vi) Arretine.
TRUE/FALSE
State whether these sentences are true (T) or false (F).
(i) The ploughshare was used to increase agricultural production.
(ii)Most of the grihpatis were large landowners.
(iii)Extremely fine pottery was found in the southern part of the sub-continent,
(iv) Shrenis also served as banks where rich men and women deposited money,
(v) Arretine Ware was named after a city in Germany.
Answer: (i) True, (ii) False, (iii) False, (iv) True, (v) False.
MATCHING SKILL
Match the items in column A correctly with those given in column B.

VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question-1
Where were some of the largest collections of iron tools found?
Answer:
These were found in the megalithic burials,
Question-2
What was the use of iron tools?
Answer:
Iron tools were used for clearing forests.
Question-3
What did irrigation works include?
Answer:
Irrigation works included canals, wells, tanks and artificial lakes,
Question-4
Mention any one function that was performed by the grama bhojaka
Answer:
The grama bhojaka collected taxes from the village for the king.
Question-5
How did the dasa karmakara earn a living?
Answer:
They used to work on the fields owned by others.
Question-6
What do you know about Jatakas?
Answer:
Jatakas were stories composed by ordinary people and preserved by Buddhist monks.
Question-7
What were ring wells?
Answer:
Rows of pots or ceramic rings arranged one on top of the other came to be known as ring wells.
Question-8
How did people use ring wells?
Answer:
People used ring wells as toilets. They also used them as drains and garbage dumps.
Question-9
How luos wealth measured during early times?
Answer:
Wealth was measured in terms of coins during early times.
Question-10
What do you know about punch marked coins?
Answer:
Earliest coins were punch marked coins, they came to be known like this because the designs were punched on to the metal like silver or copper.
Question-11
How can you say that Mathura was a religious place?
Answer:
One could find Buddhist monasteries and Jaina shrines in Mathura. Mathura was also a place where Lord Krishna was worshipped by the people.
Question-12
Mention the occupations of people who lived in Mathura
Answer:
Goldsmiths, blacksmiths, weavers, basket makers, garland makers and perfumers.
Question-13
Why were Varanasi and Madurai famous?
Answer:
Varanasi and Madurai were famous for the manufacture of cloth.
Question-14
What do you know about Arikamedu?
Answer:
Between 2200 and 1900 years ago Aricamedu was a coastal settlement where ships unloaded goods from distant lands.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question-1
What steps were taken to increase agricultural production? [V. Imp.]
Answer:
Iron tools such as axes and iron ploughshare began to be used. Axes were used for clearing forests and the ploughshare was useful for increasing agricultural production. Apart from these new tools, irrigation was also used for this purpose. Irrigation works that were built during this time included canals, wells, tanks, and artificial lakes.
Question-2
Who was the grama bhojaka? Write about him in brief.
Answer:
The grama bhojaka was the village headman in the northern part of the country. His post was hereditary. He was the largest landowner in the village who kept slaves and hired workers to cultivate the land. He collected taxes from the village for the king. He also functioned as a judge and sometimes as a policeman
Question-3
What do you know about Sangam literature? [V. Imp.]
Answer:
Some of the earliest works in Tamil came to be known as Sangam literature. These earliest works were composed around 2300 years ago. These texts were called Sangam because they were supposed to have been composed and compiled in assemblies of poets. These assemblies were known as Sangams. They were held in the city of Madurai.
Question-4
What kind of information do we get from several inscriptions found in Mathura?
Answer:
The inscriptions found in Mathura record gifts made by men and women to monasteries and shrines. These were made by kings and queens, officers, merchants and crafts people who lived the city. The inscriptions from Mathura make us aware that people were engaged in several occupations such as— weaving, basket making, garland making etc. There were also goldsmiths and blacksmiths.
Question-5
What were shrenis? What functions did shrenis of crafts persons perform?[Imp.]
Answer:
Shrenis were associations of crafts persons and merchants. The shrenis of crafts persons performed various functions. They provided training, procured raw material and distributed the finished product. Then came shrenis of merchants who organised the trade. Shrenis also performed the role of banks where rich men and women deposited money.
Question-6
Write a short note on Arikamedu.
Answer:
Arikamedu, located in Pondicherry, was a coastal settlement between 2200 and 1900 years ago. It was a place where ships unloaded goods from distant lands. A massive brick structure which is supposed to be a warehouse was found at the site. Other discoveries include pottery from the Mediterranean region. For example, amphorae which were tall double handled jars that contained liquids and stamped red-glued pottery, known as Arretine Ware. It was named after a city in Italy.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question-1
Describe severed ways offinding out about early cities. [V. Imp.]
Answer:
Several ways of finding out about early cities include Jatakas, sculpture, archaeology and travellers.
Jatakas were stories composed by ordinary people and preserved by Buddhist monks.
Sculptures carved scenes depicting peoples’ lives in towns and villages as well as in the forest. Many of these sculptures were used to decorate railings, pillars and gateways of buildings that were visited by people. In many cities, archaeologists have found rows of pots or ceramic rings arranged one on top of the other. These are known as ring wells, which were used as toilets and as drains and garbage dumps. These ring wells are usually found in individual houses. The accounts of sailors and travellers also help us to know about early cities. One of the most detailed accounts that has been found was by an unknown Greek Sailor. He described all the ports he visited.
Question-2
Mathura was a city with many Junctions. Explain. [V. Imp.]
Answer:
Mathura has been an important city for more than 2500 years. It was important for various reasons.
It was located at the cross roads of two major routes of travel and trade – from the northwest to the east and from north to south.
There were fortifications around the city, and several shrines. Farmers and herders from adjoining areas provided food for city people.
Mathura was also a centre where some extremely find sculpture was produced.
Around 2000 years ago, Mathura became the second capital of the Kushanas.
Mathura was a religious centre also. There were Buddhist monasteries and Jaina shrines. It was also an important centre for the worship of Lord Krishna.